
Java and JavaScript are the most popular and robust programming languages that are often confused as being the same by beginners due to their similar names. But the truth is completely contradictory. Both languages have unique capabilities, use distinct programming approaches, and serve different purposes.
So, it is important to assess and identify your requirements. This will help you decide whether you need to hire a top Java development company or JavaScript developers. But to make that decision, you first need to understand the differences between Java and JavaScript.
Therefore, this blog on Java vs JavaScript provides a detailed comparison against specific industry parameters, along with a discussion on their unique set of features, pros, and cons. This will give you the necessary insights to make an informed decision.
1. What is Java?
Java is a statically typed, object-oriented programming language. Its platform independence is achieved through the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Java was the first language to build interactive web pages with visual effects. Since its inception, Java has continually evolved with each new release.
Java is a widely used programming language supported by a large community and a vast ecosystem of frameworks, tools, and libraries. Java is the primary language for Android app development. Moreover, it’s a reliable option for back-end web development.
1.1 Key Features of Java
Java is one of the most reliable programming languages because of its critical features, such as;
1. Easy and Simple to Understand
Java is designed to be simpler than many conventional programming languages. Its syntax is similar to English, which helps improve readability. It doesn’t require memory or other resources when running on any device. Java is quite similar to C-style languages, so developers with experience in C languages wouldn’t find any issue using Java. Unlike other programming languages, Java does not support pointers and multiple inheritance for classes, which often confuses programmers. Additionally, the language includes an automatic garbage collector that manages memory by reclaiming unused objects, helping improve app performance.
2. Platform-Independent
Java is a platform-independent programming language. This indicates that Java code can run on any computer, operating system (OS), or environment without modification. Along with this, Java is a general-purpose programming language, which means you write code once and run it anywhere.
3. Object-Oriented
Java provides all object-oriented programming (OOP) features, including Inheritance, Abstraction, and Composition, among others. These OOP features offer several benefits to the language, such as improved security, prevention of data redundancy, and simple debugging.
4. Compiled and Interpreted
Programming languages generally use one of two approaches to execute code. The first method involves compiling the source code into machine-specific instructions before execution. The second way is to interpret the source code during runtime.
However, Java uses a hybrid approach by compiling the source code into an intermediate form known as Bytecode. It is executed on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Using this approach, Java has been able to develop cross-platform applications.
5. Secure and Reliable
Java is a secure and dependable programming language widely used by skilled developers. It provides various features, tools, capabilities, etc. It offers secure connectivity, public key architecture, authentication mechanisms, and encryption, among other features. These capabilities help create a safe and dependable environment.
1.2 Advantages of Java
Most of the benefits that the Java programming language offers are derived from its programming concepts, such as OOP and WORA.
1. APIs
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are a set of commands or methods that define communication between different operations. Java provides a plethora of built-in APIs that streamline the development process. APIs also allow seamless integration of existing systems and new software, making them easier to manage. As a result, Java developers don’t have to start coding from scratch.
2. Great Community Support
Java has been in the market for a long time. So, it has gained support from a considerably large community. Each new version of Java not only introduces improvements but also brings new benefits that help increase the fan base of the language. The Java ecosystem consists of a large number of battle-tested frameworks and libraries for various development purposes.
Moreover, the community also provides technical support through online forums and courses. For example, Udemy has over 1000 Java-related courses, whereas Coursera has more than 300 to guide Java developers through their projects.
3. Distributed Language
Java is a distributed language, allowing it to share data and code across different systems, especially to devices connected remotely. This form of collaboration between multiple devices enhances the overall system performance. After all, distributed processing in Java is supported through Remote Method Invocation.
4. Efficient Memory Allocation
Memory allocation in Java is divided into two parts: the first one is known as the Heap area, and another is called the Stack area. When developers declare a variable in a Java program, the Java Virtual Machine allocates the memory for that variable from any one of these areas, depending on the variable type.
1.3 Disadvantages of Java
There are many benefits of using Java for software development. Similarly, there are some challenges as well. This section explores the key limitations of the Java programming language.
1. Performance Limitations
In comparison to C++ and other native languages, Java lags in performance. The Key concepts affecting Java’s system performance include thread deadlocks, garbage collection, the Java Virtual Machine, and inadequate caching configurations. This happens when you don’t manage memory properly in Java. Moreover, the interpretation and Just-In-Time(JIT) compilation take time to interpret and compile the code. As a result, the app experiences loading and performance issues.
2. Commercial License
Java is available for free downloading and commercial use. However, if you want to employ this programming language to build enterprise applications or its features, then there are significant costs associated with it.
Since January 2019, Oracle has been charging users for the business, commercial, and production use of Java Standard Edition 8. Therefore, Java users now need to pay to update their outdated versions or obtain bug fixes. The rates are determined according to the number of processors or Java users in the company.
Initially, companies were able to use and redistribute Java for general-purpose computing without paying a single penny. But nowadays, they have to monitor Java utilization and decide if it’s worth it or if it’s time to switch to a better alternative. Because the more the usage of Java and its features, the higher the costs will be for the company.
3. GUI Challenges
Using Java to create GUIs or Graphical User Interfaces can be challenging because it doesn’t offer native aesthetics and is filled with inconsistencies. Though there are some Java GUI frameworks, they aren’t advanced enough to build complex graphical user interfaces.
It is not just complex for Java to build GUIs; the language lacks the necessary features and hence fails to give a native feel and look to the desktop apps. To achieve better integration and performance, developers often seek the help of alternative programming languages or frameworks.
2. What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a programming language primarily used for client-side development. Developers use it to add dynamic features to static web pages and applications, creating an interactive user experience (UX). Web browsers run the JavaScript code on the client side, which helps reduce server load.
JavaScript, when combined with NodeJS, enables server-side programming, helping developers build full-stack applications. This capability improves the language’s usability and highlights its flexibility. Many top technology companies, including Google and Facebook, use JavaScript extensively to empower their platforms.
2.1 Key Features of JavaScript
The key features of JavaScript are listed below. Let’s explore them one by one.
1. Dynamic Typing
Dynamic typing in JavaScript allows variables to hold values of any data type, regardless of their initially declared type. This helps developers write their JavaScript code quickly and more efficiently without worrying about declaring the correct data type for every variable in their program.
This makes JavaScript a flexible programming language that can adapt to various situations, as variables can change their data type during runtime. This dynamic typing allows developers to write concise and adaptable code, which can speed up the development process and simplify maintenance.
2. Lightweight
JavaScript features a simple core design and comes with a JIT compiler. As a result, it has minimal runtime and can manage asynchronous operations without any overhead. Its code execution leads to faster loading speed and improved app performance.
Using a lightweight programming language or framework in front-end development offers significant benefits. It helps deliver a better user experience by reducing the load on the user’s device and minimizing bandwidth consumption.
3. Prototype-Based Language
JavaScript is a prototype-based programming language, meaning it uses prototypes to create new objects rather than relying on classes. In contrast to Java, where classes must be declared before objects are generated.
4. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Platform independence is one of the most appealing features of JavaScript in this modern age. The language works seamlessly with CSS and HTML to create websites, and it can also be integrated with NodeJS to build robust web apps. This enables the developers to write JavaScript code that can run on multiple platforms or operating systems, both in browsers and on servers.
In other programming languages, developers often need to write different versions of app code to support different platforms, which can be time-consuming and overwhelming. But that requirement is eliminated in JavaScript, which saves you time and accelerates the development process. More importantly, you no longer need to maintain multiple codebases for a single application.
5. User’s Input
Bug detection in JavaScript also considers validating user input. For example, if a user leaves a form field blank or enters inaccurate data, the program will not execute or show an error message. Ensuring data integrity on the client side helps reduce time spent on error detection and troubleshooting.
6. Single-Threaded Execution
JavaScript only processes one programming task at a time. Therefore, it can only execute a single thread of code at a time. As a result, your app codebase won’t have any complexities that come with multi-threading. A single-threaded model simplifies the management of concurrency.
However, when JavaScript is running a single thread, it can still handle asynchronous operations in the background using the event loop without blocking the main thread.
JavaScript’s single-threaded approach certainly helps you avoid any overhead related to multithreading issues. However, this approach can lead to poor performance when handling heavy computations on the main thread, as it blocks the user interface. In this scenario, JavaScript developers can maintain performance by leveraging Web Workers or offloading a few tasks to the server.
2.2 Advantages of JavaScript
Let us take a look at some of the benefits that make JavaScript an excellent programming language.
1. Reduced Server Load
Using JavaScript can reduce the load on the server. Because, in its case, functions like dynamic content rendering and form validation are managed by the user’s web browser instead of the server.
So, JavaScript applications often avoid repeatedly requesting specific information from the server. The browser takes care of it by managing the operations locally. As a result, the response time, efficiency, and scalability of JavaScript applications are better.
2. Rich Ecosystem and Libraries
JavaScript is one of the oldest programming languages in the market. It has a rich and mature ecosystem comprising a wide variety of development frameworks, including Angular, Next.js, and Express.js.
It also offers a large range of testing and debugging tools that help QA analysts test and maintain the quality of the code and resolve issues quickly. Many popular testing frameworks, such as Mocha, Jest, and Jasmine, offer powerful features for performing different types of tests on JavaScript apps, like end-to-end tests, integration tests, and unit tests.
Debugging tools such as Firefox Developer Tools and Chrome DevTools provide JavaScript developers with thorough debugging. They offer advanced features, including real-time code editing, step-through debugging, breakpoints, and more, to simplify the process of identifying and fixing issues in your JavaScript code.
Using these tools not only helps improve the code quality but also enhances the developer experience and reduces their time and effort spent on debugging.
3. Easy to Learn
JavaScript has a simple syntax, so learning to program in this language would be simpler. Moreover, vast resources are available online that help beginners grasp programming concepts and get started with JavaScript coding. Moreover, the community also gives online support to the developers, beginners, and experts alike if they need any type of guidance in their projects.
4. Simplified Development Process
JavaScript’s simple syntax makes coding easy. On top of that, the language’s dynamic nature and adherence to the object-oriented principles streamlines the development process. Developers can use JavaScript for both frontend and backend development. This unified approach reduces code complexity and makes it easier for developers to create and maintain web applications.
JavaScript enables developers to focus on functionality instead of getting entangled in the mess of handling multiple languages when developing a full-stack app. As a result, the overall development process becomes simpler and the developer’s productivity increases significantly.
As a platform-independent language, JavaScript allows developers to build apps that can run on any platform, browser, or device. They no longer need to write multiple codebases for different platforms. This greatly improves the speed and efficiency of the development process.
5. Versatility
Versatility is one of the key benefits of JavaScript. As we discussed earlier, the language isn’t limited to frontend web development, but also has the capabilities for backend development, desktop, and mobile app development.
The advent of Node.js allowed JavaScript to run on the server side. Meanwhile, frameworks such as React Native and Ionic help JavaScript developers create mobile applications that provide a native like experience. Cross-platform desktop apps can also be developed using JS-based frameworks like Electron.
2.3 Disadvantages of JavaScript
JavaScript is indeed a battle-tested programming language providing countless advantages in the development process, but it is necessary to know that there are potential drawbacks to using JavaScript as well.
1. Security Risk on the Client Side
The implementation of JavaScript varies depending on the browser, making it vulnerable to cyberattacks. It becomes easy for hackers to exploit the differences to infiltrate the client systems by injecting malicious code.
Since JavaScript works on the client side, any modified or malicious scripts can be executed without immediate detection, potentially leading to unauthorized access and data breaches. To mitigate such a level of vulnerability, developers must adhere to vigilant coding practices and implement robust security measures, ensuring the safety of JavaScript-based solutions.
2. Debugging Issues
Errors appear only during runtime when using JavaScript. So, locating and debugging them becomes a significant challenge. Since multiple browsers support the language, the details provided by them also vary. Due to cross-browser differences, a bug might surface in one environment but not in another.
Moreover, there are high chances of type-related mistakes, as JavaScript supports dynamic typing. These errors also arise during execution, not compilation. It might become difficult to find the root cause as async code obscures the stack traces and control flow. Minified production builds remove the names and formatting that might have helped debug after deployment. But you can solve this issue by using source maps.
3. Inconsistent Browser Support
Although JavaScript is highly compatible with every available browser, there are inconsistencies in the code execution from browser to browser. The reason behind this is that different browsers support different sets of JavaScript features, especially the ECMAScript specifications.
Now, these inconsistencies cause unnecessary compatibility issues, increasing the developers’ workload. They have to utilize transpilation or polyfills to ensure that JavaScript behaves consistently across all browsers.
Tools like Babel are used to transpile modern JS code into a backward-compatible version. Moreover, the language also provides some libraries and frameworks that can help resolve the browser compatibility issues.
3. Key Difference Between Java and JavaScript
Java is platform-independent and designed to be a general-purpose programming language that runs on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). JavaScript is also an object-oriented programming language, primarily used to create dynamic HTML pages. Java vs JavaScript has recently been a popular topic of conversation. Let’s discuss some points:
3.1 Purpose
Java is widely used for building server-side apps, games, desktop software, mobile applications, and enterprise-level systems. It is also utilized in scientific computing and big data processing. It is also useful for programming hardware and devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
On the other hand, JavaScript helps develop client-side apps, creates dynamic content, and improves the interactivity of web pages. Server-side development is possible when JavaScript is integrated with Node.js. This programming language can also be used in developing games and mobile apps.
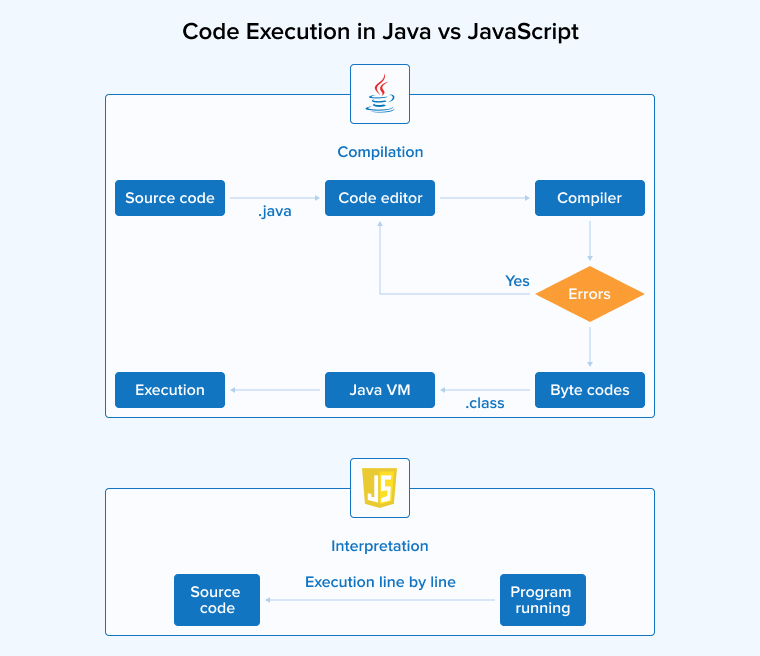
3.2 Compiled vs Interpreted
Java is a compiled language that requires a compiler to convert the source code into bytecode. The Java Virtual Machine can then run this bytecode on various platforms without making any changes. During compilation, the compiler checks for syntax errors to rectify them before they cause any issues. Bytecode allows for faster execution because it is closer to machine language. But due to the same reason, it has low human readability.
JavaScript, an interpreted language, requires an interpreter to read the code before executing it in the web browser according to the written syntax. Modern web browsers are equipped with Just-in-Time compilers for code optimization. Interpreted languages like JavaScript can run the same code on any device that has a compatible interpreter, making them highly portable. Interpreted languages are generally slow but more flexible and easier to use, specifically for building dynamic web apps.
3.3 Learning Curve
Java is a complex language. The Java core consists of various features and concepts, including inheritance, data abstraction, polymorphism, and encapsulation. Java developers need to learn all these fundamental concepts to get started with actual programming.
Meanwhile, JavaScript is quite easy to learn. It’s not even a programming language, but a scripting language. It directly embeds the scripts into the web browser. These browsers have built-in JavaScript engines that run these scripts. Learning the fundamentals of JavaScript is easy, and you can start programming in a short time.
3.4 Syntax
Both Java and JavaScript have different syntaxes. Java has a rigid and verbose syntax because it is a statically typed language. Developers must declare the type of variable they are using in programming. This helps reduce errors, but the lines of code required to complete the task increase.
On the contrary, we have JavaScript, a dynamically typed language with concise syntax. This programming language is flexible, so developers don’t have to declare variable types. This helps speed up the programming process but may also open it up to various runtime errors.
3.5 Security
Java doesn’t experience many runtime errors because, being a statically typed language, it has strong type checking. As a result, the Java programs have fewer security vulnerabilities.
Java allows the use of private variables and methods to improve the security of data and functions against unauthorized access. Java source code is compiled into bytecode, a platform-independent form that the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) executes. This adds an extra layer of security to Java code by isolating it from the system.
JavaScript is less secure than Java. It has loose type checking because it is a dynamic language, making it prone to specific kinds of errors. The JavaScript code is typically executed in a browser environment, making it vulnerable to cyberattacks such as Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS).
3.6 Code Execution
Java is commonly used on the backend to manage server-side operations like database management and authorization handling. Before execution, the Java code is compiled, during which it is thoroughly evaluated for errors. After verification, Java allows for seamless code execution, which is ideal for creating highly efficient and robust server-side applications.
Meanwhile, JavaScript code runs on the client side to handle the frontend of the web application. Being an interpreted language, JS-based code is run line by line in response to the user’s actions, such as text inputs and button clicks. This allows for easy dynamic updates for websites and web applications, enabling a more interactive and enhanced UX.
Sometimes, the code execution also determines the nature of the application. So, opt for Java if you are building an app to manage sensitive user data, and choose JavaScript if you need a responsive web interface.
3.7 Typing System
Java is a strongly and statically typed programming language. It defines objects and variables in a clear and specific manner. Once a developer declares the type of a variable, that variable’s type cannot be changed or converted into another type.
Java allows implicit conversions between certain primitive data types, where the int type can be automatically converted to a float type. Java rejects the program before execution if it identifies any errors in the typing. Java also offers exception handling, memory management, and a garbage collector, which contribute to its robustness.
On the other hand, JavaScript is a dynamically typed programming language. There is no need to declare a data type for variables in JavaScript. Hence, the data types of the variables can be easily changed later. Because the program is not checked during compilation, it is filled with various errors, which are only revealed during runtime, that can potentially crash the application.
3.8 Performance
Performance optimization techniques help improve the application’s loading speed. Both Java and JavaScript offer different techniques for performance optimization.
Java uses a Virtual Machine for quick code execution, which enables faster loading. Moreover, it supports methods such as multi-threading and automatic garbage collection, which help improve performance. Multi-threaded code execution in Java allows parallel processing of large chunks of data, ensuring high performance through predictive analytics and machine learning models.
On the contrary, JavaScript apps are lightweight and can run quickly in web browsers. JavaScript ensures multiple real-time interactions, such as those in online streaming platforms, games, and live chats, as it is capable of processing user-generated events simultaneously.
Based on the performance features of these programming languages, choose Java for applications that must handle heavy computations. However, if you are building an app that can process user interactions in real-time, then pick JavaScript.
3.9 Concurrency
Concurrency is the capability of a program or language to perform multiple tasks at the same time. Java supports the execution of multiple threads simultaneously. Meanwhile, JavaScript works with NodeJS on the server side, uses a queue-based system known as the event loop, and a forking system mechanism called Node.js clustering to manage concurrency while the main thread remains single-threaded.
Though both languages support concurrency through different mechanisms, Java generally performs better for multithreaded workloads because it uses shared-memory threads, whereas JavaScript typically uses isolated processes or worker threads that communicate via message passing (IPC).
3.10 Famous Companies Using Java and JavaScript
While discussing the differences between Java and JavaScript programming languages, along with their benefits and challenges. Let us take a look at the companies that are leveraging these languages to empower their digital platforms and enhance business operations.
| Brands that use Java | Brands that use JavaScript |
|---|---|
| Airbnb | PayPal |
| Uber | Netflix |
| Netflix | Groupon |
| Spotify | Uber |
| Meta (Facebook) | |
| eBay |
4. Conclusion
Java and JavaScript are two different programming languages with distinct purposes. Both come with robust features beneficial for programmers as well as users. The choice of picking a language depends largely on the team’s experience, preferences, and the project’s requirements.
If your project is a large one or requires heavy computation, then choosing Java would be wise. Whereas building small or responsive web apps demands the capabilities of JavaScript. Consider the advantages, disadvantages, and differences discussed in this blog to pick a suitable programming language for your upcoming project.






Comments
Leave a message...