In the past, developers had to limit themselves to making native apps that were compatible with specific hardware, operating systems, and other platforms. Over time, new approaches like porting an app to multiple platforms began to emerge in the mobile app industry and ecosystem. The concept of cross-platform development came about in this way. Therefore, in this post, we’ll go over a debate of Native vs. Cross-platform app development and discuss their benefits and unique parameters.
1. What is Native App Development?
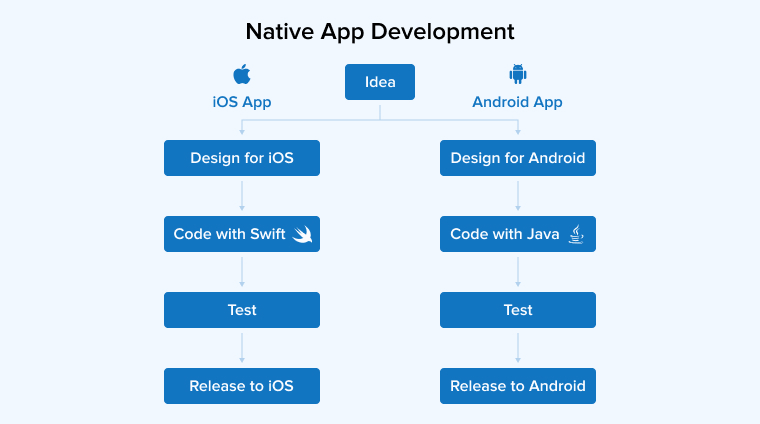
Native apps are typically platform-specific. To develop an app that is native to a mobile platform, developers must utilize tools and languages that are specific to that particular platform. For example, developers creating Native apps for Android often work in Java or Kotlin; iOS native app developers, on the other hand, often work in Objective-C or Swift. This allows them to create apps that are unique to their platform of choice and make the most of all the features it offers.
Although it’s more expensive and time-consuming, developing in native code yields superior performance and UX, including more tailoring and customization options. Apps requiring a lot of data processing or complicated features, like a product inventory app or a game app with 3D animations, must be built using a native method.
1.1 Benefits of Native App
Developing native mobile applications offers a range of advantages. Among them are:
- Enhanced Efficiency: You can develop customized native applications tailored for a certain platform. In addition, you can compile them by utilizing the platform’s primary programming language and APIs. This enhances their speed, efficiency, and responsiveness to consumers’ inputs.
- High Security: Native applications can improve the security of your users’ data. They possess the ability to utilize security mechanisms that are specifically designed for a certain platform.
- Excellent User Experience: Native applications offer a more seamless user input and output experience. Consistency of the appearance and feel is achieved through the inheritance of the device’s operating system interfaces. They adhere to design guidelines particular to the operating system, enhancing the app’s user experience by creating a more intuitive flow.
- Complete Access to All Features: Native mobile applications can utilize all the device’s capabilities and functionalities, resulting in a more comprehensive and seamless user experience. Additionally, they gain access to services such as push notifications, which play a crucial role in stimulating user engagement.
- Minimal Errors: Native application developers are granted immediate access to the latest software development kits (SDKs) upon their release. Each of these releases consistently includes enhancements and new functionalities.
1.2 Examples of Native Apps
Familiar examples of native applications include:
- Applications for social networking platforms, such as Instagram.
- A mobile application that enables users to generate and categorize electronic notes, memos, and task lists, such as Evernote.
- Financial management applications such as Mint.
- Community applications, such as Mighty Networks.
- Gaming apps where you can play with candies and complete challenges, such as Candy Crush Saga.
- Mobile banking applications, such as Discover.
- Language acquisition software or digital flashcard applications, such as Duolingo.
- An immersive music streaming application that offers a vast selection of songs, enables playlist creation, and supports music discovery, such as Spotify.
- Applications for enhancing creativity, such as Adobe Lightroom.
- Productivity applications, such as Hive.
2. What is Cross-Platform App Development?
Cross-platform mobile development refers to the method of creating software apps that can run on several mobile operating systems or platforms. These applications are platform-agnostic, indicating that they can be utilized regardless of the operating system that powers the mobile device.
2.1 Benefits of Cross-Platform Apps
Following are the benefits of cross-platform apps:
- Budget-Friendly: Developing apps that can run on several platforms may be a more cost-efficient approach compared to creating individual apps for each device. Additionally, it can decrease maintenance expenses since improvements and corrections for bugs can be applied to a single codebase instead of multiple codebases, particularly to each platform.
- Expanded Reach: By developing a unified application that is compatible with several platforms, you can expand your target audience and strengthen your market presence. Instead of focusing on a single platform, you can reach people across various platforms.
- Accelerated Development: By utilizing a common codebase, developers can accelerate the development process compared to creating individual applications for each platform. The reason for this is that they are able to reuse code and prevent the need for duplicating efforts for each platform. Accelerated development can result in reduced expenses and quicker time-to-market for the application, which is essential in a competitive industry.
- Simplified Maintenance: Due to the presence of a unified codebase, upgrades and support for cross-platform programs are comparatively quick and easy. Developers modify the singular codebase instead of many codebases specific to different platforms, hence decreasing maintenance expenses and minimizing app downtime.
2.2 Examples of Cross-Platform Apps
Prominent examples of cross-platform mobile applications are as follows:
- A widely used application for video and audio calls shows the achievement of developing a great program that can be used on cross-platforms, such as Microsoft Teams.
- A prominent social media platform that has revolutionized the ways of sharing and connecting stands as an extraordinary triumph in the realm of cross-platform application development, such as Instagram.
- A pioneering company in the travel and housing sector, which has transformed the process of discovering and reserving accommodations worldwide, is Airbnb.
- A highly praised language learning program stands as an impressive example of successful cross-platform software development, such as Duolingo.
3. Cross-Platform vs. Native Mobile Development: A Detailed Comparison
Selecting one development strategy over another is a challenging decision to make. Each project offers particular priorities and a specific set of requirements.
Choosing between native and cross-platform development is challenging. To make the correct decision, it is essential to take into account certain important factors.
3.1 Budget Overview
As is already apparent, cross-platform development is a more cost-effective choice compared to native mobile app development. The latter involves the deployment of two separate applications for each operating system, which requires hiring more developers, allocation of more resources, and finally, incurring higher expenses.
If you have limited financial resources, choose cross-platform development. Nevertheless, if you have sufficient financial resources and desire to give utmost importance to user experience and app updates, opting for native app development will be the most suitable decision.
3.2 Time to Market
One of the primary criteria for comparison between cross-platform vs native mobile development is the speed at which an application product can be launched. Although cross-platform development enables faster creation and iteration, native app development is more labor-intensive, but it offers an improved and consistent user experience.
If your business requires rapid deployment of the app to get valuable customer feedback, cross-platform development would be the ideal choice.
3.3 Application Performance
The desired performance of your app will influence the choice between cross-platform and native mobile development. Mobile applications can have intensive computational needs, particularly in the case of gaming apps. If your business needs a high-performing application that offers a smooth and uninterrupted user experience, a native app is the most suitable choice.
If your primary objective is not aligned with company goals, and you prefer to maximize your audience reach and expedite time-to-market, it is advisable to use a cross-platform mobile application.
Further Reading on: How to Boost Web Application Performance?
3.4 Practical Test Assessments
A thorough testing phase is crucial to complete your corporate mobile app development process. The choice between native and cross-platform development is also important in this context since native apps provide a greater testing challenge as they require separate testing of distinct app versions for each operating system. In contrast, cross-platform applications are more convenient to test due to their unified codebase.
If you possess the necessary time and resources to dedicate to a thorough allocation towards the native app testing phase, then you can continue with it. Nevertheless, if you have limited resources and desire to expedite the shipping process, choose cross-platform development.
3.5 App Security
When considering opting between native and cross-platform development for your business’s mobile app, it is crucial to prioritize security as well. Security is of utmost importance, particularly for applications that manage large volumes of data, such as a mobile banking application. In such cases, opting for a native application is advisable since it offers enhanced security measures due to being developed within the unique operating system environment. Native app development involves utilizing native libraries, allowing developers to ensure robust app encryption.
Nevertheless, if your major focus is on maintenance, a cross-platform mobile application may be more suitable. As previously stated, cross-platform app development offers simplified maintenance due to the same codebase. Furthermore, consolidating into a single integrated app instead of two separate ones can lower the expenses associated with maintaining the app.
In a nutshell, let’s summarize the superiorities of both development types in a short overview below!
Cross-platform App Development Offers a Competitive Advantage in the Following Areas:
- Accelerated product launch.
- Minimizing or reducing expenses associated with development.
- Reduced workload and costs associated with app maintenance.
- Enhancing code reusability across iOS and Android platforms.
- Less resource-intensive applications, such as those without extensive animation or complicated logic, do not heavily utilize the CPU and GPU.
- Ensuring uniformity in the interface and navigation across several platforms, particularly when the user interface is comparable on both platforms.
- Conducting a comprehensive evaluation of a concept, hypothesis, or prototype on many platforms.
Native App Development Provides an Advantage in the Following Areas:
- Optimizing application performance and enhancing speed.
- Security measures for applications.
- Flexibility and customization of features and user interface/user experience.
- Applications with cutting-edge, platform-specific user interfaces and user experience.
- Efficient and streamlined implementation of upgrades and new features.
- Developing an application with improved responsiveness.
- Utilizing the hardware capabilities of a mobile phone, such as its camera.
- Resource-intensive applications, such as mobile games, and those that have complex animations.
- These are apps that belong to a comprehensive set of applications and may have common code.
4. Summing Up
The first step in developing a reliable, popular, and well-received mobile app is deciding which operating system you would like your app to work with. Each approach to building mobile apps, whether native or cross-platform, has its advantages and disadvantages. In contrast to cross-platform applications, which developers design to run on multiple operating systems, developers make native apps compatible with only one operating system.
However, when it comes to creating a mobile app, there is no magic recipe. It is important to always keep scalability, speed, and security in mind while developing your app, regardless of whether your customers use iOS or Android.
The specific requirements of each project have a significant impact on the development outcome. To ensure a smooth process, research your market and objectives; if you have any questions, feel free to contact the TatvaSoft team.
FAQs
What is the difference between cross-platform and native mobile development?
Native mobile development is platform-specific, whereas cross-platform development is platform-agnostic.
Should I start with native or cross-platform?
Both native and cross-platform development serve different needs. Therefore, after considering your requirements and end goals, you can proceed with either.






Comments
Leave a message...