Choosing the right technology stack is crucial in any web development project. When it comes to building high-performing, scalable applications, Laravel and Node.js are two popular contenders. Laravel, a robust PHP framework, excels in simplifying backend development with elegant syntax and built-in tools, making it a favorite among many PHP development companies. On the other hand, Node.js provides a fast, event-driven runtime environment for JavaScript. It is well-suited for building real-time applications and other high-performance applications. Both technologies have their unique strengths, use cases, and communities, which can make choosing the right one challenging depending on the project requirements.
This blog examines the key features of Laravel and Node.js, then delves deeper into the differences to help web developers, startups, and businesses make an informed choice based on their project needs and goals. Whether you’re leaning towards traditional PHP frameworks like Laravel or a modern JavaScript runtime like Node.js, understanding these options is essential for successful web development.
1. Overview of Laravel
Laravel, developed by Taylor Otwell, is an open-source, PHP framework designed for server-side web development. Despite the rise of several feature-rich frameworks and libraries, which have reduced PHP’s overall popularity. However, it’s not wrong to say that Laravel saved PHP from completely vanishing. According to a survey by BuiltWith, currently, around 688,627 websites are powered by Laravel. Simplicity and elegance are the two fundamental goals behind Laravel development. Additionally, Laravel can be integrated with other frameworks like CodeIgniter, Yii, and Ruby on Rails, as it facilitates smooth integration with their components.
1.1 Features of Laravel
The following are the fundamental characteristics of the Laravel framework:
1. MVC Architecture
Laravel adopts the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture, which separates presentation and business logic layers. The following are the three components:
- Model: This layer deals with the application’s data and business logic. It’s responsible for interacting with the database and performing the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations.
- View: The Blade templating engine is used as the View layer to combine multiple templates with data from the Model, producing the final user interface. This layer manages what the user sees and interacts with.
- Controller: The Controller acts as an intermediary between the Model and View layers. The user input received by the View layer comes to the controller for processing. It interacts with the Model layer to process data and finally returns the result to the View layer for display.
2. Security
Laravel includes robust built-in security features to protect applications. It uses hashed and salted passwords to prevent password recognition by attackers. Specifically, Laravel uses the Bcrypt hashing algorithm to hash passwords, ensuring that plain-text passwords are never stored directly. Laravel protects against SQL injection attacks by using prepared SQL statements. The automatically generated CSRF tokens save the web application from cross-site scripting (XSS) and cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks. These CSRF tokens validate every request to prevent exploitation of user sessions.
3. Artisan Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Laravel provides a command-line tool, known as Artisan, to facilitate development tasks and avoid repetitive manual tasks. It eases database management by handling tasks such as creating database structures, generating boilerplate code, and managing database migrations. Artisan can produce MVC files and govern assets and their associated configurations. Besides these, developers can create custom Artisan commands tailored to their specific needs and use them conveniently during development.
4. Eloquent Object Relational Mapping (ORM)
Laravel’s Eloquent is an ORM that simplifies database interactions by allowing you to write complex SQL queries using the PHP syntax instead of raw SQL. Every table in the database has its corresponding Eloquent model, which follows the ActiveRecord implementation for effective database interaction.
2. Overview of Node.js
Node.js is a widely used backend technology to develop JavaScript-based server-side applications. It is an open-source runtime environment that allows execution of JavaScript code outside the web browser. Node.js is compatible with multiple operating systems, including Windows, Linux (Unix-based), and macOS. It is built on Google’s V8 JavaScript engine, which compiles JavaScript code directly into the given machine code. Node.js enables full-stack development, eliminating the need to use different programming languages or various Node.js frameworks for client-side and server-side development.
2.1 Features of Node.js
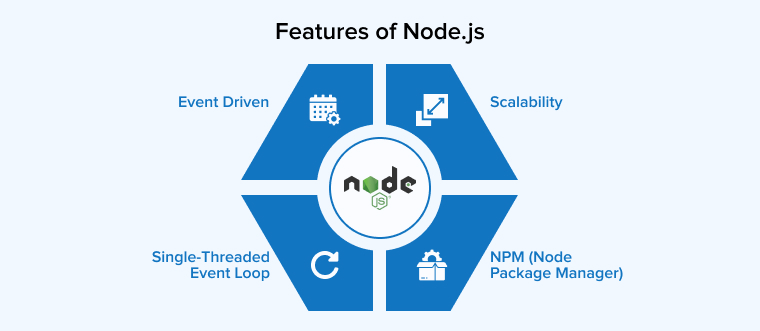
Below are the four key characteristics of the Node.js runtime environment:
1. Event Driven
Node.js is built on an event-driven architecture. It uses JavaScript to handle the events, i.e., incoming and outgoing requests, asynchronously. There’s a module named “Event” in Node.js. It contains the “EventEmitter” class to create and handle different events, like clicking a button. Every event is associated with a callback function that executes in response to that event.
2. NPM (Node Package Manager)
The Node Package Manager, or NPM, is a collection of open-source libraries and modules. It provides access to the world’s largest ecosystem of open-source libraries and modules. You can download and install packages according to your requirements, thus easing the development process. It even helps to include third-party code into your project by simplifying dependency management.
3. Single-Threaded Event Loop
Node.js operates on a single-threaded event loop that handles asynchronous, non-blocking operations. Unlike many other web technologies that create a new thread for each incoming request, Node.js uses a single thread to manage multiple concurrent requests. As a result, Node.js applications are lightweight with no overhead of managing separate threads for every request.
4. Scalability
Node.js is highly scalable due to its non-blocking, event-driven architecture, which efficiently handles multiple simultaneous connections. This makes it ideal for real-time applications and services requiring high concurrency. By using asynchronous programming, Node.js maximizes resource utilization, enabling applications to grow smoothly as user demand increases without significant drops in performance.
3. Node.js vs Laravel: A Detailed Comparison
Now, we’ll compare the two popular web development technologies, i.e., Laravel and Node.js, based on seven key parameters:
3.1 Performance
- Laravel: The code is written in PHP; hence, Laravel is synchronous. Therefore, it handles requests sequentially, decreasing the application’s speed. It is well-suited for CPU-intensive tasks such as managing backend logic and server-side HTML rendering, especially when real-time processing is not a requirement. Performance improvements can be achieved by using the OPCache extension, which caches precompiled PHP bytecode in memory. Additionally, PHP-FPM can be used to manage multiple PHP processes efficiently, helping Laravel handle high loads.
- Node.js: The non-blocking or asynchronous I/O and event-based architecture increases the speed of Node.js applications tremendously. The V8 JavaScript engine enhances speed, allowing efficient multitasking without consuming excessive resources. Real-time applications, such as chat apps and IoT solutions, require processing of concurrent requests, i.e., heavy I/O operations, making Node.js a perfect fit. Additionally, Node.js is an excellent choice for developing microservices-based applications.
3.2 Structure and Flexibility
- Laravel: In terms of underlying structure, Laravel is influenced by the MVC architecture. Therefore, Laravel developers can focus on developing business logic and core functionality instead of dealing with project setup and managing dependencies. The convention-over-configuration approach in Laravel restricts developers from defining custom configurations for application-specific needs.
- Node.js: Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop architecture to manage multiple client requests simultaneously. It leverages JavaScript callback functions and the event loop to manage blocking and non-blocking operations. Node.js allows developers to use different architectural patterns in developing applications rather than imposing any rigid structure.
3.3 Scalability
- Laravel: Horizontal scalability of Laravel systems can be increased by using HTTP load balancers to distribute incoming traffic across multiple web servers, database sharding, and implementing caching strategies.
- Node.js: The asynchronous architecture and event-based mechanism make Node.js applications inherently scalable. Different tools and libraries, such as M2, Nginx, and Redis, help to divide the heavy load across multiple Node.js server instances. Additionally, Node.js provides a built-in cluster module for creating multiple application instances and distributing load accordingly.
3.4 Database Support
- Laravel: Laravel is a PHP framework that supports various relational databases, like MySQL and SQLite. Its built-in ORM, called Eloquent, eases the database interaction by facilitating the use of PHP syntax.
- Node.js: The Node Package Manager (NPM) hosts a wide variety of database drivers and libraries that help developers connect with both SQL and NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and many others.
3.5 Community
- Laravel: PHP has been in existence for a long time. Therefore, Laravel developers actively benefit from the existing community in terms of tutorials, support tools, community platforms, etc. Also, Laravel has its own emerging community contributing to all types of development assistance required.
- Node.js: Node.js has a huge community of active developers worldwide that contributes to extensive libraries, packages, documentation, and tools. In terms of all the frameworks and libraries, it has the largest ecosystem. Wherever you encounter difficulties during development, abundant online support is available to assist you, preventing potential disruptions.
3.6 Security
- Laravel: Laravel includes several built-in security features to protect applications and user data. It uses the Bcrypt hashing algorithm for securely storing passwords. To prevent CSRF tokens, Laravel protects against SQL injection by using prepared statements through the PDO (PHP Data Objects) extension. Also, the Eloquent ORM makes use of PDO or the PHP Data Object class, which contributes to the robust security of the database, protecting sensitive user data.
- Node.js: Node.js is secure, but it lacks the intensive built-in security features provided by the Laravel framework. The security here is highly dependent on the developer’s implementation of third-party modules and packages. The external libraries may pose security threats, making the application vulnerable to unknown security threats. To deal with this to some extent, Node.js has implemented automated vulnerability scanning, anti-CSRF tokens, and cookie session modules for protecting user sessions.
3.7 Learning Curve
- Laravel: Having a good understanding of PHP, HTML, and CSS, the learning process becomes quite easy, and the period gets reduced. Also, Laravel’s extensive documentation and built-in libraries and templates further ease the learning process, especially for beginners in backend development.
- Node.js: Node.js is built on JavaScript, so familiarity with JavaScript helps make learning Node.js easier. However, mastering concepts such as asynchronous programming, the event loop, callback functions, and the use of NPM modules requires significant time and implementation practice for effective understanding.
4. Laravel vs Node.js: Comparison Table
The comparison table below provides a quick overview of the complete picture of Laravel vs Node.js, assisting you in selecting the right technology for your upcoming project.
| Parameters | Laravel | Node.js |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Type | A PHP framework | JavaScript runtime environment |
| Engine | Blade templating engine | Google’s V8 engine |
| Execution | Synchronous | Asynchronous |
| Language | PHP for backend development | JavaScript for both frontend and backend development |
| Types of Supported Databases | Supports SQL-based databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite | Supports both SQL and NoSQL databases, for example, MySQL and MongoDB |
| Concurrency | Multithreaded blocking I/O | Single-threaded non-blocking I/O |
| Package Manager | Compose package manager | Node Package Manager (NPM) |
| I/O model | No I/O model | Asynchronous event-driven I/O model |
| Community | Small but growing community | Huge online active community |
| Learning Curve | Short for developers familiar with PHP programming | Steep, especially for beginners in backend technology, as it requires an understanding of asynchronous programming |
| Integration with frontend libraries | Yes | No |
| Web Servers | Not required | Apache and IIS |
| Flexibility | Less due to strict adherence to the MVC structure | Provides high flexibility to the developers |
| Development Cost | Lower due to the abundance of PHP developers | Quite costly due to the shortage of skilled Node.js developers |
| API development | Laravel API resources provide various tools to develop APIs | Lightweight and easy to create RESTful and GraphQL APIs |
| Hosting and Deployment | Shared hosting, VPS, or cloud servers with a PHP-friendly environment | Cloud servers like AWS and Heroku are highly preferred |
| Microservices Support | Limited flexibility for microservices | High compatibility with microservices architecture |
| Performance | Suitable for traditional web applications with complex business logic | Can develop high-performance real-time applications |
| Security | Provides built-in security mechanisms | Requires installing third-party modules for security implementation |
| Use Cases | CMSs, eCommerce, and Enterprise applications | Chat apps, streaming platforms, gaming, and IoT applications |
5. Laravel vs Node.js: Which is Better?
The choice between the two highly useful frameworks, Laravel and Node.js, varies from project to project. There cannot be a concrete answer regarding the superiority of one over the other. Still, we’re providing some scenarios below to help you select the correct technology to suit your project and business objectives:
5.1 When to Choose Laravel?
Consider the following scenarios when deciding to go with the Laravel framework:
- If the development team members are familiar with the PHP technology as this will decrease training time and resources, ultimately reducing project costs.
- If the application has to be developed in a short time. The built-in features and pre-made templates speed up the process.
- If the application requires high security, for example, banking applications, Laravel is a better option owing to its strong security support.
5.2 When to Choose Node.js?
Consider the following scenarios when deciding to go with the Node.js framework:
- If you want speedy full-stack development, and the team already contains skilled JavaScript developers.
- If the application has to manage numerous requests at the same time without compromising the application’s speed and performance.
- If you want to develop real-time applications like monitoring dashboards, live chatting, video conferencing tools, data streaming platforms, etc.
6. Final Thoughts
Both Laravel and Node.js offer powerful solutions for modern web development, each with distinct advantages. Laravel shines with its elegant PHP framework, making it ideal for projects that require rapid development, clean code structure, and strong backend support. Meanwhile, Node.js excels in handling real-time, event-driven applications with high scalability. The choice ultimately depends on your project requirements, the expertise of your development team, and long-term goals. Understanding the strengths of each technology will help you select the right tool for building efficient, maintainable, and scalable applications.






Comments
Leave a message...