
Cloud cost optimisation can be resource-intensive and overwhelming, requiring developers to continuously manage infrastructure using techniques like usage adjustment and instance rightsizing. As a result, they often can’t focus on the more creative or innovative aspects of the project.
Rate optimisation is a strategic solution to this challenge. Leveraging AWS Reserved Instances (RIs) enables businesses to lock in long-term discounts and free up developers to focus on core activities. Top software development companies use RIs to predict cloud expenses and deliver more efficient outcomes at significantly reduced rates without putting in much manual effort.
However, to succeed with AWS RIs, a clear capacity planning strategy is essential. Businesses cannot simply purchase RIs without properly defining their requirements and conducting risk assessments. Despite the significant discounts offered by AWS RIs, over- or under-commitment can have negative consequences.
Read this article to gain a comprehensive understanding of AWS Reserved Instances, including their benefits, how they work, the different types, best practices and how they differ from on-demand instances.
1. What is AWS RI?
AWS Reserved Instances (RIs) are a cost-effective way to purchase Amazon Web Services’ computing capacity. Buying a Reserved Instance means committing to an upfront payment for a specific amount of computing capacity over a fixed period, usually ranging from one to three years.
By committing to use computing resources for a longer term, you can receive significant discounts compared to on-demand pricing. These discounts can go up to 72% depending on the instance type, term length, region and payment option.
AWS RIs are ideal for businesses with long-term infrastructure needs or predictable workloads. They help save money while ensuring your company has the computing resources necessary to run its applications or services efficiently.
It’s worth mentioning that AWS RIs are not physical instances but a billing construct. Purchasing AWS RIs does not guarantee access to any specific instance; rather, it provides the right to launch specified instances at reduced costs during the committed period.
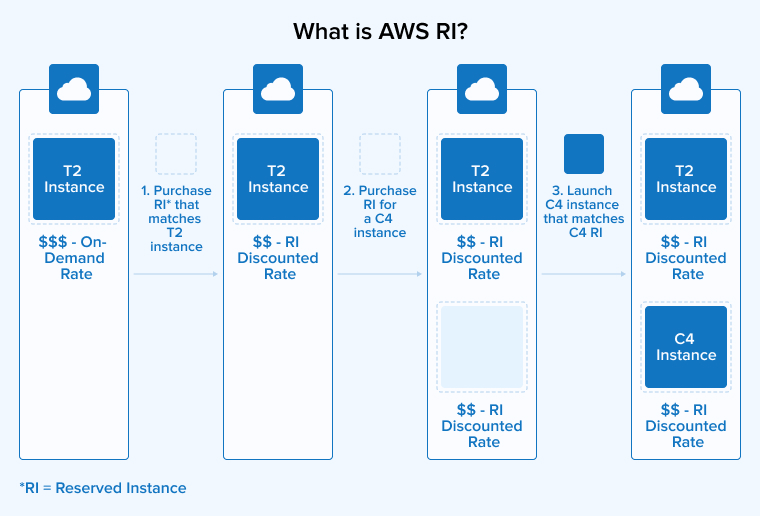
1.1 What are the Advantages of Using AWS Reserved Instances?
Utilizing Amazon Web Services RIs across supported services offers numerous benefits, including but not limited to:
1. Significant Cost Savings
You can receive up to a 75% discount on the base price of on-demand instances when using standard RIs. If your business has a consistent long-term need for computing capacity, RIs provide a cost-effective pricing model that meets your needs without sacrificing performance.
2. Improved Budget Predictability
By locking in the prices of computing capacity for a fixed period, one to three years, businesses can predict costs more accurately and prepare their budgets accordingly.
3. Flexible Payment Options
RIs support flexible payment models, including All Upfront, Partial Upfront, and No Upfront options, allowing businesses to align cost commitments with their cash flow.
4. Instance Size Flexibility (ISF)
Reserved Instances offer size flexibility for services such as RDS and EC2, allowing developers to resize instances within the same family and region. Although discounts continue after resizing, they may be smaller than those offered by standard RIs.
5. Resell Value
If you have committed standard RIs, you can sell them on the AWS Reserved Instance Marketplace. However, RIs that have been converted or obtained at a discount are not eligible for resale.
6. Many Options
While Saving Plans apply only to AWS Lambda, Fargate, and EC2, reservation models are available across many services, including EC2, OpenSearch, DynamoDB, ElastiCache and RedShift.
1.2 Limitations of AWS Reserved Instances
Along with numerous benefits, reserved instances have a few limitations that could hinder a project or an organization’s growth. Before committing to any RIs, it is important to understand these limitations and make appropriate decisions.
1. Reserved Instances can’t be Cancelled
Once purchased, reserved instances cannot be cancelled or refunded. This is the trade-off for securing computing capacity long-term at a significant discount. Such inflexibility may disadvantage companies whose workloads keep changing continuously. Therefore, AWS RIs are best suited for businesses with clear and consistent workload demands over an extended period.
2. Demands Commitment for Either One Year or Three Years
The commitment to reserved instances must be long-term, i.e., one year or three years. While there is flexibility in the payment mode, you are sure to be billed for the instances you committed to, whether you use them or not. Such a commitment can only be made if you are not planning to scale your workload for the given time. If your business is experiencing a constant shift in workload demand, like rapid growth or downsizing, then locking in with AWS RIs can prove to be a substantial financial risk.
3. Limited Flexibility in Scaling
Reserved Instances come with specific instance types and regional restrictions, which limit your ability to scale infrastructure. If your application’s demands change over time, you may require different instance types or more powerful instances than those covered by your existing reservations. In such cases, companies often need to rely on on-demand instances, which can significantly increase costs. The only exception is convertible RIs, which allow modifications but offer lower discount rates compared to standard RIs.
2. What is the Difference Between On-Demand Instances and Reserved Instances in AWS?
On-demand and reserved instances offer the same configurations and compute options. The primary difference between them lies in the billing model.
A reserved instance is purchased for a fixed term at a discounted rate compared to the standard prices of AWS on-demand instances. By committing to use the reserved instance for a specific period, you benefit from lower hourly or per-second charges.
In contrast, on-demand instances provide flexibility to scale usage based on changing requirements, with no long-term commitment, but at a higher cost since there is no usage guarantee or discount.
3. How Does AWS RIs Work?
It starts with purchasing an AWS Reserved Instance. To do this, you must first define several attributes, such as:
- Instance type (m5.large, c4.xlarge)
- Platform (Linux/Unix, Windows, RHEL, SLES)
- Tenancy (default or dedicated)
- Availability Zone (AZ) within a region
- Term length (1 year or 3 years)
- Payment option (All Upfront, Partial Upfront, No Upfront)
When you commit to an AWS Reserved Instance, AWS provides a discount on the instances running in your account that match the specified attributes within the capacity you bought.
Purchasing Reserved Instances doesn’t mean launching specific instances categorized as reserved. Instead, you commit to paying for specific instance types over a fixed term. When the bill is generated, AWS automatically applies the RIs to matching instances in your account, resulting in reduced rates.
It is important to mention that committing to pay for an instance for a specific time period means you will be charged for that computing capacity regardless of whether you use it. Reserved Instances only provide the opportunity to use instances at a discounted price. Therefore, ensure you purchase AWS Reserved Instances only for instance types and configurations that your business requires for long-term usage.
4. Types of AWS Reserved Instances
AWS offers two main types of Reserved Instances: Standard and Convertible. These categories differ primarily in their post-purchase flexibility, which affects potential cost savings. Therefore, it becomes necessary to understand the difference between these types for selecting the right instance depending on your growth plans, workload stability and risk tolerance.
4.1 Standard Reserved Instances
Standard Reserved Instances (RIs) are the most commonly used type with the highest discounts compared to on-demand prices. However, they are not very flexible after the purchase. You can not exchange these RIs for a different configuration. Once you reserve capacity for one or three years, you are locked into the selected instance type, platform, and other specifications. The payment options for Standard RIs include All Upfront, No Upfront and Partially Upfront.
Standard RIs are the only type that can be sold on the AWS Reserved Instance Marketplace if you no longer need them. They are ideal for predictable workloads with consistent capacity requirements over a long period, providing significant cost savings.
4.2 Convertible Reserved Instances
Convertible Reserved Instances (RIs) offer greater flexibility than Standard RIs. They allow you to modify the reservation by changing the instance type, family, or operating system. Although this flexibility typically results in lower discounts, Convertible RIs are ideal for businesses with dynamic workloads or those that want to adopt new instances as soon as they become available.
Converted RIs can be exchanged based on a simple principle: the value of the new reservation must be equal to or greater than the value of the original one. Moreover, these RIs can’t be transferred to another buyer or sold on the marketplace. Therefore, once you purchase Converted RIs, you are committed to either using them or exchanging them.
5. How To Purchase AWS Reserved Instances?
Buying an AWS RI is a straightforward process, whether you use the AWS Management Console, CLI or API tools. Follow the steps below to complete a successful purchase:
- Sign in to your AWS account and open the AWS Management Console. Navigate to the relevant service dashboard and click on the “Reserved Instances” button. Here, you will find all available RIs.
- Locate and select the Reserved Instance you need. Then, specify the instance type, quantity, term length, payment option, and region. Be sure to consider your workload requirements when providing this information.
- The pricing model will provide three payment options: All Upfront, No Upfront, and Partial Upfront.
- Carefully review the selected instances and their details to ensure the configuration fits your requirements. Significant savings occur only if the instances you commit to align with your actual usage.
- After reviewing, confirm your purchase to complete the transaction.
Once you buy Reserved Instances, the billing discount will be automatically applied to the instances that match your RI attributes.
6. Best Practices To Make the Most of AWS Reserved Instances
Using Reserved Instances is beneficial, but adopting strategically could bring in greater benefits. Here are a few tips to consider when working with AWS RIs.
6.1 Use a Mix of RI Types
Using a mix of different types of Reserved Instances to align with your usage patterns is highly recommended for most AWS environments. Standard RIs are suitable for steady, predictable workloads. Convertible RIs offer flexibility for dynamic workloads by allowing instance modifications. Scheduled RIs can be used for tasks run at specific times, providing additional cost savings. Clearly assess your requirements and prepare the right combination of RI types to match your system’s dynamics. This approach helps optimise actual usage and maximise cost efficiency as low as possible.
6.2 Monitor RI Utilization
To ensure desired cost savings, regularly monitor your AWS RI usage. Use the Cost Explorer tool to review the RI Utilization and Coverage reports provided by AWS. These reports indicate how well your Reserved Instances align with your actual usage.
- RI Utilization Report: This report shows the total usage percentage by comparing the instances running in your AWS account against the RIs you have purchased. A low utilization rate indicates that many of your Reserved Instances are unused, meaning you are paying for capacity you do not need. In such cases, consider selling or modifying your Reserved Instances to better match your requirements.
- RI Coverage Report: This report displays the percentage of your total instance usage covered by RIs. A low coverage percentage indicates that most of your instances are running on-demand, resulting in fewer savings. This suggests that purchasing additional RIs could increase your cost savings.
Careful evaluation of both reports provides valuable insights into your RI usage and optimization opportunities. The goal is to avoid wasting reservation spend while increasing RI purchases that align with your needs to maximize savings.
6.3 Use Historical Data to Guide Purchase Decisions
Evaluate actual usage patterns and trends using the Cost and Usage Report (CUR) and AWS Cost Explorer reports before purchasing the Reserved Instances (RIs). RIs that have been running for over three to six months with stable configurations offer the best coverage.
6.4 Distribute Non-Compute RIs Over Time
RIs for services such as OpenSearch, ElastiCache and RDS are less flexible compared to compute-based commitments because they can’t be exchanged. Distributing purchases over time using a rolling approach is an AWS best practice that helps avoid overcommitment upfront.
This means you don’t have to commit a large sum at once when purchasing non-compute RIs. For instance, instead of paying $60 upfront for 1-year RIs, you can spread your purchase evenly across 12 months, paying only $5 per month.
This breaks down your commitment into twelve monthly segments: each month, a new commitment begins while one-twelfth of the previous commitment expires. You can choose whether to renew, increase, decrease, or let the commitment lapse based on your actual RI usage.
With the rolling approach, you implement an adjustment mechanism that allows you to respond to workload changes and maintain the flexibility to avoid being locked into computing capacity that no longer fits your needs in the long term.
6.5 Stay Informed on AWS Policy and Pricing Changes
Keep yourself, your team, and your organization informed and updated on the pricing structures and resale policies of AWS Reserved Instances. Having this knowledge empowers you to make smarter long-term decisions and avoid financial risks.
6.6 Track Effective Savings Rate (ESR) and Commitment Lock-in Risk (CLR)
Avoid relying solely on simple metrics like coverage and utilization to assess financial results; these metrics only indicate usage and coverage efficiency. AWS experts recommend using the Effective Savings Rate (ESR) to understand your actual savings and the Commitment Lock-in Risk (CLR) to evaluate how much cost is at risk due to your long-term commitments. Using both metrics together provides a holistic view of risks versus savings.
7. Conclusion
AWS Reserved Instances (RIs) act as an effective cost optimization tool for organizations running applications on Amazon EC2. By committing to a term length of one or three years, businesses can avail themselves of substantial discounts ranging from 30 to 70% compared to standard on-demand instance rates.
To maximize the benefits of RIs, it is essential to use the right combination of Standard, Convertible and Scheduled AWS RIs. Even if your needs change over time, you can optimize your Reserved Instances and secure maximum savings by regularly analyzing your usage data, maintaining high RI utilization and coverage, and reselling unused RIs on the RI marketplace.
Regardless of how your AWS environment is, implementing a carefully crafted AWS Reserved Instance strategy can yield significant savings. These savings can be reinvested in new projects, used to purchase additional resources, or allocated to other core business areas.
FAQs
What are AWS reserved instances?
AWS RIs are the compute capacity reserved on Amazon EC2 and Amazon RDS by organizations to use at discounted prices. Reserved instances provide a billing discount that applies to specific instance types. Companies can choose from different instance otpions based on operating system, term length, region, availability zone and tenancy specifications. AWS RIs have a flexible payment structure and can also be exchanged within the same instance family or moved to a different availability zone within the same region.
What is the difference between on-Demand and reserved instances?
On-demand and Reserved Instances represent two distinct pricing models for Amazon EC2 instances in the AWS cloud. Functionally, both provide the same compute resources; the main difference lies in their pricing and commitment.
When using on-demand instances, users pay by the hour or second with no long-term commitment and only pay for what they actually use. These instances can scale automatically to meet changing workload demands. In contrast, RIs require a long-term commitment for a fixed term but offer significant discounts of 30-70% depending on the RI type. However, this pricing model is less flexible: users are billed for the reserved capacity regardless of actual usage.
What is the difference between AWS Savings Plan and Reserved Instances?
The key differences between Savings Plans and Reserved Instances lie in flexibility, procurement methods, applicable AWS services, and how discounts are applied. Reserved Instances require a commitment to use an instance at a predetermined price for a fixed duration. Savings Plans require a commitment to a consistent hourly expenditure over a defined period but provide more flexibility across instance types and regions.




Comments
Leave a message...