
Choosing the right web framework is a crucial decision that can shape the future of your application. Two of the most popular choices today are Django and Laravel, each offering distinct advantages, strong community support, and being suited to different types of projects. Among existing web frameworks, Django and Laravel consistently rank as popular web frameworks in the web development world, recognized for their wide adoption and robust features.
Django, built with Python, is praised for its clean architecture and rapid development features. Laravel, developed using PHP, is a web application framework that offers flexibility, an elegant syntax, and a wide range of built-in tools, and benefits from the vibrant PHP community that supports its growth and resources. As businesses seek efficient and scalable solutions, the debate between Django and Laravel continues. For companies already working with PHP or considering expanding their tech stack, partnering with a skilled PHP Development Company can make a significant difference in project success.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at both frameworks, comparing their features, similarities, and differences for various projects, to help you determine which one best fits your development goals and preferences.
1. Overview of Django
Django, developed by Adrian Holovaty and Simon Willison, is an open-source Python web framework. The framework’s objective is to increase the pace of web development while maintaining high quality. Django follows a “batteries included” philosophy, meaning it provides a wide range of built-in tools and features so that developers rarely need to rely on external tools and libraries. The built-in tools and functionalities, such as verification systems, investment fund management interfaces, and data analysis tools, allow web developers to focus on core development instead of handling different configurations and settings.
Django works on the Model-View-Template (MVT) architectural pattern, where the application is divided into three components:
- Model: The Model represents the application’s data layer. It defines the database structure and handles various operations associated with interacting with the database.
- View: The View is responsible for rendering the user interface and processing user requests by interacting with the Model and the Template. In the context of Django, views are implemented as Python functions or classes.
- Template: The Template is the presentation layer that displays data to the users using HTML with Django Template Language (DTL). The Templates are made in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
1.1 Features of Django
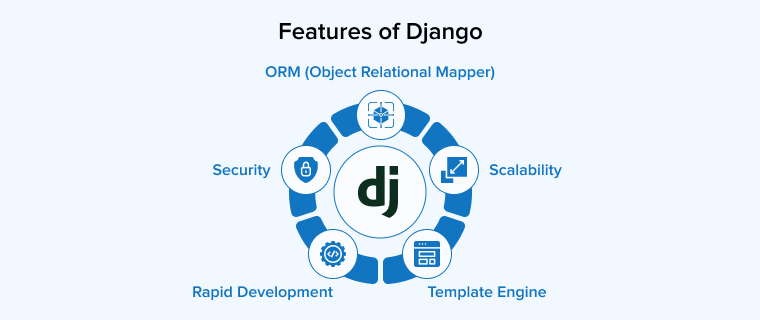
Let’s understand the five key features of the Django framework that make it an outstanding choice for web development, especially among Python developers:
1. Security
Django is considered a highly secure web framework that comes with several built-in features to protect applications from common security threats. Its architecture is designed to offer strong protection against attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), cross-site request forgery (CSRF), and clickjacking. One of Django’s key strengths is the ability to hide source code from the browser, adding an extra layer of protection. Django also supports secure file uploads and access control features. Backed by an active open-source Django community, it is a frontrunner in identifying and addressing security flaws quickly and effectively.
2. Scalability
Django follows component-based, “shared-nothing” architecture. As the components are loosely coupled, they can be changed or replaced independently based on the application’s needs. Django integrates smoothly with load balancers, allowing incoming traffic to be efficiently shared across multiple servers. This setup helps maintain performance by avoiding overloading a single server, making Django a suitable framework for scalable applications.
3. ORM (Object Relational Mapper)
An ORM allows developers to interact with a database using Python syntax instead of writing raw SQL queries. This abstraction layer makes it easier to query, update, and manage the database without the need to write SQL queries manually.
- Database Migration: Django’s ORM offers seamless database schema updates through migrations, allowing structural changes without data loss. It monitors model changes and creates migration scripts automatically for easy deployment.
- Support for Multiple Databases: Django provides built-in support for several major databases, such as PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite, and Oracle. Django is even capable of working with multiple databases simultaneously.
4. Template Engine
Django consists of its built-in templating engine, known as the Django Template Engine. This template engine enables developers and designers to work independently, as it separates the business logic from the presentation layer. Developers can even go for using third-party templating engines. The two main characteristics of Django Template Engine are:
- Template Inheritance: Django supports template inheritance, allowing developers to create a master layout that contains common components like headers, footers, and navigation menus. These components are reusable across different pages.
- Filters and Tags: Django provides built-in tags and filters for dynamic data handling, for example, formatting text, dates, or numbers directly in templates.
2.5 Rapid Development
Generally, backend development typically requires expertise in server-side programming as it forms the core of web development. However, with Django’s “batteries-included” approach, simplifying many development tasks, such as creating server files for data creation and connecting them, routing, authentication, etc, are handled by the pre-built components. Developers can focus on building unique components instead of repetitive coding and spending time on the above-mentioned common development tasks. As a result, the development process accelerates and time-to-market reduces, benefiting project goals.
2. Overview of Laravel
Laravel is a PHP-based server-side web framework designed to help in website development using the PHP scripting language. It is an open-source framework that focuses on two major goals: simplicity and elegance. Laravel shares certain similarities with other PHP frameworks like CodeIgniter, Symphony, and Yii, as well as with programming languages like Ruby.
The working of the Laravel framework is based on the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architectural pattern, where:
- Model: Acts as an intermediary between the application and the database, encapsulating data-related operations.
- View: Represents the UI of the application, using the Blade templating engine to create UI components.
- Controller: Serves as a bridge between the Model and View layers. It receives user requests from the View layer and processes them by interacting with the Model.
2.1 Features of Laravel
We shall now move towards discussing some important features of the Laravel framework:
1. Artisan CLI
Laravel includes a powerful command-line interface called Artisan, designed to streamline and automate common development tasks. It simplifies database operations, generates boilerplate code, and manages migrations efficiently. Artisan also supports the creation of MVC components and handles asset configurations with ease. Developers can even build custom commands tailored to their workflow, making the development process faster, more organized, and highly customizable.
2. Powerful Routing System
Laravel offers a powerful and flexible routing system that simplifies how developers manage web application URLs. It supports a wide range of HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, allowing precise control over request handling. Developers can define dynamic routes using parameters, assign names for easy reference, and group routes to apply shared middleware or attributes. Laravel also includes features like resource routing to quickly build RESTful APIs, route model binding for automatic injection of model instances, and route caching to boost performance in production environments. With its clean syntax and advanced capabilities, Laravel’s routing system makes URL management efficient, organized, and scalable for both small projects and complex web applications.
3. Unit Testing
Laravel is a preferred choice among developers due to its strong support for unit testing. It allows seamless testing of new features to ensure that existing functionality remains intact. The framework is known for its reliable and stable releases, making it a trusted option in the development community. Additionally, Laravel simplifies the process of writing and running unit tests efficiently.
4. Authentication
Laravel possesses a strong built-in authentication system called Laravel Breeze, which efficiently manages user login, registration, and password recovery. This authentication system uses secure hashing algorithms like bcrypt to protect passwords from exposure. AutoAuth also includes CSRF protection and secure session handling, adding multiple layers of defense to protect user data and enhance overall application security.
5. Migration of the Database
Laravel’s migration system enables developers to modify the database structure without rebuilding it from scratch, significantly reducing the risk of data loss during updates. By using PHP instead of raw SQL, changes become more manageable and consistent across teams. With the help of Laravel’s Schema Builder, developers can easily create tables, define columns, and add indexes as required for efficient database management.
3. Django vs. Laravel: Basic Comparison
The comparison table below provides a quick overview of the complete picture of Django vs Laravel, assisting you in selecting the right technology for your upcoming project.
| Parameters | Django | Laravel |
|---|---|---|
| Developed By | Adrian Holovaty and Simon Willison | Taylor Otwell |
| Architecture | MTV (Model-Template-View) | MVC (Model-View-Controller) |
| Language Type | Interpreted Language | Interpreted Language |
| Base language | Python | PHP |
| Development Time | Lesser time | Comparatively time-consuming |
| Learning Curve | Low learning curve as Django is developer-friendly and easy to learn | Quite difficult, especially if unfamiliar with PHP, resulting in a steep learning curve |
| API Support | No built-in API support. API development requires external packages | Provides built-in API development support |
| Scalability | Very high scalability due to Python | Good horizontal scalability, but less scalable than Django, as PHP is quite slow |
| Routing | Difficult due to a lack of a built-in API | Simple |
| Maintained By | Django Software Foundation | Laravel community developers |
| Middleware Support | Only HTTP middlewares | Supports multiple middlewares |
| License | 3-Clause BSD | MIT |
| Ease of Testing | Easy to test Django applications | Testing is quite time-consuming |
| Performance | Faster due to Python’s speedy execution | A high number of features makes Laravel slower than other PHP frameworks |
| Front-end support | Somewhat hard to connect with a front-end JavaScript framework. | Fully support Vue.js without requiring extra configuration |
4. Django vs Laravel: An In-Depth Comparison
Let us compare Django and Laravel by discussing the similarities and differences between them in the context of the following ten key parameters:
4.1 Django vs. Laravel: Performance
- Django: It uses the Python language, which can affect code execution and compilation speed. Database communication is handled using Python syntax through an ORM, which optimizes the database querying and processing capabilities. Performance is a critical factor in software development, as it directly impacts user experience and scalability. Slowdowns may occur during JSON serialization, converting database queries into Python objects, and using middleware to execute requests. These inefficiencies can be overcome by efficient hardware and following web development best practices.
- Laravel: Laravel consists of extensive built-in capabilities that, although easing development, can also impact the application’s performance. Therefore, in case of high traffic, Laravel websites may respond slowly compared to websites built with Django. With the release of PHP 7, Laravel has experienced a boost in performance and memory efficiency.
4.2 Django vs. Laravel: Scalability
- Django: Django leverages the scalability and powerful Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning capabilities of its parent language, Python. It integrates with other technologies as needed by the application, without sacrificing speed and performance. For large applications, you’re free to implement cloud and CDN solutions to ensure that flexibility issues do not hinder the application’s performance.
- Laravel: You can increase the Laravel application’s scalability by properly using load balancers and choosing the right database. Additionally, leveraging cloud solutions like AWS and implementing effective caching strategies can enhance Laravel’s horizontal scaling capacity. However, compared to Python, PHP generally has performance limitations. As a result, Laravel is often considered less scalable than Django when it comes to adapting to evolving trends.
4.3 Django vs. Laravel: Architecture
- Django: It works on the Model-View-Template (MVT) pattern, which is a variant of the traditional Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture. In this pattern, the template file, comprising HTML and Django Template Language, handles the presentation layer and performs the controller’s task of creating intuitive web experiences. This provides a personalized user experience.
- Laravel: It works on the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, which divides developer responsibilities. For example, frontend developers handle the View layer, while backend developers manage the controller logic. This architecture gives you complete control over the application. It’s up to you to customize the look and feel and specify the routes.
4.4 Django vs. Laravel: Ecosystem and Community
- Django: It benefits from the extensive Python community, which contributes advanced AI/ML libraries, third-party packages, online tutorials, and comprehensive documentation.
- Laravel: Laravel has a large and active community. Being a PHP framework, it also benefits from a wide range of support through a repository of tools and components that cater to various development needs.
4.5 Django vs. Laravel: Database Support
- Django: The Django ORM allows developers to avoid the intricacies of understanding database structures by using Python to write queries. It provides built-in support for databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, and SQLite. If you want to work with databases other than these, you can do so using third-party libraries and packages. Additionally, Django supports multiple databases simultaneously. Hence, we can say that Django provides comprehensive database support.
- Laravel: The Eloquent ORM and the raw SQL query builder in Laravel ease the process of communicating with the database. These query builders use models to define the relationship between tables in the database. Laravel also supports the four databases MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, and SQLite, like Django.
4.6 Django vs. Laravel: Security
- Django: Python has established itself as one of the most secure programming languages, which ensures Django’s robust security features. Django protects against threats such as cross-site scripting, cross-site request forgery, clickjacking, and many more. You can be assured of the privacy of user accounts and passwords with the robust authentication system of Django.
- Laravel: It has implemented several security measures, such as the Bcrypt hashing algorithm, CSRF tokens, and salted, hashed passwords to store encrypted passwords instead of plain text. Thus, cyberattacks like XSS, SQL injection, and data interception, to some extent, protect Laravel from the security threats commonly associated with PHP.
4.7 Django vs. Laravel: Learning Curve
- Django: For developers familiar with Python syntax, learning Django will take less time for at least the basic developmental aspects. However, advanced concepts require an in-depth understanding of fundamentals, making it quite time-consuming. Beginners in Python may find Django somewhat difficult, but thanks to the extensive online community support and resources available, the learning curve is moderate rather than steep.
- Laravel: It has a steep learning curve, especially if you have no experience in PHP programming. The syntax of PHP is similar to that of basic programming languages like C, C++, and Java, which can result in a longer learning time despite the abundance of documentation and resources.
4.8 Django vs. Laravel: Testing and Debugging
- Django: As Python’s syntax is short and English-like, testing Django applications becomes easier. Additionally, there are many debuggers and tools available online to facilitate testing. You can also use the extensive documentation to separately test each logic layer of the application for comprehensive testing and deployment.
- Laravel: There are two levels of testing Laravel application code: feature tests and unit tests. Laravel also provides extensive testing documentation to support each level and ensure error-free application deployment. Laravel even allows mock testing of application code and events using a variety of testing tools.
4.9 Django vs. Laravel: Microservices Compatibility
- Django: It is well-suited for implementing a microservices architecture due to features like rapid development and built-in security. Breaking down the application into small, independent services allows for more effective scaling. It also facilitates the incorporation of machine language features into your application.
- Laravel: PHP is compatible with the microservices architecture, and so is Laravel. A Laravel application can be broken down into individual functional units, where these units interact through language-agnostic APIs. For a more effective microservices implementation, Laravel developers created a lighter version of the framework known as Lumen.
4.10 Django vs. Laravel: REST API
- Django: It lacks built-in support for API development. Therefore, you have to rely on third-party packages and libraries to develop REST APIs. The most popular web framework for this purpose is the Django REST Framework (DRF). It provides features like serialization, authorization, response rendering, and more for REST API development with Django.
- Laravel: It provides built-in API support. The rich set of tools and features, like Eloquent ORM, middleware, and rate-limiting features, makes it easier to develop a well-structured API.
5. Key Similarities Between Django and Laravel
Let us now closely look at some of the similarities between Django and Laravel:
- Both are web development frameworks: Both ease the web development task with their rich source of built-in functionalities that avoid coding everything from scratch every time.
- Both are free and open source: You aren’t required to pay licensing fees for using the source code for developing any kind of project, be it small or enterprise-grade. The source code is available for free on GitHub.
- Both follow MVC architecture: Laravel works on the MVC pattern, whereas Django uses the MTV pattern, which is conceptually equivalent to the MVC pattern. Both enable parallel development, as working on a component does not affect the other one.
- Both use ORM: Laravel uses Eloquent ORM, whereas Django uses the Django ORM for simplifying database operations.
- Both have a strong ecosystem: Both Laravel and Django have an extensive community support that provides help through various tools, libraries, tutorials, community forums, etc.
6. Final Thoughts
Both Django and Laravel have unique strengths and limitations, catering to modern software development requirements. Django’s scalability, security, speed, and integration with AI/ML technologies make it a preferable choice for data-intensive projects. On the other hand, Laravel’s elegant syntax, ease of use, extensive ecosystem, and rapid evolution with access to new features make it a go-to option for projects seeking quicker iterations. If you’re a beginner in Python, learning Django will take quite time, whereas PHP developers may find Laravel easy to catch up. Consider factors such as project complexity, team expertise, scalability demands, security requirements, and the desired development timeline when making your decision. By carefully evaluating these aspects, you can choose the framework that best empowers your team to build a successful web application that meets your objectives.
FAQS
Which is better, Laravel or Python?
This completely depends on the project and the development team’s needs. If you’re developing a structured and feature-rich application, choose Laravel; otherwise, select Python if performance, AI/ML integrations, and security are the essential priorities.





Comments
Leave a message...