
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, digital health has advanced. Therefore, the key objective of healthcare companies wanting to offer patients healthcare services remotely is telemedicine applications.
Everything you require for telemedicine app development is right here in this blog. As an experienced healthcare software development company, We’ll discuss the economic, design, and technical aspects of telemedicine app development.
Entrepreneurs, especially those who have already started their businesses, and those who work in product management may find this article useful.
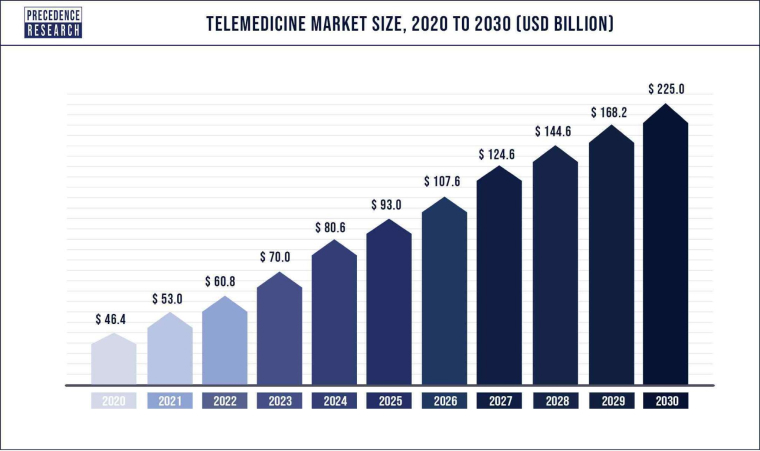
The global telemedicine market size was valued at USD 60.8 billion in 2022 and it is expected to reach USD 225 billion by 2030, growing with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.16% during the forecast period 2022 to 2030. – Precedence Research
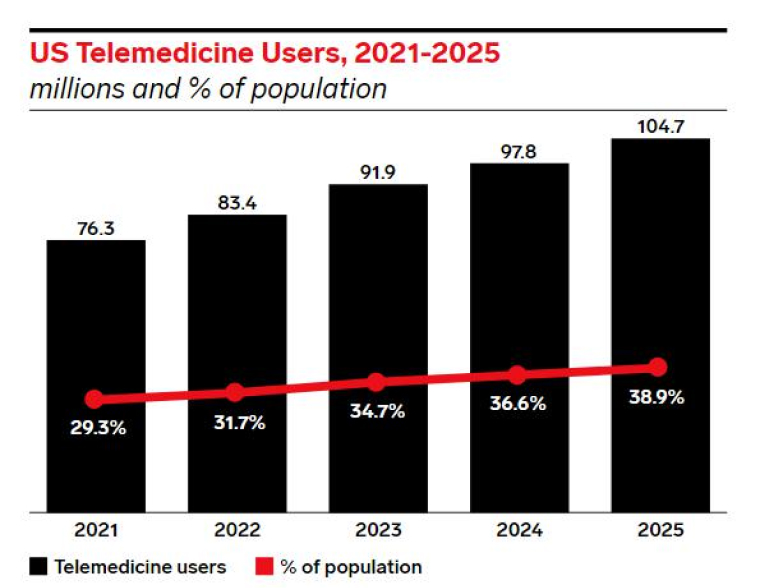
If we talk specifically about the telemedicine users in the US, here is what we anticipate to receive till 2025. After surveying the past years we can say it is supposed to only rise in the upcoming years. Take a look!
1. What is a Telemedicine App?
Telemedicine apps are software designed to help patients in need. With the use of telemedicine applications, patients can communicate with healthcare providers remotely through the use of modern digital technology. You would be surprised at how many other things these apps are capable of doing, beyond only facilitating remote consultations between patients and doctors.
Remote counseling and therapy, virtual care and treatment, patient monitoring, follow-up, medication prescription renewals, and a plethora of other services are all within reach with telemedicine apps.
Patients can more easily consult with doctors using telemedicine applications which are quicker as well. Doctor appointments are more convenient, and patients don’t have to endure long wait times or tedious travel. From the convenience of their own homes, they may access professional medical advice.
1.1 Types of Telemedicine Apps
Explore the different types of Telemedicine applications.
1. Real-Time Telemedicine Apps
Live video telemedicine apps allow doctors and patients to talk over video chat in real time. These applications provide the facility of a face-to-face conversation, enabling doctors to remotely evaluate patients’ health and offer guidance. A variety of contexts can benefit from video consultations, including general care, mental health counseling, dermatology, and follow-up visits. By skipping travel and queues, patients may save both time and money with these applications. Also, people who live in rural regions or have mobility issues won’t have to leave their homes to get the specialized treatment they need.
2. Remote Monitoring Telemedicine Apps
Another great and common form of telemedicine that lets patients self-monitor their health with different technology solutions is remote monitoring. Such apps let individuals collect vital health data using wearable gadgets as smart footwear, wristwatches, skin patches, or heart monitors. Device apps receive this data and forward it to a telemedicine server housed on a cloud.
It can take vital signs and record them so they can be reviewed later. Patients with chronic conditions including diabetes, asthma, cardiovascular problems mainly find this method to be really useful. Such patients should have constant vital monitoring. Advanced telemedicine technologies like RPM let patients, when needed, record, monitor, and pass on vital data record with healthcare practitioners.
It’s also a common approach for remotely keeping an eye on patients or those just released. It also encourages more information exchange and access to medical histories at far-off locations.
3. Store-and-Forward Telemedicine
Long-distance access to patient information and other medical data is made easier with store-and-forward telemedicine. Medical imaging, test results, bio-signals, and a plethora of other valuable data may be collected and sent across great distances. One major benefit of this form of telemedicine app is that it does not need the full focus of both the sender and the receiver. An expert, caregiver, or field technician can get the data needed, upload it, and then another professional can review it thoroughly afterward. Many specialized medical professions depend on this type of telemedicine every day, including dermatology, pathology, and radiology.
1.2 Why Build a Telemedicine App?
Telemedicine is the use of electronic communication to facilitate the transfer of clinical data across geographic distances for the benefit of patient care.
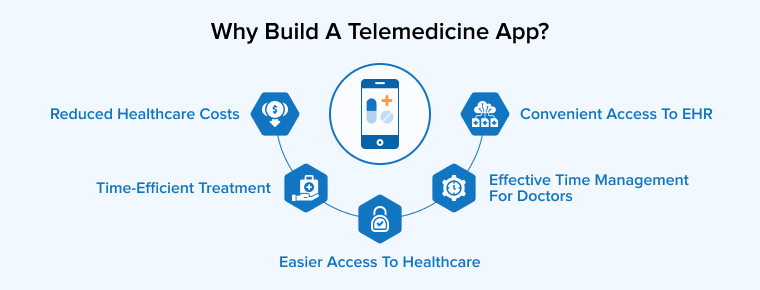
Through telemedicine, physicians and patients may streamline the consultation process and stay in constant contact. The need for private practice doctors to lease clinical space has been eliminated, and hospitals have a better chance of lowering their readmission rates. Healthcare data analytics coming from telemedicine apps help medical service providers access a new and effective avenue for marketing and sales. Read on to find out what goes into creating a telemedicine app, how much telemedicine app development costs, and what features it would include.
All of the confusion about telemedicine has been resolved. But what exactly are the upsides of this program from a clinical and commercial perspective? Let us separate each of them.
1. Reduced Healthcare Costs
In the healthcare industry, companies may save money on office space costs by offering remote medical services to clients. This allows for a larger pool of qualified and independent medical professionals to serve the market. They have worked for a corporation up until now, but the telemedicine app features have given them the freedom to work for themselves.
The emergence of telemedicine apps has wider implications beyond only helping out solo practitioners. As a result of patients no longer having to wait in lines, clinics see an increase in client flow, and the consultation process as a whole is sped up. This allows hospitals to increase their income in a shorter amount of time. The study also found that when telehealth applications were used, maintenance expenses were cut by 100$ on average per episode of care.
2. Time-Efficient Treatment
Some medical professionals may be on vacation or may not be on duty in a regular hospital. That being said, It may take a few weeks to complete a thorough medical examination. Telemedicine changes that. Allow patients to schedule visits with their healthcare providers online at their leisure. You may schedule back-to-back consultations since the consultation begins promptly.
3. Easier Access to Healthcare
Apps that facilitate telehealth connections between medical professionals and patients in remote locations are a boon to those who live there. It is sufficient to have access to a mobile network or WiFi and an app if no surrounding healthcare facilities are available. Additionally, people from nations with inadequate healthcare systems have access to medical advice from healthcare providers in other countries. For instance, in middle-income countries, approximately 75% of patients with mental problems go untreated. The availability of constant, mobile-based mental health assistance is made more manageable and efficient by the creation of dedicated apps.
4. Effective Time Management for Doctors
The ability to efficiently manage time is a skill that is shared by both independently practicing doctors and those who work in healthcare organizations and clinics. The app’s built-in appointment calendar and push alerts ensure that doctors never miss a patient’s scheduled consultation. Businesses, meanwhile, may link customer relationship management systems to healthcare apps during development. Both the administrative staff and the doctors benefit from the increased utility offered by this telemedicine app feature. Physicians may request sick days and shift changes using the app, while the administration can monitor the doctors’ workloads to ensure they have time for a healthy work-life balance.
5. Convenient Access to EHR
To facilitate on-demand access by medical professionals, telehealth programs archive EHRs (electronic health records). Having all of a patient’s medical history in one location is convenient for doctors. Patients can monitor EHR updates as well. The only real problem is with safety. Unfortunately, one slip-up can result in astronomical penalties for leaking sensitive medical information. HealthIT.gov reports that three-quarters of physicians believe that electronic health records help them provide better care to patients and reduce the number of drug mistakes they make.
1.3 Telemedicine App Benefits
In the following section, let’s explore the benefits of using a Telemedicine app for patients and medical health professionals.
1. Benefits of a Telemedicine App For Patients
Following are the benefits of a telemedicine app for patients:
1. Cost-savings
Costs associated with telemedicine are low for everyone involved, from patients to doctors. Traveling from home, taking time off from work, paying for daycare, and parking, and finding alternatives all add up to costs for the patient. These costs are on top of what the doctor already charges. Traveling to or waiting in the doctor’s office could cause unforeseen delays. These costs and hassles can be eliminated with telemedicine.
2. Better Compliance With Medical Treatments
The use of telemedicine has increased communication between patients, physicians, and other healthcare professionals. Relying on drugs too heavily might cause the therapy to fail. By using telemedicine, doctors can keep tabs on their patients and make sure they stick to their treatment plans.
3. Tracking health made possible
A wide variety of smart wearable devices, including watches, wristbands, bracelets, and glasses, may “inhabit” telemedicine apps in addition to smartphones. With the help of these Internet of Things (IoT) healthcare solutions, vital signs like blood pressure, glucose levels, and heart rate may be tracked continuously and transmitted to a doctor in real time. With this kind of information readily available, doctors may take immediate action if they feel a patient’s condition is deteriorating.
4. Minimal Patient Visits
The hospital doesn’t have to keep patients for longer when they are exhausted. If the level of surveillance required is minimal, patients can be discharged home. Doctors and nurses may still keep tabs on them from afar. It eases the discomfort associated with recovery.
2. Benefits of a Telemedicine App For Healthcare Providers
Following are the benefits of a telemedicine app for healthcare providers:
1. Easy access to a patient history
Via a telemedicine app, doctors have complete access to any medical records and remote patient monitoring. It is rather handy as there is no need to go through a lot of paperwork including test results and past opinions. Patient profiles help to neatly organize everything.
2. E-Prescriptions
With this feature, medical professionals may electronically prescribe medication to their patients. As a result, patients may use their prescriptions to access the app’s medication and other health services, such as tab testing.
3. Improved clinical outcomes
For healthcare practitioners, the consistency in telehealth monitoring has delivered warning signs concerning patient health at the proper moment. The digitization of monitoring has greatly enhanced clinical outcomes and exceeded standard on-site treatment results.
4. Enhanced patient engagement
Being able to communicate or phone a doctor at any moment helps a patient to build confidence in them. This lets doctors assist each patient keep a healthy lifestyle over time, teach them self-care, and spend more time with each one of them. Your clients will therefore have a more customized experience, which will help to lower dissatisfaction.
5. Appointment Notifications
The app notifies the physicians in advance of their scheduled appointments. Additionally, remind the patient whenever they schedule an appointment or make any changes to it. This way, doctors may swiftly decide whether to accept it or not, depending on their availability.
1.4 Features of Telemedicine App
There should be a doctor’s side and a patient’s side features and functionalities for any telemedicine app. Depending on their functions, they each have a unique set of characteristics.
1. Telemedicine App Features for Patients
Registering, making phone calls, uploading electronic health records, and other patient-facing features are all essential. Let’s focus on one at a time.
1. Registration
The first step is to register the patient. Patients find it simple and trustworthy when they only have to give a few information and go through a safe authentication process. When the information needed for registration is minimal with enhanced features for submitting the photo of other documents, patients find it simple to get started.
Following simple and quick registration, people can pick the doctor depending on their medical condition and make an appointment. Rather than typing, the patients can submit past medications, insurance verifying documentation, and their medical records.
2. Profile Management
After signing up, users must complete their profiles. Title, sex, and date of birth are just a few of the pieces of generic personal information that are included. The user’s EHR is the most crucial piece of information on a profile. It aids clinicians in diagnosing patients’ illnesses and reviewing their medical records. Remember that this is sensitive patient data that should be shared only with the treating physician.
3. Search & Filters
Patients will be able to locate the best physicians with the use of search algorithms. Users may refine their searches based on a variety of criteria, including location, language spoken, reviews, and medical specialty.
4. Video Conferencing Meeting

It is a crucial feature of telemedicine apps. The video should be sent to the doctor in the best possible resolution to observe any injuries or other symptoms. The sound should be crisp and audible as well. Every user has a unique internet connection, therefore app will need to adapt the video quality to prevent buffering automatically. However, the real-time connection must be maximized to the fullest extent feasible.
5. Live Text Chat

Patients can write to doctors when video calls aren’t necessary. Because texting doesn’t need a separate session, it may be used to resolve small difficulties. The doctor’s attention may be diverted from other patients during video conversations, whereas text messages can be replied to in the doctor’s free time. The ability to send files and photographs via text message is a fantastic bonus.
6. Calendar/Manage Appointments
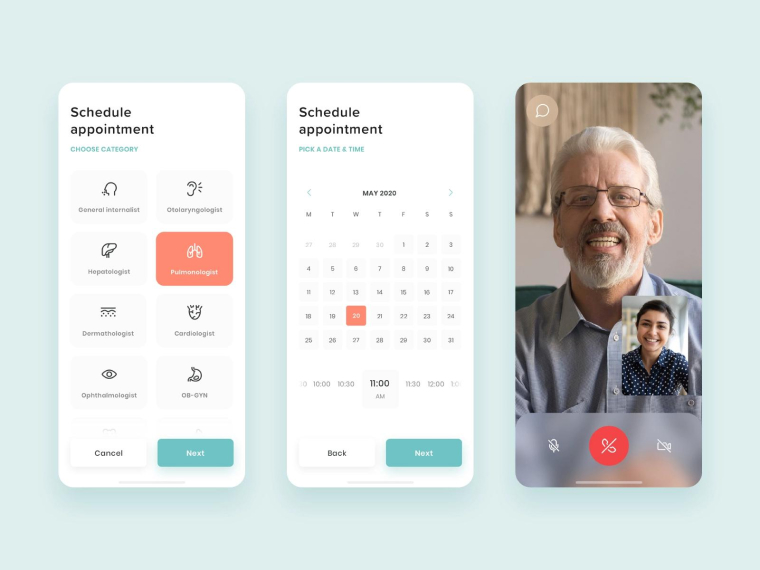
Patients may keep tabs on and organize doctor consultations with the help of the app’s built-in calendar. Patients can make modifications to the appointment time on the calendar and await the doctor’s clearance if necessary. Using the Google Calendar API, the schedule may be synchronized with Google Calendars, allowing users to get reminders directly from Google Calendar and view the relevant dates using a handy widget.
7. Mobile Payments
Allowing payments through mobile devices can make telemedicine applications easier to use. This lets users within the mobile telehealth app safely pay healthcare providers for services. You can quickly and safely pay through mobiles online for appointments. Payment services not only accelerate billing for patients but also provide thorough sales data monitoring and reporting for healthcare institutions, thereby improving financial control.
2. Telemedicine App Features for Physicians/Doctors

Telemedicine app features are also available from the doctor’s perspective. Let’s explore those features in further detail.
1. Physician Profile
On the app, a doctor has to be able to enter their qualifications, areas of competence, years of experience, and availability. Based on in-app authentication procedures, the app must also show the doctor’s review according to the rating by their past patients that visited them. This encourages doctors who regularly take good care of their patients and encourages improved healthcare from them.
2. Doctor’s Calendar
Every time a patient picks a timeslot, a doctor might accept, turn down, or provide an other time. Then the calendars are modified by default to prevent double-booking. This feature lets nurses spend more time with patients and substitutes for manual administrative work.
3. E-Prescription
The doctor must be able to present a valid computerized prescription, acceptable at any other healthcare facility and drugstore, thereby completing the in-app consultation. Along with the patient’s, the prescriptions must routinely store themselves on the cloud to the doctor’s personal database.
4. Payment Processing
Clinicians can develop and send invoices, make reminders, and handle payments with this feature. You can also provide report-generating solutions to let medical professionals remain updated with their finances.
2. Telemedicine App Development Steps
Telemedicine is an ideal solution because it combines the portability of in-person care with the ease of remote monitoring. Therefore, it has revolutionized health management and access to healthcare in every country. However, if you want your telemedicine app to be built successfully, it’s important to adhere to the proper development approach.
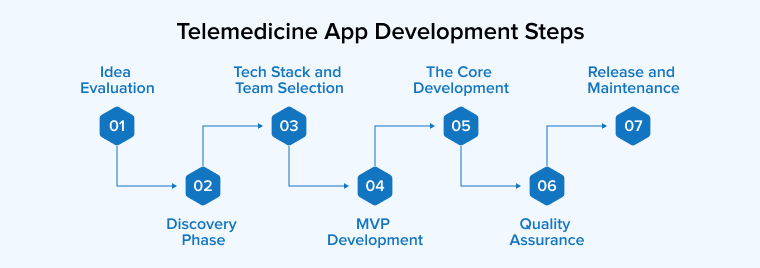
Here is the whole approach for developing a telemedicine app for your healthcare business:
2.1 Idea Evaluation
Before putting time and money into making a product that no one wants, you should see if your idea will work. Figure out what issue your product will address, do some initial business evaluation, find out how much demand there is for the future app, define the customer profile and customer base, study the industry and competition in the sector, and come up with your telemedicine solution’s unusual selling point. Apart from that, you should attentively review the telemedicine laws to make sure your software follows all essential rules.
2.2 Discovery Phase
An idea is the foundation of every project. Starting with a comprehensive market study and economic analysis can help you check your idea and ensure demand for it:
A part of business research is figuring out who the target figures are—the people who might use your app. List their issues and concerns; then, decide how your answer could help to resolve them.
Research on markets and rivals helps you to find your primary rivals’ advantages and drawbacks. Look for your position in the market by paying attention to assessments and remarks given by customers. Both these studies will help you create a unique offering of value. Copying another app probably won’t help you make a great product. Bringing your personal touch to the business will attract fresh audiences.
Research findings guide you to create a requirements document with mobile app parameters, objectives, performance, integrations, and essential parts of the future app.
2.3 Tech Stack and Team Selection
Choose the operating system, resources, frameworks, programming languages, and technologies that will be used depending on the features you want to offer. You also need to name the professionals assigned to handle the project.
For a medium-sized telemedicine app, a standard team consists of a project manager, a business analyst, a DevOps engineer for software development, a UI/UX designer, two frontend and two backend engineers, and a QA expert. If the project’s scope calls for it, strengthen some areas with more staff.
2.4 MVP Development
You can start the programming process when you have finished the design. Most businesses decide to create an MVP, a working form of the application with minimum necessary features. Delivering the minimum functions to the end user is the primary goal since it will help to get useful feedback with minimal expenditure. Because software development is costly, MVPs have become somewhat well-known in the field. The MVP development is briefly run through this way:
- Tech stack: Choose among languages, platforms, frameworks, libraries, and the appropriate collection of tools required to create the application. At this stage, one should consider elements like scaling expenses, and security.
- Backend and infrastructure: The backend of the program is behind-the-scenes where you work with databases and APIs, and manage transactions and inquiries. Spending time on this component is crucial as the foundation of the whole solution will be located here.
- Feature implementation: Start developing the functions of the app we already discussed at this point. This covers features as well as navigation and user interface.
2.5 The Core Development
Starting with the MVP, you strengthen and improve until you have a final product on your plate with all its functions, integrations, and APIs.
2.6 Quality Assurance
An important stage that lets developers test the solution and ensure it runs safely and correctly is quality assurance. Many tests will be conducted by your QA staff to guarantee the effectiveness, scalability, quickness, and more of the app. But in building of telemedicine apps, another consideration concerns security. You must ensure adherence to industry standards and privacy rules.
2.7 Release and Maintenance
Post-release activities are the last phase in the telemedicine app development cycle. Once the code has been processed, it’s time to release the product online and into app stores. To appeal to a larger readership, make the response accessible on iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS. This is just sending the app to specified markets and waiting for clearance. Your team will offer continual fixing of issues, fresh features, and continuing maintenance soon after public release. Furthermore, keep an eye on feedback from customers and consider it while deciding whether to add fresh features or delete existing ones.
3. Telemedicine App Development Technology Stack

The Telemedicine app development process involves and necessitates the usage of several distinct technologies, including different programming languages, frameworks, third-party tools, and cloud storage.
The following technologies and platforms can be used for Telehealth application development.
- Programming languages:
- Android app development: Kotlin, Java
- iOS app development: Swift
- Web app development: JavaScript, PHP, Java, HTML, CSS, etc.
- Frontend Frameworks:
- Angular, Vue, React.js, etc.
- Backend Frameworks:
- Node.js frameworks: Express.js, Next.js, etc.
- PHP frameworks: Laravel, CakePHP, symphony, etc.
- .NET Core
- Java frameworks: spring, Hibernate, etc.
- Databases:
- SQL databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.
- NoSQL databases: MongoDB, DynamoDB, HBase, Cassandra, etc.
- Other Tools:
- Video Conferencing tools: Twilio, RTMP, WebRTC
- Chat Tools: Twilio, Interakt
- Client server communication tools: Socket.io library, TCP/IP protocol suit
- API testing: Postman, Apigee, etc.
- Maps: Google Maps
- Alerts: Firebase Cloud Messaging
- Mails: Gmail Integration, Elastic Emails, etc.
4. Telemedicine App Development Cost
For this evaluation, let us pretend that we are creating a telemedicine mobile app that allows users to find and consult with doctors using various digital mediums, including text, voice, and video calls.
Expenditures for the telehealth app development process will be estimated in three phases.
4.1 Analysis and Planning for Businesses
Developing a telemedicine app requires first completing a market analysis and designing. An app’s business analyst’s role is to investigate the app’s market, rivals’ markets, potential development avenues, and target users’ wants and requirements. Both the user interface (UI) and the user experience (UX) need to be designed. For 1.5 to 2 months, expect to pay between $8,000 and $12,000.
4.2 Development and Support
The most significant portion of your budget will go into paying for the creation and maintenance of telemedicine software. This is the bare minimum of functionality that should be included in any ambitious telemedicine consultation software.
The following functionalities are required for patients:
- Administration of User Accounts.
- Schedule and take care of bookings.
- Pay finances.
- Check out receipts and handle cash accounts.
- Talk to the doctors and nurses.
- Join in on phone calls.
- Search the doctors based on location.
- Video consultation & chat with doctors.
- View past appointment history.
The following functionalities are required for doctors:
- Administration of User Accounts.
- Schedule events and meetings.
- E-Prescription facility.
- Calendar and Daily Schedule Reports.
- Follow their financial dealings and control their own wallets in real-time.
- Communicate with patients by phone, text, and other means.
- Get in touch with the IT department.
It takes around 5–6 months and $1,00,000 to $1,20,000 to build a fully featured app with all these capabilities for iOS, Android, and the web.
4.3 Advertising
The marketing phase begins after the app has been released and consists of several inbound and outbound advertising techniques. Improve your marketing efforts by conducting channel research in the market. You should expect marketing expenses to vary widely depending on the channels and methods you choose.
5. Challenges in Telehealth App Development
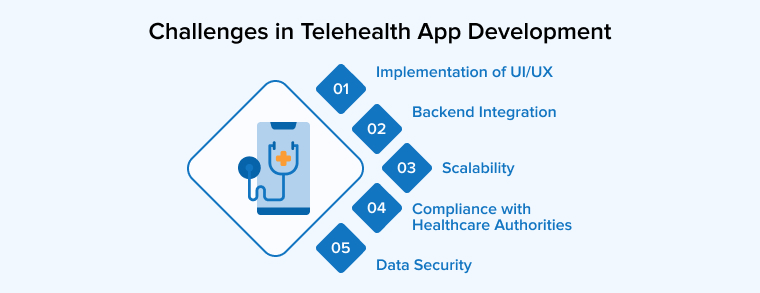
The development of a telemedicine app is a laborious process that requires a lot of time and knowledge. Here are a few examples of the most difficult obstacles:
5.1 Implementation of UI/UX
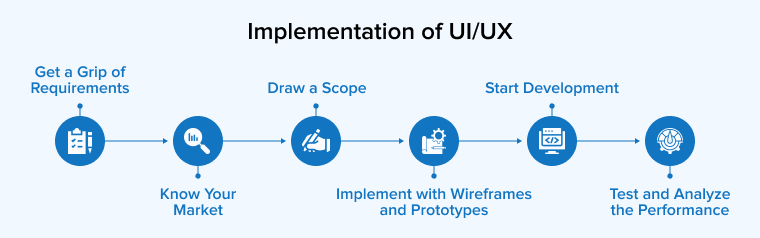
Developing a novel program that is compatible with several platforms is a prerequisite for implementing the UI/UX. The most difficult task for the designers of telemedicine apps is to make a user interface that appeals to a wide variety of people. What a doctor finds important to see on the screen may not be the same as what a patient finds useful. And likewise.
Solution
Here is how a development team handles this issue while creating a telemedicine app:
- Your team of programmers will need to create two variants of the program when working on a telemedicine app. Both the doctor and the patients will need one.
- The doctor’s edition will have one set of functions and healthcare services, while the patient’s version will have another.
- The design and functionality of both should be designed with the doctor and patient in mind.
A developer’s understanding of how to create a telemedicine app hinges on the quality of the user’s experience and their ability to navigate the app’s UI.
5.2 Backend Integration
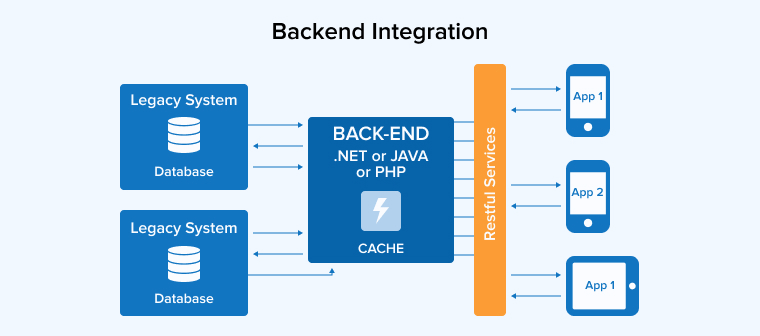
Integrating the back end guarantees that information may be sent quickly and accurately between the patient and the doctor. However, it is far more difficult to put this approach into action. Many HIPAA-compliant elements must be integrated during the construction of a telemedicine app. In addition, developers have to integrate a plethora of other services like payments, geolocation, and more.
Solution
- All of HIPAA’s components are analyzed, and features are crafted before they are included in the telemedicine software.
- Integrating third-party solutions into your telemedicine app calls for a variety of technical approaches. Thus, a defined API description is required to speed up the development process.
- Research into several frameworks and architectures that may be employed in the integrating procedure.
- Define a collection of protocols to guarantee bidirectional data synchronization.
A solid and reliable backend procedure is essential for offering the best telemedicine app development solution. It facilitates the establishment of a standard method of exchanging information between the patient and the physician.
5.3 Scalability
Several components are essential in a telemedicine app development solution to make it useful. Most telemedicine app creators overlook the challenges of scaling their software to meet growing demand.
As the app’s popularity grows, so does the demand for it and the number of people using it.
If the development team isn’t prepared to handle such a volume, then it becomes difficult to deal with the problem.
Solution
An update to your telemedicine app can be made before:
- Ensure that the team knows they need to create an autoscale feature before they start working on a telehealth app.
- Because of this, server resources may be automatically increased in line with rising demand.
- To build a scalable database for a healthcare app, it is helpful to manually analyze the code and optimize the poorly specified areas.
- Cloning the application server is a method for deploying many identical application servers.
5.4 Compliance with Healthcare Authorities
Developing a telemedicine app that complies with HIPAA and GDPR is a significant problem. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) establishes guidelines that must be followed in the development of the app. The patient’s health information is the target of these procedures’ safeguarding efforts.
Solution
- For developers, the most pressing issue is figuring out how to incorporate these standards into the functionality of your telemedicine software. As a result, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine app development entails: synchronizing the login controls, tracking processes, and data storage.
- There must be zero chance of information leaking out or being accessed without permission.
- Successful execution of these standards is facilitated by the use of tools like AWS CloudTrail and AWS CloudWatch in the creation of telehealth apps.
- The best way to protect information during transit is through SSL-enabled endpoints.
Once your telehealth app’s content is HIPAA compatible, only then you will consider the development to be complete. Data sharing is made more secure and safe from hacking attempts.
5.5 Data Security
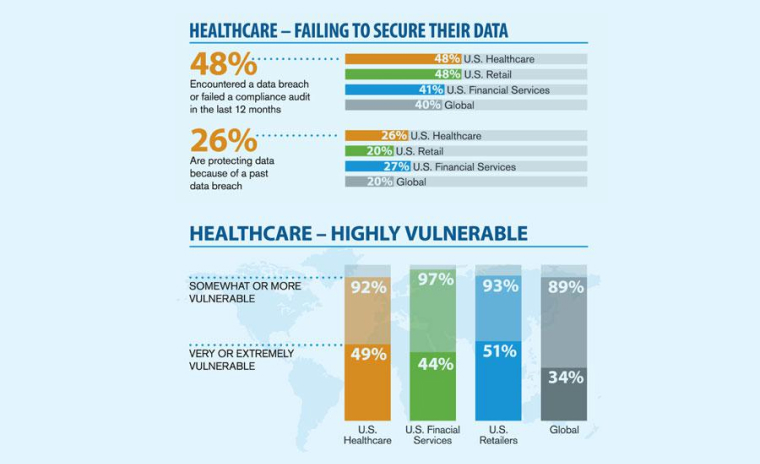
The data must stay safe. The majority of programs now utilize cloud storage and server access. Insufficiently robust and unprotected backend infrastructure makes it easy for hackers to gain access to sensitive information. That is why developers of telemedicine apps devote so much consideration to the structure of their databases.
Cross-site scripting is one of the biggest obstacles to securing the application. Broken authentication is a challenge, as it creates issues with session management and the abuse of private information. The backend team has to have sufficient experience to build a highly secure, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine software.
Solution
Therefore, the following considerations should be made to improve telehealth app security:
- Only rely on proven models.
- Developers of telemedicine apps should check for and install all available security updates for all used libraries and frameworks.
- Data storage solutions that meet HIPAA standards, such as AWS (Amazon Web Services), should be employed.
You can guarantee the safety of your telemedicine app development procedure by employing secure API frameworks and libraries.
6. How Telemedicine Apps Make Money?
Multiple business models are needed for developing a telemedicine app that can be used to make money. It is imperative that telemedicine app developers carefully plan and design these models before beginning the development. These apps primarily monetize themselves through the collection of user fees. Doctor on Demand, for instance, takes 25% of the patient’s total payment after each successful consultation.
A sustainable business model is vital for your product growth. The technical design of your telemedicine app might be improved by sharing your revenue strategy with the developers.
So to comprehend how to design a telemedicine app and generate money with it, let’s go forward and analyze the models in depth.
6.1 Subscription Model
- The most common business model for telemedicine applications is subscriptions of varying lengths (monthly or yearly).
- Patients and doctors both have to pay a charge to use the program.
- Membership plans may be created on a yearly or quarterly level, and discounts can be offered to encourage enrollment. This is a smart strategy for attracting more people to use your app.
6.2 Advertisement Model
- You can make a lot of money from an app if you implement in-app adverts.
- Paid advertising helps the economy and provides a workaround for the creation of telemedicine apps.
- Marketers in a variety of industries are constantly on the lookout for popular venues in which to showcase their wares to a wide audience.
- However, losing telemedicine users because of too many ads is not worth it, so moderation is key.
- A scalable advertising strategy for a telemedicine app is a priority for the telemedicine business development team.
6.3 Franchising Model
- To avoid having to travel to a clinic or hospital for treatment, telehealth apps are developed.
- It’s not hard to imagine this incredible idea being implemented everywhere in the world. Now you know that franchising your app’s distribution internationally is the key to maximizing your app’s global earnings potential.
- SkyHealth, a famous telemedicine program, performs the same. Their franchise fee for hospitals and other medical facilities is $3,000.
The aforementioned models are your best bet for creating a successful healthcare app or telemedicine program.
7. Examples of Telemedicine Apps
Here are a few examples of well-known telemedicine applications.
7.1 Doctor on Demand
Doctor on Demand is an online service that provides instantaneous connections to licensed medical experts around the clock, including general practitioners, psychologists, counselors, chiropractors, and many more. They offer individualized, all-encompassing virtual care that may be accessed across several platforms.
With Doctor on Demand, users may get in touch with doctors in a matter of minutes, from the convenience of their home. There’s a place for people to connect emotionally throughout and after treatment, too. From amongst a ranked group of Doctors, patients can pick the one that best fits their needs.
7.2 Teladoc
Teladoc lets you talk to a broad variety of doctors virtually, quickly, and for free using your current healthcare plan, no matter what kind of medical issue or specialty you need help with. To get the help of an expert, all you have to do is call in, start a video or phone chat with the doctors, and wait for a response with a prescription or expert health assistance.
Telemedicine has greatly increased access to video medical consultations and assistance via digital media. Anywhere in the globe, you can get medical treatment whenever you need it.
7.3 MDLive

Over the years, MDLive has provided patients with affordable, convenient, and safe access to online medical advice. To consult with a doctor, therapist, psychiatrist, or dermatologist, patients can utilize a telemedicine smartphone app.
MDLive is a great way for doctors to collaborate with telehealth professionals. They can also receive training in the field of telehealth. Medical facilities may cut down on patient waiting lists and healthcare costs by utilizing teleconsultations made possible by a cloud-based telehealth technology.
8. Conclusion
Building a useful telemedicine app takes more work than you may expect. Creating a telemedicine app may indeed seem like a lot of work, but the payoff might be well worth it.
Demand for telemedicine applications is expected to grow in the next few years, as seen by the market’s current trajectory and projections. Therefore, now is the perfect time to begin the development of your telemedicine app.
FAQ
How to create a telemedicine app?
follow these steps:
- Idea evaluation
- Discovery Phase
- Tech stack and team selection
- MVP Development
- The core development
- Quality Assurance
- Release and Maintenance
How much does telemedicine app development cost?
For only one platform, such as iOS or Android, the cost to design a telemedicine app can range from $40,000 to over $200,000 depending on the features and hours.
How Long does it take to develop a telemedicine app?
Developing a fully-fledged Telemedicine App usually takes 6-9 months. However, depending on the scope of the project, requirements, and manpower the duration may vary.





Comments
Leave a message...