
Businesses need software solutions to scale or optimize their processes. However, building software is challenging and expensive. In-house solutions take too much time and money, while outsourcing can often fail to provide complete control or oversight of the project and the development team.
In such cases, establishing an offshore development center is the most suitable way to fulfill your requirements and gain additional advantages. It is completely different from hiring an offshore software development company.
Read this article to understand the concept of ODC, its benefits, different models, a step-by-step guide to set up an ODC, best practices, and more.
1. Overview of Offshore Development Center
An Offshore Development Center (ODC) is a software development facility located in another country, often operating in a different time zone. Dedicated offshore software developers work as an extension of your IT department, speeding up your development process. The company managing the offshore development centers is responsible for recruiting, training, and maintaining high-quality resources for optimal performance.
An Offshore Development Center is also referred to as an Offshore Delivery Center or Offshore IT Development Center.
1.1 What is the Difference Between ODC and Outsourcing?
When a corporation faces a significant shortage of software engineers or desires to reduce in-house development expenses, outsourcing could be beneficial. Global spending on outsourcing reached an estimated USD 744,623.5 million in 2024 and has been steadily increasing ever since. – grandviewresearch
There are a variety of models to explore under the traditional outsourcing strategy. When a business has established the project’s needs, scope, and success criteria, a fixed-price software outsourcing model can be an excellent option.
When project specifications are ambiguous or the project requires long-term offshore support, an offshore development center can develop your software project from scratch.
Nevertheless, there are further important distinctions that should be considered when picking between different recruiting methods.
We establish six fundamental characteristics that distinguish ODC from outsourcing. These include:
1. Project Duration
The project duration is long-term under the offshore development center model. The client is required to set up a dedicated team to work on the project for an extended period. The ODC helps scale resources gradually and supports continuous collaboration by providing ongoing development, support, and maintenance.
Meanwhile, outsourcing depends on a fixed-term contract that covers a specific set of tasks or a limited timeline. Outsourcing projects involve short- to medium-term engagements in which the software vendor delivers a product or service at a predetermined quality and timeline.
2. Team Size
Outsourcing typically enables you to hire a single developer to solve your technological deficiencies. In contrast, the ODC strategy provides an entire development team of experts.
3. Hiring Method
When hiring software developers for your ODC team, the tech provider typically conducts a stringent assessment, which is common for all. Whereas, for outsourcing projects, all the developers are carefully selected to meet the specific needs.
4. Control and Management
In an ODC model, you have a dedicated team working exclusively on your project. This approach gives you full control over project management, team management, processes, and workflows.
If you don’t want to deal with daily project details, outsourcing is better because you generally won’t manage the project processes and development teams. If you need project operations to align with your company standards and customer requirements, an ODC is more helpful.
5. Costs
Establishing an offshore development center requires a significant initial capital investment. Paying the team, buying or renting the space, and setting up and maintaining the infrastructure are the biggest expenses in ODC; they continue to drain funds even on days off and holidays. Despite this, ODCs are argued to be cost-efficient in the long run. It helps effectively allocate resources, optimize operations, costs, and improve product quality.
On the contrary, outsourcing is often considered a cost-saving measure. Charges are lower, and you don’t have to worry about paying team salaries or buying expensive resources. Although there might be some hidden costs, overall, outsourcing is a more cost-efficient option.
1.2 Advantages of Offshore Software Development Center
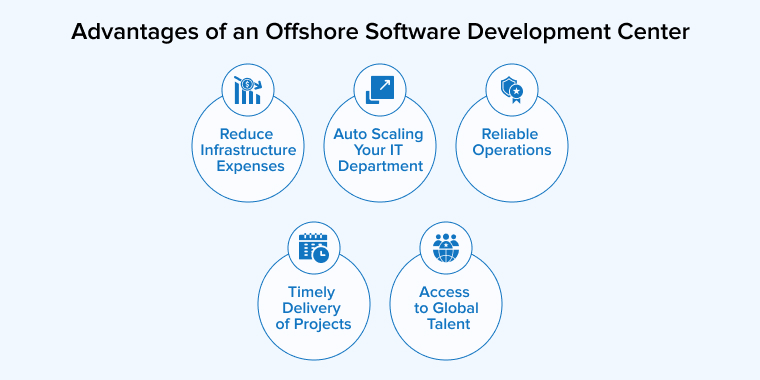
Developing a business relationship with a dedicated Offshore Development Center offers several advantages for your firm. These are the benefits of possessing an ODC team:
1. Reduce Infrastructure Expenses
Cost savings are one of the primary reasons businesses set up offshore development centers. Establishing a facility in a country with a low cost of living lets companies obtain the required professional expertise at lower wages, delivering a quality product with reduced development costs. Moreover, companies can save significantly on office rent, infrastructure and technology maintenance, and utility bills, since these costs are generally lower in offshore countries.
2. Auto Scaling Your IT Department
Autoscaling is the technique of adjusting resources periodically to meet operational demands. Depending on the objectives of certain projects. The amount of resources that your organization needs may vary. Enterprises may require a high level of assets at times and a lower level at other times.
During these situations, you may be required to reassign or reduce assets and responsibilities within your team, which may necessitate a complex resource-management process. An ODC simplifies allocation by allowing the offshore team to assume the functions and responsibilities of the in-house team.
3. Reliable Operations
To attract customers into a marketplace, the processes used by leading ODCs are quick, lean, and trustworthy. These companies maintain accountability and transparency with their clients through the use of effective assessment and reporting methods. You will be able to evaluate and track the development of their initiatives in real-time. Depending on the terms of your agreement with the offshore development center, you may request a revision of the project at no additional expense if you are unsatisfied with its outcome.
4. Timely Delivery of Projects
An ODC works in a well-equipped environment and uses efficient business processes to ensure your tasks are completed on time. From project strategy, design, programming, training, and delivery, they closely adhere to the deadlines that you establish. The continuous coordination between the in-house and offshore team members enables the project lifecycle to be completed in less time.
5. Access to Global Talent
When you build an offshore development center, you need to hire people from that country to run operations. Offshore countries in Asia, Eastern Europe, and other regions have large pools of talented developers with a varying set of skills and expertise. Opening ODCs in these countries gives you direct access to these experts, who follow international standards for quality and product delivery.
1.3 Challenges of Offshore Development Center
Let’s look at some challenges faced by offshore development centers.
1. Security Risks
Security is a major concern in any offshore operation. Sharing sensitive information across borders increases vulnerability and the risk of data breaches. Even with necessary security measures in place, such as access controls and encryption protocols, data migrations are susceptible to leaks and cyberattacks.
2. Cultural Differences
Offshore centers are often halfway around the world, so you can expect differences in values, beliefs, and behaviors. These differences can cause conflicts between offshore and in-house teams. For example, some cultures value long working hours while others prioritize work-life balance. Friction is likely when people from these different cultures must collaborate on the same project.
3. Time Zones
You may experience challenges in communication and coordination because of large time zone differences, such as delayed responses, miscommunication, and inefficient coordination. With a large time-zone gap, even a simple task of scheduling meetings becomes difficult. Unless both teams adjust their working hours to establish an overlap, they cannot collaborate effectively to discuss project plans, share updates, and address issues.
4. Communication Barriers
Communication becomes an issue when both teams speak different languages. Even if you have a common language, such as English, the lack of proficiency on one side can create confusion and miscommunication that can seriously harm your project.
Not communicating your requirements and issues clearly creates problems. Failing to communicate regularly to check project progress can also cause problems. Using unreliable communication channels can cause delays and, consequently, more problems.
Ensure both teams are proficient in the same language to enable clear communication. Also, use reliable, robust platforms to maintain seamless connectivity.
5. Quality Control
Working with remote teams might make it challenging to monitor the software development process and maintain quality standards. In addition to investing in training, conducting frequent audits and inspections, organizations must have thorough quality control procedures. To further aid in quality control, businesses should set strict requirements and apply a consistent set of quality assurance tests for every project.
2. Different Models of Offshore Development Center
Various ODC models are seen in the market, catering to different types of business requirements. Let us understand the types of offshore development center models to choose the right fit for your project.
2.1 Product Engineering
This ODC model covers the entire project lifecycle, including ideation, design, development, testing, and scaling. The project engineering model makes significant investments in project research, maintains a complex infrastructure, and relies on a diverse team to handle every aspect of the project.
The scope of work and objectives are not fixed; they are defined based on the outcomes of the research and planning stages. Businesses can build an innovative software solution by leveraging this ODC model. Companies choose this model when they want to handle every stage of the software development lifecycle, from ideation through ongoing updates.
2.2 Build-Operate-Transfer Model
This ODC model has three stages: build, operate, and transfer. The BOT model is considered one of the best ODC approaches and offers optimal control over the project.
In this approach, the offshore development company builds a dedicated team, sets up the required infrastructure, and runs operations for the initial years. Once both teams validate the success of the ODC, the company transfers ownership to the client.
The BOT model lets businesses have a foreign presence without building a team or setting up infrastructure themselves. It’s the right choice for companies planning a permanent offshore presence and for projects with long-term potential.
2.3 Project-Based Model
When working on a project with a clear scope and a definite timeline, you can opt for a project-based ODC model. This model suits small projects or specific parts of a larger project. The dedicated team is built with a focused skill set. This helps you achieve desired outcomes.
With a predetermined scope, objectives, milestones, and timelines, resource allocation and progress monitoring become easy. If you are building a website or a mobile application, then a project-based offshore development center is the best option. This model encourages managed costs, streamlined communication, and focused delivery.
In project-based ODC models, operations are time-sensitive, and quality is expected to be high. Such rigour allows businesses from domains like e-commerce, fintech, and healthcare to achieve their goals efficiently.
2.4 Customer Model
When clients set up and operate an offshore development center themselves to fulfill their requirements, it is known as a customer model in an ODC. The client either hires new personnel from offshore countries or relocates their existing employees to work at the ODC.
True to its name, the customer model gives the client complete control over their project, including the flexibility to adapt to new trends and other changes. In short, this ODC works as a subsidiary of the client’s parent company.
Every team member at the ODC is a full-time employee of the client. This model allows the company to really have their own extended business unit overseas, handling specific IT operations for them. The client bears every cost, including the infrastructure, management, and technical resources.
2.5 Dedicated Team Model
In a dedicated model, you have a team of software experts working exclusively for your company from a remote location. The offshore software development company handles setting up the essential infrastructure.
This model enables you to scale your team size according to changing business requirements. The dedicated ODC model is ideal for both startups and enterprises. With this model, you get a remote team providing complete IT support or assistance to your in-house team.
3. How to Set Up an Offshore Development Center?
Depending on your requirements, you might have to set up an ODC for your software development project. Follow this step-by-step guide for effective outcomes.
3.1 Defining Your Needs and Goals
First, get clarity on your requirements. Define your project objectives and the scope of the work. This will help determine whether an offshore development center is the best option and, if so, which engagement model would suit you best. You can set up an effective ODC and strategize an efficient development plan only if you first clearly understand your project objectives and requirements.
3.2 Select the Right Offshore Location
When choosing the right offshore location, you must consider multiple factors. Each offshore location has its own advantages and challenges. Compare them against your requirements to find the right fit. Here’s what you need to look for:
- Top Offshore Regions: Compare all the top offshore regions, such as Asia, Eastern Europe, etc., to find where it would be more advantageous for you to set up an ODC.
- Talent Pool: Assess the best locations for the availability of professionals with the skills required for your project. There is no point in establishing an ODC if you can’t access the global talent pool.
- Time-Zone Alignment: Examine the time difference between your company’s geographical location and the offshore site to identify overlapping hours that allow real-time collaboration.
- Costs: Offshore locations often have lower costs of living and, consequently, lower labor costs. Compare costs across regions to find the option that best fits your budget.
- Cultural Compatibility: Verify whether the offshore region—or at least the specific ODC—has a work culture compatible with yours. Consider languages, work ethics, communication styles, and other cultural factors.
- Law and Regulations: Understand the law and regulations in the country where you plan to build an offshore development center. Compliance with relevant regulations is essential to avoid any legal issues.
- Political and Economic Stability: Regions with unstable politics or weak economies pose a higher risk of operational disruption. Choose a location that offers long-term viability.
3.3 Choose the Right ODC Partner
Once you decide on an offshore location, it’s time to find a suitable development partner that can help you build an ODC for your project. Start by searching for companies on platforms like Clutch and DesignRush, reviewing services offered, client reviews and ratings, and previous projects. Shortlist a few options, then compare them on factors like experience, portfolio, pricing, etc. A careful evaluation will help you find the right ODC partner.
3.4 Legal and Compliance Issues
Every country has its own laws and regulations regarding taxes, employment, and data privacy. Therefore, if you set up an offshore development center in a foreign country, it is important to comply with their regulations to avoid fines and other legal issues.
Additionally, you must legalize and regulate the partnership between the software vendor and your company. This requires signing various legal contracts—such as NDAs to protect sensitive data, IP rights to retain ownership of intellectual property, and SLAs to define responsibilities, deliverables, and more.
3.5 Set Up Infrastructure
Building an offshore development center requires setting up essential infrastructure such as office space, power supply, internet connectivity, IT systems, hardware, software, backup systems, and security measures. It takes a lot of time and money to establish the infrastructure, and it can be a significant hassle.
Therefore, many businesses choose to outsource this task to a software vendor. A software development company sets up the infrastructure and then transfers the ownership to your company.
3.6 Create Communication and Collaboration Strategies
Since the ODC will be located in a foreign country, continuous coordination and communication are needed to ensure that the project progresses according to the predetermined timeline and that issues are addressed as soon as they arise. Here are a few tips for effective communication:
- Conduct regular meetings to discuss the latest project updates.
- Use robust and reliable platforms for communication and project management.
- Outline a clear project plan and create a detailed workflow to accomplish it.
- Implement communication and collaboration protocols to avoid and address potential issues.
3.7 Monitoring and Adjusting
Consistent quality outcomes require continuous monitoring of ODC performance. Identify and track key performance indicators, and set up a feedback loop. Monitoring reports will reveal system problems and areas that need improvement.
You can track the performance of the overall team and the system, or you can also track the productivity of an individual team member or the efficiency of an individual system module. Periodic performance reviews and security assessments are also quite helpful.
Based on the assessments and feedback, you can optimize the workflow and business processes of the offshore development center, and help team members improve their skill set and, ultimately, their performance.
4. Conclusion
The establishment of an offshore development center has proven to be one of the most profitable investments for driving digitalization within organization. ODC is an efficient business model that extends a company’s market presence in a foreign nation, improves access to tech talent, and reduces upfront and infrastructure expenses.
As the trend of offshore software development continues to grow, an increasing number of outsourcing destinations have begun offering offshore development center services. However, the Indian IT industry is renowned for being the leading offshore development center. In addition, you’ll need an ODC supplier like Tatvasoft for all of these benefits to function properly.
FAQ
What is an offshore development Center?
An Offshore Development Center (ODC) is a development center that is located in another country and in a different time zone. In this model, dedicated offshore software developers function as an extension of your IT department and accelerate your development process.
What does an offshore developer do?
A team of offshore developers can handle various aspects of your tech project, including creation, implementation, support, and testing. They bring a blend of technical expertise and soft skills.
How do I set up an offshore development center?
Follow these steps to set up an ODC:
- Determine the Location
- Partner up with an ODC provider
- Establish your team
- Start the Project





Comments
Leave a message...