
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Services (EKS) is a popular managed service for running Kubernetes on AWS. However, Kubernetes is an open-source solution, and it comes with some inherent security risks. Managing Kubernetes clusters on EKS is not easy either. Knowing you need AWS EKS to run Kubernetes on AWS is one thing, but doing so effectively is the real challenge.
You need expert guidance from a popular software development company to create and manage Kubernetes clusters efficiently for your containerized application. They follow best practices to ensure optimum results.
Amazon EKS best practices are essential guidelines for optimizing and securing EKS clusters across cost, security, and reliability. If you don’t know about these practices, then this blog is for you.
1. What is Amazon EKS?
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is a managed service that allows you to run Kubernetes on AWS without the need to install, operate, and maintain the Kubernetes control plane or nodes. Developers can use Kubernetes to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized apps.
EKS runs and scales the Kubernetes control plane to provide high availability across various AWS Availability Zones. Depending on the load, EKS can automatically scale the control plane instances. It can detect and replace unhealthy control plane instances. EKS also offers automated version updates and patches for them.
More importantly, EKS allows seamless integration with multiple AWS services to ensure the scalability and security of your apps. This integration provides many amazing capabilities, such as elastic load balancing and IAM (Identity and Access Management).
Kubernetes is an open-source system with an active community that continuously contributes to its advancement. EKS is part of the broader Kubernetes ecosystem, supporting standard Kubernetes features and tools while ensuring compatibility with best practices in deployment, security, and performance. EKS ensures your app runs on an updated version of Kubernetes and has access to all available plugins and tooling options from the community.
It doesn’t matter if your app is running on public clouds or on-premises; if it is equipped with Amazon EKS, it will be compatible with any standard Kubernetes environment.
AWS EKS Architecture:
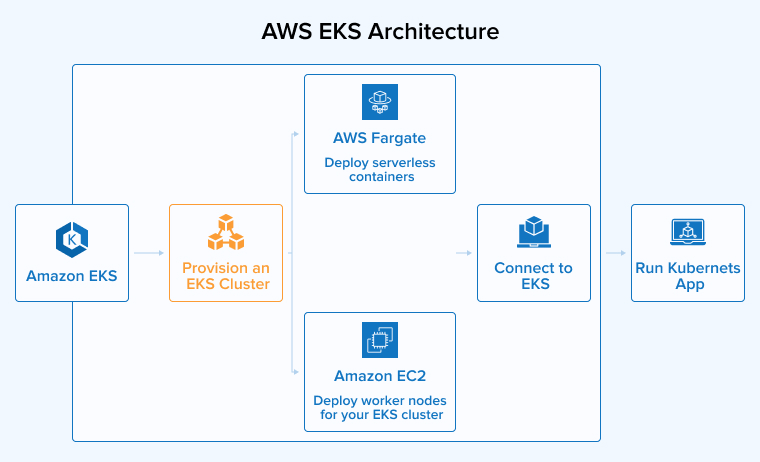
In Sep, 2021 AWS launched AWS EKS Everywhere to easily create and operate Kubernetes clusters on-prem.
No need to contain excitement for containers. ☁️ 📦 💻 With Amazon EKS Anywhere, easily create and operate #Kubernetes clusters on-prem—on your own infrastructure in one installable software package. https://t.co/inWq7Vso35 #AWS #CloudComputing #Developer pic.twitter.com/g0JtALxj5j
— Amazon Web Services (@awscloud) September 8, 2021
1.1 Key EKS Features
It is essential to review some features before moving to EKS best practices.
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Services (EKS) provides an integrated console for managing Kubernetes clusters.
- The eksctl simplifies cluster management and operations, like handling nodes and add-ons.
- Running Kubernetes apps on Amazon EC2 and AWS Fargate is possible through the utilization of Amazon EKS.
- Users can gain visibility into EKS administration activities, including audit history, by integrating Amazon EKS with AWS CloudTrail.
- Amazon EKS allows you to create, update, scale, and terminate cluster nodes with a single command.
- Amazon EKS offers a highly available and scalable Kubernetes control plane that runs across multiple AWS Availability Zones.
- Amazon EKS clusters provide robust security configurations, version management, and compliance features as part of their core capabilities.
2. Top 10 EKS Best Practices You Must Know
When handling AWS EKS clusters, it is essential to follow the best practices to ensure reliable application performance.
2.1 Use a Version Control System
The first step when starting with EKS or other AWS services is to create the required resources. Traditionally, this was the norm to manage the infrastructure manually, whether on the cloud or on-premises. However, creating the resources manually is no longer effective and has been replaced by Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC). The same applies to AWS EKS clusters.
In a version control system, developers save configuration files related to Kubernetes deployments, services, ingresses, and other objects before pushing them to a cluster. Similarly, save the IaC files used for creating EKS clusters in the version control system to maximize the benefits of IaC. This also helps you track all changes implemented to the EKS cluster, along with who made them and when.
Using IaC ensures that you can provide the same environment. IaC enables consistent EKS cluster configuration and deployment across different environments, making it easier to manage infrastructure setups for development, staging, and production. Moreover, IaC provides configuration management, enabling you to document your configuration standards and prevent ad hoc and undocumented configuration changes through coding.
Like software source code, the configuration files used for creating an EKS cluster are also subject to source control. When you deploy EKS as code, it is broken down into modular components that can be automatically combined in various ways to build a diverse range of solutions. Therefore, it is recommended that you use the IaC approach to create an EKS cluster and save its IaC files in a version control system.
2.2 Implement a Strong Cluster Configuration
An EKS cluster with proper configuration is essential for application security. Therefore, when setting up a cluster, it is best practice to use appropriate security parameters and to update them regularly.
Use the latest EKS-optimized AMIs: The recently launched Amazon EKS-optimized AMIs come pre-configured with new security enhancements. However, it is still necessary to apply the latest security patches to keep them updated.
Updating EKS Cluster to Use the Latest AMI
eksctl upgrade cluster --name=cluster-name --approve |
Enable audit logging: If there are any suspicious activities, analyzing the audit logs can help identify them. An audit log is a record of events and is critical for compliance and security auditing.
Enabling Audit Logging in EKS
--region [region] \ --name [cluster-name] \ --logging '{"clusterLogging":[{"types":["api","audit"],"enabled":true}]} |
2.3 Avoid Running Singleton Pods
A pod that runs alone in Kubernetes without being part of any StatefulSet, Deployment, or ReplicaSet is called a singleton pod. Running them in AWS EKS can hurt the app’s reliability, especially if the node hosting the singleton pod fails.
This risk can be easily mitigated by avoiding running critical apps as singleton pods. Instead, it is recommended to run them as part of a StatefulSet or Deployment. This allows the Kubernetes control plane to reschedule the pod on a different node if the node hosting that pod fails.
To mitigate the risks of zone failures, replicas should be spread across different availability zones, ensuring high availability.
2.4 Isolate Kubernetes Nodes
Make sure that Kubernetes nodes do not have any direct connection to the general corporate or public network. Always locate them on a separate network. This is achieved by isolating the data traffic and Kubernetes control traffic. Without this isolation, they both might flow through the same network path.
To further enhance security, restrict remote access to node groups, and configure security group rules to prevent unauthorized access. Properly setting inbound rules in your security groups helps ensure that only trusted sources can connect to your EKS cluster nodes.
Open access to the data plane means open access to the control plane, posing high risks to EKS security. Use an ingress controller to configure nodes so that only connections from the master node are allowed through a specified port in the network access control list.
2.5 Utilize Multi-Tenancy with Namespaces and Resource Quotas
To deliver enhanced performance and security in a multi-tenant EKS environment, isolate workloads and manage resources efficiently.
Set Up Namespaces for Workload Isolation: In the same EKS cluster, you can separate different projects, teams, and environments using Kubernetes Namespaces, as they act as virtual clusters.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: dev-team |
Define Resource Quotas to Manage Resource Allocation: Implementing resource quotas allows you to control the amount of resources, like memory and CPU, consumed by each tenant and namespace. This prevents any single tenant from monopolizing cluster resources. Additionally, you can set maximum number limits on resources, such as pods, to ensure no tenant exceeds the cluster’s capacity or Kubernetes limits.
apiVersion: v1 kind: ResourceQuota metadata: name: dev-team-quota namespace: dev-team spec: hard: requests.cpu: "4" requests.memory: 8Gi limits.cpu: "6" limits.memory: 16Gi |
2.6 Right-Size Your Workloads
The best practice for right-sizing workloads in Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service allows effective cost optimization. The first step is analyzing app resource usage. While doing so, monitor for performance bottlenecks and consider implementing cluster scaling strategies to ensure optimal resource management. Next, adjust the requests and pod limits as per resource usage. Many unnecessary costs stem from over-provisioning resources, so avoid this mistake. Review and adjust resource allocations using tools like Container Insights and Amazon CloudWatch, ensuring that you only pay for resources you use or need. Additionally, consider data transfer costs when designing network architecture and scaling strategies to further optimize expenses.
2.7 Build a Rolling Update Strategy
Building a rolling update strategy will strengthen the security of your Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Services. This approach allows deployment updates with minimal downtime by incrementally replacing pod instances with new ones.
Even after scanning the deployment artifacts during the CI/CD stage, clusters can still be attacked at runtime. To enhance security, ensure that container images are regularly scanned and updated to address vulnerabilities. Therefore, it is important to perform a vulnerability scan at runtime. Overall, agent-based security solutions are generally more effective than agentless solutions.
2.8 Leverage Amazon S3 Storage Options
Utilizing Amazon S3 for persistent data storage is more cost-effective compared to storage volumes attached to EC2 instances, especially if you don’t need high-performance access. Amazon S3 comes with a wide range of storage classes optimized for different use cases and cost points. Cost optimization becomes easier when you have a thorough understanding of these classes.
For data that is accessed frequently, use S3 Standard for its high availability, performance, and durability. For data that is accessed less frequently, save costs with S3 One Zone-IA, S3 Standard-IA, and S3 Intelligent-Tiering.
2.9 Restrict Network Access to the EKS Cluster
The cluster endpoint of an EKS cluster has public access on the internet by default. Although it’s convenient, it poses significant risks if not managed properly. Therefore, it is highly recommended to restrict public access and enable private access instead. This minimizes exposure to potential threats as it ensures that all traffic to your API server travels through a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
To control inbound and outbound traffic to the EKS cluster, you can use Network Access Control Lists (NACLs) and security groups. Specifically, configuring the EKS security groups to restrict access to the cluster endpoint ensures that only authorized sources can reach your Kubernetes API server.
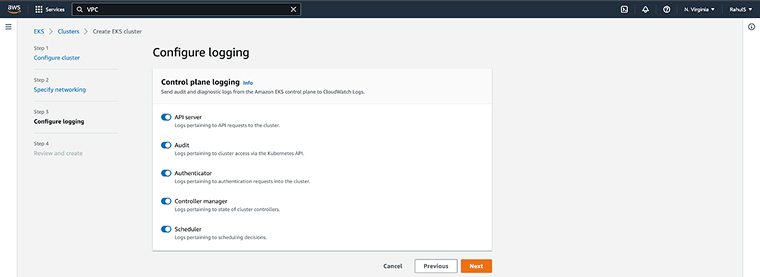
2.10 Kubernetes Cluster Logging
The Kubernetes control plane is used to control Kubernetes clusters and generate logs for auditing and troubleshooting purposes, including audit logs that track all API requests and changes for enhanced security and compliance. It utilizes Amazon EKS to enable logs for different components of the control plane, such as audit logs, which are later sent to CloudWatch.
You have to enable the control panel logs in the AWS EKS clusters to publish authenticator logs, controller manager, APIs, scheduler, and audit logs to AWS CloudWatch Logs. After activating the logging capabilities of the EKS control plane, Amazon EKS sends the audit logs and diagnostic logs directly to AWS CloudWatch Logs. Use these logs, especially audit logs, to operate EKS clusters securely and effectively and to monitor access to sensitive resources like Kubernetes secrets.
However, the CloudWatch Logs just don’t receive cluster control plane logs by default. So, during submission, enable every single log separately to send them all to the cluster. For every cluster you run using the Amazon EKS control plane, the charges for Amazon EKS are usual. Additionally, you have to pay for storage, CloudWatch Logs data ingestion, and any logs you send to CloudWatch Logs from your clusters.
Sample Terraform Snippet:
resource "aws_eks_cluster" "my_eks_cluster" { name = "prod-eks-cluster" version = "1.29" encryption_config { resources = ["secrets"] provider { key_arn = "arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:123456789012:key/xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" } } vpc_config { subnet_ids = [ "subnet-0abc1234...", "subnet-xxxxxxxxx..." ,"subnet-0ghi9012..." ] security_group_ids = [ "sg-0123abcd..." ] endpoint_private_access = true enabled_cluster_log_types = [ "api", "audit", "authenticator", "controllerManager","scheduler" ] } role_arn = "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/YourEKSRole" } |
Configuration in the EKS Cluster Configuration Console: Follow the given path to find these configuration settings:
EKS -> Add Cluster -> Create -> Next -> Next -> Configure logging -> Control plane logging |
From here, enable the following components:
- API server
- Audit
- Authenticator
- Controller Manager
- Scheduler
3. Conclusion
The above blog discusses the best practices to follow when creating and managing EKS clusters. Adhering to these practices provides a wide range of benefits, like effective data management, cost optimization, security, availability, and more. Although the list of practices given in this blog is brief, it can be highly effective even for large and complex projects. Make sure to follow AWS EKS best practices from the moment you start building clusters.




Comments
Leave a message...