
Both Spring and Spring Boot are popular and widely used frameworks in the Java ecosystem. After its introduction, the Spring Framework was widely adopted as a lightweight and robust web development solution. Spring Boot followed as a more streamlined and feature-rich framework, created as an extension of the Spring framework to simplify and accelerate development. Now, the community is often divided in its preferences between the two, which can make choosing the right approach for an upcoming project a confusing task.
As a leading Java development company, we offer both reliable solutions and data-driven insights. This article provides an in-depth understanding of these frameworks. It compares them against certain factors to determine the differences, which will help you make an informed decision.
1. Java Spring Framework Overview
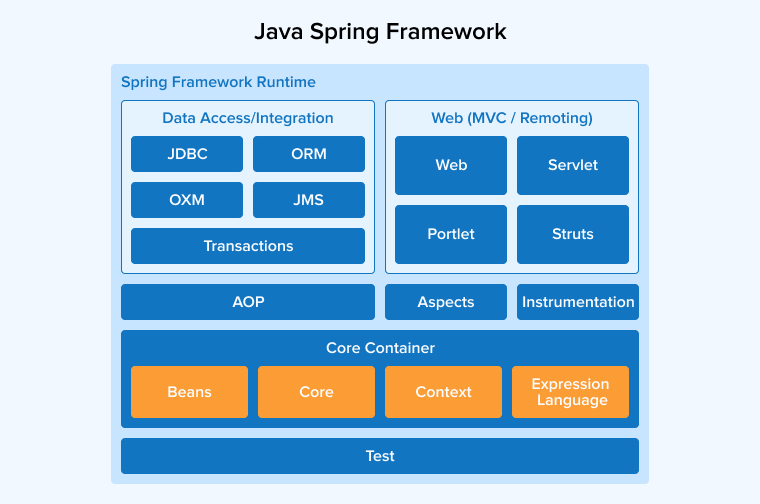
Spring is a lightweight, open-source, Java-based framework primarily used to create enterprise apps. It is a set of sub-frameworks or layers, like Spring Web MVC and Spring Web Flow.
Server-side technology abstraction, data access, transaction management, security, and other features provided by this framework help boost the productivity of Java developers. Spring is popular for its flexibility as it can address various aspects of the app development process. Spring’s modular architecture and support for dependency injection (DI) further enhance developer productivity.
Spring Framework promotes the use of Plain Old Java Objects (POJOs), emphasizing that business objects should remain independent of runtime environments and specific frameworks. Implementing this approach provides agile maintenance, code reuse, and easy testing. The Spring Framework has around 38.7k forks on GitHub.
1.1 Key Features of Spring Framework
Spring is a popular Java development framework as it offers some amazing features to help developers bring ideas into reality. Here we discuss the most important features:
1. Dependency Injection
Spring supports dependency injection, handling dependencies as well as injecting them into objects. This reduces the need for manual wiring. Dependency injection also enables loose coupling between components, which simplifies testing and maintenance of the codebase.
2. IoC (Inversion of Control) Container
This feature of the Spring Framework is used to create Java objects and manage their lifecycles. The IoC container comes with assembler code that enables configuration, increasing the configurability of a Spring application. It also allows developers to set up and tear down the objects with less boilerplate code.
3. Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP)
Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP) in Spring addresses cross-cutting concerns such as transaction management, security, and logging. These logics are often used in multiple aspects of the app code. With AOP, you write the related logic once and apply it across multiple places in the code without any changes or modifications. This Spring functionality promotes code reuse and modularity.
1.2 Advantages of Spring
Having advanced features allows Spring to offer numerous benefits. However, we will discuss only a few critical advantages here.
1. Lightweight
Being a lightweight framework, Spring doesn’t need heavy resources or extensive setup. As a result, it can offer both faster startup times and enhanced performance. The configuration in Spring-based apps is easy and minimal, which helps reduce overhead and makes the app easy to scale and maintain.
2. Easy Testing
Spring is a good option for testing because its dependency injection feature makes components easier to test. Moreover, Spring promotes modular design and loose coupling, which makes it easy to test the app, even if it is large or complex. Thanks to modularity, you can test each unit independently. Spring supports multiple test types—unit, integration, and functional—and provides the Spring test module to facilitate integration and unit testing within the framework. Running these tests in an existing CI/CD pipeline helps solve the issues before the code is deployed to the production environment.
3. Modular Design
Spring has a modular design where all components are loosely coupled. Its modules — such as the web, core container, testing, and data access/integration modules — work together while remaining independent. Spring adheres to the MVC pattern, where the view receives user requests and sends back appropriate responses. It has a model for data-based operations and a controller to request the correct method.
2. Spring Boot Overview
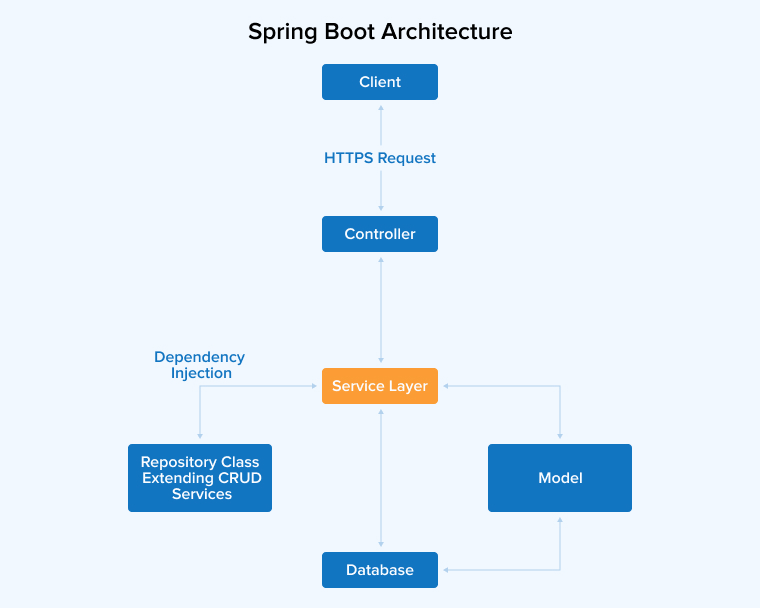
Since it is built upon the Spring framework, Spring Boot offers all the features of Spring. Java developers can use this microservice-based framework to simplify and accelerate the app development process, as it reduces the code length. Building robust, production-grade, and standalone apps becomes easy with Spring Boot. Spring Boot streamlines the process of creating Spring-based applications and Spring projects. It provides a pre-configured platform to build apps with annotation-based configuration and minimal XML. You only need to run a single command to launch the Spring Boot-based app.
2.1 Features of Spring Boot
To understand the app development capabilities of the framework in detail, we need to take a look at Spring Boot features. Here we discuss a few crucial ones:
1. Auto Configurations
Spring Boot configures your application automatically. It considers the added dependencies you add and makes reasonable guesses about the settings and beans required, so you don’t have to set it up and write complex Java or XML configuration manually. However, proper configuration is still important for enabling specific functionalities, especially when developing REST APIs.
For example, if you add a database library like MySQL or H2, Spring Boot automatically configures the connection pool as well as the data source. As a result, you need minimal boilerplate code, which accelerates the development process. Such auto-configurations actually help developers focus on writing better and more accurate business logic instead of worrying about setups.
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration using conditional annotations that check for the presence of specific properties or classes. This allows the framework to apply sensible default settings that can be overridden as needed. The auto-configurations feature is especially useful for projects that require minimal configurations and quick startup times, such as standalone and microservices applications.
2. Standalone Application
Spring Boot, a Java framework, provides the capabilities to build standalone applications. This means that Java developers can build a single app that can run on multiple platforms using a shared codebase.
Standalone apps don’t need an external server. It is embedded in a web server like Netty or Tomcat during initialization, allowing it to run independently. Now, you can deploy your Spring Boot application on any platform you want using just a single run command. You can also turn off this feature in Spring Boot if you don’t want to embed the app with a web server.
3. Command-Line Interface (CLI)
To run quick code or test an idea during development, use the Spring Boot CLI. You don’t need to create the whole application, you can write a small script in Java or the Groovy programming language and run a Spring-based app directly from the command line.
The Spring Boot CLI is an ideal option for running short-lived services, conducting batch operations, and testing small code snippets. It feels like rapid prototyping without an extensive design process.
2.2 Top Benefits of Using Spring Boot
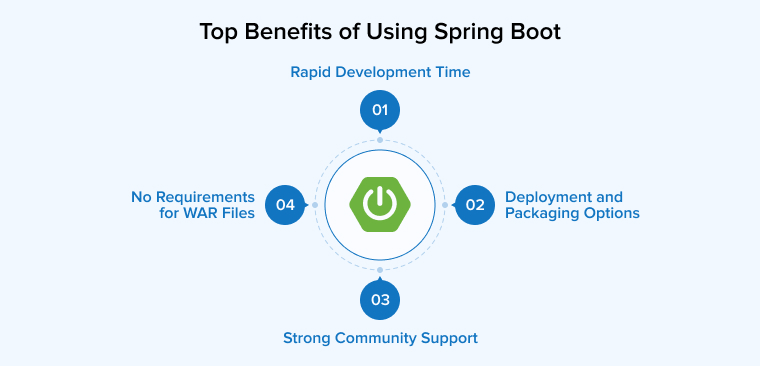
Businesses need the Spring Boot Java framework to build microservices-based web and mobile apps. Using it for your upcoming project offers the following advantages:
1. Rapid Development Time
With a combination of convention-over-configuration and auto-configuration, Spring Boot encourages developers to focus on business logic instead of infrastructure setup, enabling rapid application development. Spring Boot also reduces the need to write boilerplate code by automating configuration and setup.
Spring Boot selects a set of dependencies to add by default based on previous use cases or a web form filled out through Spring Initializr. This Spring Boot starter simplifies dependency management and gets you started with app development.
2. Multiple Options for Deployment and Packaging
Spring Boot allows Java developers to package applications into JAR files and deploy them as standalone programs. The framework also makes it easy to design high-performance Docker images. To create these images directly from the application, Spring Boot developers just have to make some extra configuration and parameters. As a result, they can easily containerise the entire Spring Boot app.
Spring Boot provides simple commands to run and stop an app, which simplifies app management. This makes quick testing and deployment easier and improves the developer experience. Additionally, Spring Boot provides intuitive default settings for integration tests, making it easier to validate applications before deployment.
3. Strong Community Support
Hailed as one of the best Java frameworks by online platforms, Spring has successfully garnered great community support. The Spring Boot community is the largest within the Java ecosystem and spans the globe. It provides extensive documentation, regular updates, and an active forum where they leverage their knowledge and expertise to help the community by solving errors, sharing updates, and best practices.
4. No Requirements for WAR Files
Spring Boot supports web application resource files, but it doesn’t need them because it also supports Java Archive files. JAR files are more beneficial to both users and developers as they offer a simple and succinct structure. These files are lightweight, enabling quick connectivity between the apps and tools needed to run them.
Having the choice of selecting from WAR and JAR is also beneficial for the Java development team. They have the choice to pick an option of their preference. Choosing WAR may affect performance, but it can allow them to launch their product to market as soon as possible.
3. Spring Vs Spring Boot: Key Differences
Let’s take a glance at the key differences between the frameworks to help you pick a suitable option for the upcoming project.
| Factors | Spring | Spring Boot |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration Style | Need manual configuration explicitly. | Uses auto-configuration and starter kits. |
| Development Speed | Takes a lot of time to set up and configure. Hence slower. | Built for rapid development. Hence, quick setup, configuration, faster iterations, and deployment. |
| Ideal Use Cases | To create applications. | To design REST APIs and microservices-based apps. |
| Database Support | Doesn’t support an in-memory database. | Supports in-memory databases like H2. |
| Boilerplate Code | Needs to write too many lines of code even for a simple task. | Offers starter kits to reduce boilerplate code. |
| Dependencies | Multiple dependencies | Single dependency |
| Testing | Since the source code is large and complex, testing is very difficult. | With minimal source code, testing becomes easy. |
| CLI Tools | Does not provide any CLI tools. | Supports CLI tools to develop and test Spring Boot apps. |
| Plugins | No plugin support. | Includes build tool plugins for Gradle, Maven, and more. |
| HTTP authentication for security | Need standard dependencies like spring-security-web and spring-security-config. | Only needs to define the dependency spring-boot-starter-security. |
4. When to Use Spring?
The Java development team can utilize the Spring framework in the following instances:
- Enterprise-grade Apps: Spring’s flexible and modular architecture is a good fit for building applications with high specifications. So, Spring can easily help you build intricate and large-scale apps.
- Custom Solutions: Spring’s configurability gives you total control over the app’s settings. You can easily modify each element of the app to suit your unique project requirements.
- Legacy Systems Integration: Spring simplifies the process of adding a new feature or integrating advanced technology into an old legacy system. This allows you to improve or modernize the legacy programs without major redesign.
5. When to Use Spring Boot?
Spring Boot can streamline and increase the efficiency of Java development for the following types of projects:
- Small to Medium-scale Applications: Spring Boot is particularly useful when speed is critical. It is opinionated, provides sensible defaults, and has convenient tools, which save developers’ time and increase project efficiency.
- Prototyping and MVPs: The framework’s simplicity helps create minimum viable products and rapid prototyping. Its auto-configuration feature enables you to build essential features without dealing with extensive app configurations.
- Microservices: For microservices-based applications, Spring Boot is a good fit. Its minimalistic approach and rapid setup make it suitable for building and deploying scalable, easy-to-manage services. Spring Boot is also well-suited to develop REST APIs, as its auto-configuration and embedded server features simplify the process of creating RESTful services.
6. Conclusion
This article on Spring vs Spring Boot discusses the features and benefits of each in detail, and includes examples to illustrate key concepts and differences. It also compared both frameworks against common industry factors to determine critical differences between their functional capabilities. Since both are Java-based frameworks and Spring Boot is built upon Spring, they share many similarities, but differ significantly in their approaches to Java development. Depending on their traits and offerings, we also considered the use cases where each framework will prove to be more beneficial. If you still have any confusion or project-specific queries, feel free to contact our experts.
FAQs
Can Spring Boot replace Spring?
Since Spring Boot is built upon the Spring framework, it comes with all the Spring functionalities and more. Spring Boot is a microservices-based framework that allows you to build a production-grade app very quickly. Moreover, it comes auto-configured. In short, Spring Boot is feature-rich and more convenient compared to the Spring framework.
Which is faster, Spring or Spring Boot?
Every element and attribute in the Spring Boot app is auto-configured. It also offers starter kits to start off Java development quickly. The reduced amount of boilerplate code and setup time makes Spring Boot faster than Spring.





Comments
Leave a message...