
Changes in rules and policies, improvements in administrative procedures, and more technical knowledge and data utilization, the doctors’ work is becoming increasingly challenging.
That’s why EHRs are so crucial; they allow clinicians to devote their whole attention to their patient satisfaction. They now have instant exposure to patient data, assurance of security, and simplified routine tasks. As expected, a significant investment of time and energy is required to master and implement EHR in a healthcare organization. Nevertheless you can obviously take help from a healthcare software development company to develop and implement EHR in a smoother way.
However, what is an EHR? And what do the EHRs do? We explain it all here.
1. What is an Electronic Health Record?

The Electronic Health Record (EHR) is a computerized copy of a patient’s medical history that is maintained by the doctor throughout time. It may contain the patient’s statistical profile, challenges, prescription drugs, pulse rate, previous health history, immunizations, laboratory tests, and radiology test results, among other things. Electronic health records (EHR) automate data access and may help healthcare providers in saving time. Through its many interfaces, the EHR may also facilitate tasks such as quality monitoring, data analysis, and evidence-based predictive modeling, which makes it a more detailed technology than an electronic medical record (EMR).
Electronic health records (EHRs) are the next stage in the evolution of healthcare, with the potential to improve communication between doctors and their patients. Improved decision-making and care delivery will result from timely access to accurate data. Take a look at Quora user answer about EHR experiment and inception –
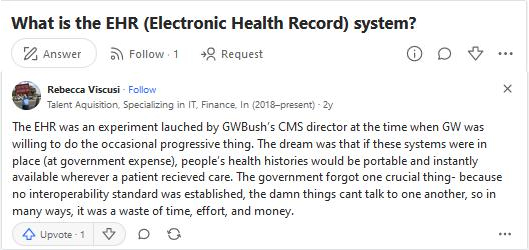
A few ways in which the EHR can enhance medical treatment for patients are:
- Improving the quality of medical paper records in order to reduce the occurrence of medical errors.
- Providing access to personal health records, minimizing unnecessary examinations, speeding up the treatment process, and empowering patients to make educated decisions are all benefits of this approach.
- Improving the quality and readability of medical records to reduce medical mistakes.
1.1 Features of EHR
Now, let’s understand the features of EHRs that can ease out the overall work between hospitals, doctors, and patients by incorporating them into the system:
1. Electronic Health Records for Office Administration
- Effective scheduling is made possible with the use of a user-friendly interface for schedule management.
- Check-in, rooming arrangements, changes, alerts, and reports on patients’ conditions are all observable.
- Setting the sequence of assignments, assigning duties to others, and monitoring their progress may all be handled.
- Care schemes, organizational standards, and order entry for individual patients can all be prepared as part of the clinical recording process.
2. Electronic Health Records to Support Physicians
- The information needed can be immediately retrieved from patient charts.
- Clinicians can add details to patients’ records by a variety of recording methods, such as filling out templates, dictating, or making notes by hand.
- Physicians can swiftly generate patient-specific reports including medication lists, visit summaries, treatment plans, client histories, and care orders using the report-generating features of modern medical software.
- With ePrescribing, doctors may write prescriptions online and have them sent electronically to a pharmacy’s computer system. Drug interaction alerts can also be flagged by the system at the time of prescription ordering.
- Preventive services, exams, and appointments can be reminded of patients via automated reminders. The system has the capability to monitor the status of tasks and issue reminders if necessary.
- Administrators can use data segmentation to categorize and share specific elements of patients’ electronic health records, keeping private information secure.
3. Electronic Health Records for Patient Portals
- Patients can take an active role in their treatment by communicating with their physicians using tools such as online messaging, online bill payment, online medication refill requests, and online access to their medical records.
1.2 The Benefits of EHRs
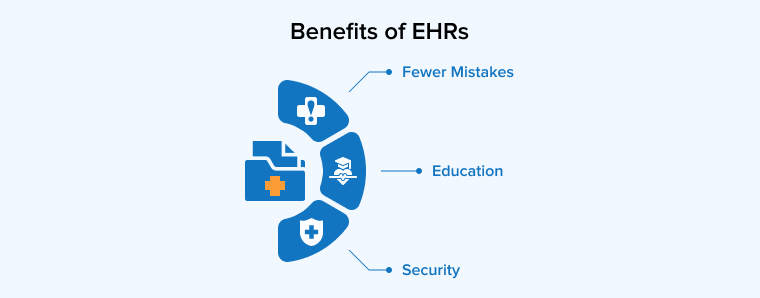
EHRs can optimize the therapy since they provide better communication and coordination between doctors and patients. Some examples of their usefulness are as follows:
1. Fewer Mistakes
Doctors and nurses may use abbreviations to shorten the time it takes to write comments. Therefore, there is a possibility that a reader of the chart will not comprehend the abbreviation and will need to search for the meaning. Clinical staff may improve their thoroughness and efficiency with the aid of EHR software, which guides them via a succession of questions and selection menus.
2. Education
Your active participation in your personal health care is enhanced by your access to medical records. Test reports, glucose levels (for those with diabetes), directions from the medical staff, and the possibility of human mistakes are all accessible.
3. Security
Paper documents can be easily misplaced or destroyed if not properly stored. Electronic data are less likely to go missing, and even if they do, most are password-protected to prevent unauthorized access.
1.3 Uses of EHRs
When stored on a server or in the cloud, patient information in electronic health records is encrypted to ensure that only approved individuals may access it. A record’s contents may be difficult to discover for the general public, but individuals with the proper permissions may access it. Electronic health records (EHRs) are primarily used by doctors and their patients. To avoid abuse of this information, biometric and two-factor access methods are gaining popularity.
1. For HealthCare Providers
Health data used to be originally developed to alleviate the burden of paper charts on healthcare professionals. Doctors can utilize this electronic document to look up information, including a patient’s medical history, current medications, and imaging results. They are able to write new prescriptions, renew existing ones, request and examine diagnostic imaging and laboratory tests, and respond to patients’ phone calls and messages.
As an added benefit, they may coordinate with the patient’s other care professionals. Most doctors today use electronic health records (EHRs) for patient recording. Also, provider groups may manage sales invoices and patient transactions within the EHR, eliminating the requirement for paper bills in many cases.
2. For Patients
Patients today can benefit immensely from having access to the EHR, despite the fact that it was likely developed with the healthcare practitioner in mind. The EHR is primarily used by patients to convey information to their doctors, such as inquiries about treatment options or concerns about side effects.
Patients may also be able to conveniently seek refills on medications, make payments, and examine lab results as soon as they become accessible, all inside the same system. Numerous websites offer health education information to enable patients to become more active in their personal care.
2. How Does an EHR System Work?
Electronic health records are dynamic files that can follow a patient’s care wherever they go and can be viewed by more than one person at once, unlike the cumbersome hard copies from the past. It is a reflection of the patient’s overall health and aids doctors in achieving optimal results. As a result of its useful consequences, electronic health records have become an integral part of modern health care.
2.1 Give Access to Healthcare Information
To begin, the electronic health record (EHR) makes the patient’s whole medical history easily accessible to their treating doctors and other clinicians, as well as the patient themselves. As previously noted, this comprises the patient’s record of complete medical history, including past and present conditions, significant demographic information that may impact the treatment plan, and all clinical reports. Additionally, doctors may utilize aspects of this record to deliver outcome-based treatment and make the most informed judgments for their patients.
Medical providers now visit more patients than ever before, yet thorough documentation in any health care system is still essential for providing excellent treatment. In order to maintain high-quality treatment, clinicians can save time and effort by using electronic health records. Electronic records are constructed with a digital interface, which allows for easy sharing between different medical institutions to ensure that all treating clinicians have access to the same comprehensive patient records.
2.2 Collect All Patient Information in One Place
Second, the EHR eliminates the possibility of a vital piece of data being omitted from a patient’s documentation. Rather, this data is kept digitally and in a centralized location (such as a server or the cloud) where it can be accessed by anybody with the proper credentials at any time. Decisions may be made quickly and confidently based on the data stored in the EHR. Allergies, co-existing conditions, dates of last vaccination, and other relevant data are readily available to help providers make the best possible decisions for their patients’ health. Everything is organized and easy to locate. In reality, the patient’s electronic health record (EHR) may go with them everywhere they go, regardless of where they receive treatment because it can be exchanged with other digital health care systems.
3. How to Implement an EHR System?
Follow these steps to successfully implement and EHR system:
3.1 Build an Implementation Team
Include the doctors, nurses, front desk workers, aides, auditors, and administrators. These individuals shed light on the situation and possible difficulties.
3.2 Consider the Space Layout
In order to keep accurate electronic health records, users need access to PCs, laptops, or mobile devices. Placement of these items, from the reception area to the exam room, should take patient privacy and convenience into account.
In designing waiting areas and testing rooms, think about the way attendees will be seated and interacting. The medical staff should not ignore patients in favor of entering information into the EHRs.
3.3 Determine Required Hardware
Engage with the electronic health record installation contractor to find the necessary hardware to operate the new systems. It’s not just about servers here. Think about the types of people who will be using the electronic health record system.
Adding extra printers to different areas of the business, for instance, may help boost efficiency. Servers may be kept in a secure, off-limits area. The provider of the EHR system and their team members can help with the hardware evaluation.
3.4 Configure the Software
Software setup is something that can be aided by the company implementing the electronic health record. Identifying data, including patient background and payment details that should be incorporated into the new system, will speed up the process.
Also, safety should be a top priority. Security measures are crucial for achieving HIPAA compliance.
3.5 Transfer Data
After the new electronic health record system has been set up with the necessary hardware and software, data must be transferred to it. In order to guarantee that all relevant data is transferred to the new system, it is helpful to create a checklist of the data to transfer.
It’s advised to keep the old systems around for a while once the data transfer is finished, just in case something was missed. Involve an IT professional in the destruction of any old systems containing sensitive data after all data has been transferred to the new electronic health record system.
3.6 Develop a Launch Plan
When the EHR installation has been finished, there are two alternatives for preparing for launch—gradually or entirety at once. Both strategies have their advantages. Think about the practicalities of implementation and the advantages and disadvantages of each option as you make your decision.
3.7 Create a Plan for When the EHR System Goes Down
The effects of a system outage can be mitigated with adequate planning. Spend some time crafting a strategy outlining what your team should do in the unlikely scenario that the EHR system goes down. Aside from keeping a duplicate of these instructions in the cloud for safekeeping, we also advise making printed copies available.
3.8 Set up a System for Collecting Feedback
Constant fine-tuning is essential for the efficient operation of an EHR system. Get customer feedback and utilize it to fix problems and create progress.
4. Importance of Electronic Health Records

There are several ways in which patients and medical facilities of all sizes can benefit from the use of electronic health records. The perks extend from the business side, where they can save money and boost customer happiness, to the medical side, where they can reduce medical mistakes and boost the quality of treatment provided to patients. Once doctors get the hang of using an electronic health record (EHR) system, they may visit more patients in less time without sacrificing the quality of treatment.
4.1 Well-Linked Health Care Information
Integrating all aspects of patient care system wide is a key motivation for many health organizations and healthcare providers to switch to electronic health records (EHRs).Data may be accessed from any desktop in the workplace clinics, such as those in exam rooms, at patient bedsides, and at nurses’ workstations. These connections aren’t limited to the patient’s primary care physicians, though. In this way, all professionals are working together to give the best treatment possible, which in turn leads to better patient results.
4.2 Medical Error Minimization
There has been growing recognition that electronic health record (EHR) use can cut down on preventable medical mistakes. Electronic health records (EHRs) give a second way for doctors to double-check prescriptions and test results, alerting them to probable drug interactions, potentially harmful readings, and urgent medical issues. The stress that physicians feel when they think a portion of a paper record has been misplaced can be alleviated when they have access to an electronic version of the same document.
4.3 More Efficiency in Health Care Settings
EHRs have the potential to increase physicians’ effectiveness and output once they are properly integrated across different healthcare software. The most significant factor is that the doctor may view the whole chart without waiting for a paper copy to be mailed to them. Doctors can save time by avoiding the need to decipher illegibly written instructions, completing less paperwork, accelerating the prescription procedure, and taking advantage of the system’s built-in voice detection software. Since insurance claim numbers may be created mechanically, this also helps hasten to invoice.
4.4 Improve Patient Care Coordination
Nowadays, it’s not uncommon for people to relocate across the nation, and even those who don’t end up moving every few years may end up using a different health organization or clinic in their current town. The electronic health record’s main advantage is that it allows the patient’s whole medical history to go wherever the patient goes. Thus, one may rest assured that no vital medical records will be lost to the sands of time.
4.5 Enhance Patient Outcomes
A patient’s health outcomes will improve since doctors will be better equipped to manage and prevent accidents and illnesses if they have access to their complete medical history at all times. No need to fret about prescriptions interacting with one other or unnecessary treatments being repeated. Moreover, the graph is regularly updated.
4.6 With Minimum to Zero Paperwork
Previously, preserving paper records required costly archive spaces, and substantial resources were allocated to the clerical work involved in updating and organizing the corresponding charts. The loss of this data has caused delays in treatment in some circumstances. The paper chart could only be viewed by one doctor at a time. Because the EHR stores all records digitally, they are protected from loss and can be accessed from anywhere, eradicating all of these issues. Data that was previously unreadable due to incomprehensibility or other causes has been restored because of the widespread use of computers and electronic health record systems.
4.7 Cost Savings
Adopting an electronic health record (EHR) is a cost-saving move that should be considered by almost every healthcare facility. By working more efficiently, medical professionals may tend to more patients in the same amount of time, which in turn reduces costs. Moreover, healthcare facilities can save costs on operational expenses related to the storage and restoration of paper data. Several payments for hospitals and other healthcare organizations that use EHRs were authorized under the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act stimulus package in 2009. Policies mandating EHR use for Medicaid coverage were also adopted.
5. EHR vs. EMR: What’s the Difference?
Electronic health records (EHRs) and electronic medical records (EMRs) are electronic copies of patient records. Nevertheless, electronic medical records (EMRs) are not easily transferable between hospitals or other healthcare facilities or easily accessible by other medical professionals. In contrast, electronic health records (EHRs) are made to be shared across all parties engaged in a patient’s treatment, including physicians, laboratories, and specialists.
However, electronic medical records limit the information that may be viewed about a patient. A variety of information about patients, including their demographics, diagnoses, treatments, and illness progression, may be retrieved via an electronic medical record. A patient’s medical history is recorded in detail in an electronic health record, which includes the same information as a paper chart. While EMRs provide some information on a patient’s past, EHRs provide a far more comprehensive picture.
6. Conclusion
In an age where patients expect instant access to their medical information and data without needing to personally visit their doctors’ offices, technological alternatives are a need. Keeping a patient’s medical record on paper may be time-consuming and labor-intensive for healthcare providers. This is when healthcare software development comes into play!
The capabilities of EHRs extend beyond those of EMRs. They are intended to include more data about a patient’s condition and clinical history than what was initially saved and input by the health institution. They can even help with administrative tasks in the healthcare industry, such as schedules and invoicing.
If you’re looking for a hassle-free clinical workflow among the hospital staff, doctors and patients, reach out to us so we can serve you in the most technical and creative way!
FAQ
What is an EHR in HealthCare?
The Electronic Health Record (EHR) is a computerized copy of a patient’s medical history that is maintained by the doctor throughout time. It may contain the patient’s statistical profile, challenges, prescription drugs, pulse rate, previous health history, immunizations, laboratory tests, and radiology test results, among other things.
What is the Difference Between EMR and EHR?
Electronic health records (EHRs) and electronic medical records (EMRs) are electronic copies of patient records. Nevertheless, electronic medical records (EMRs) are not easily transferable between hospitals or other healthcare facilities or easily accessible by other medical professionals. In contrast, electronic health records (EHRs) are made to be shared across all parties engaged in a patient’s treatment, including physicians, laboratories, and specialists.





Comments
Leave a message...