
Healthcare information systems have undergone a significant transformation, evolving from paper documents and traditional file systems to digital and cloud data storage. Access to sensitive medical information must be strictly restricted for authorized personnel, ensuring patients’ privacy and the security of the information. Data security has improved since the advent of digitalization, particularly through the healthcare development and implementation of standards like HL7 or FHIR. These standards promote interoperability by enabling secure data sharing between hospitals and healthcare providers, and help deliver better patient care while securing sensitive health data both at rest and in transit.
A reliable healthcare software development company can develop software solutions that comply with the necessary standards while efficiently performing all the administrative tasks.
However, you must know which standard from HL7 or FHIR is applicable or should be implemented in your healthcare organization and software solution. Let us understand both these healthcare standards, their similarities, differences, and pros and cons.
1. What is HL7?
Health Level Seven is a set of international standards for the exchange of clinical and administrative healthcare data. Health Level Seven International, a non-profit organization, created these standards to improve healthcare interoperability.
Compliance with healthcare data standards provides a framework that enables the secure and consistent exchange of healthcare information between organizations. Both public and private organizations often have unique methods for handling and sharing data. This could complicate things when two organizations with different policies need to exchange crucial patient information. That’s why we need HL7 to standardize healthcare data exchange across the industry.
1.1 Benefits of Using HL7
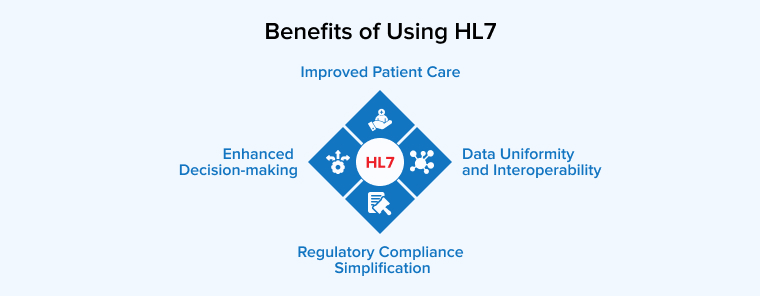
Adapting HL7 standards in healthcare organizations provides several benefits, including but not limited to:
1. Data Uniformity and Interoperability
The HL7 interface is used to standardize the exchange of healthcare information, enabling healthcare providers to easily access and share medical records between different systems without risks of data duplication. It also helps ensure that the shared data is accurate and up-to-date.
As a result, HL7 not only streamlines data exchange but also maintains the uniformity and interoperability of healthcare data.
2. Improved Patient Care
Access to more information—such as test results, previous diagnoses, and treatment plans—provides medical staff with a comprehensive clinical view of the patient’s medical history. This helps them to make informed decisions and offer more accurate and personalized care.
3. Enhanced Decision-making
HL7 standards enable medical professionals to have easy and immediate access to healthcare data, including patients’ medical records, test results, previous treatments, and more. This is possible through the integration of two or more healthcare software systems.
HL7 standards enable organizations to maintain a secure and continuous flow of health information, spanning various disciplines and departments across systems. With more accurate and better quality data at their disposal, doctors and physicians can easily make informed decisions about patient treatments.
4. Regulatory Compliance Simplification
Sharing electronic data through HL7 standards between healthcare organizations and regulatory bodies facilitates easier compliance with regulatory requirements and other important public health reporting standards. HL7 bears the burden of the administrative handling of healthcare data, allowing hospitals and clinics to focus on providing better patient care.
1.2 Disadvantages of HL7
As there are benefits of adopting HL7 standards, so are some challenges. With proper planning and preparations, they can be solved easily, but before that, you must clearly understand them.
1. Security and Privacy Concerns
Security and privacy concerns remain critical when managing sensitive healthcare information, even with the implementation of robust security measures. Organizations are required to take data protection measures like continuous monitoring, role-based access control (RBAC), and strong encryption. If privacy and security concerns persist, then collaborate with HL7 integration experts to identify and resolve vulnerabilities. Proactive steps must be taken in matters where sensitive patient information is at risk.
2. Risks Involved in EHR Migration
The health records are most vulnerable when they are in transit from one system to another, especially if the execution of that migration is poor or unplanned. Inadequate migration can result in data loss, which may disrupt healthcare operations and compromise patient care. This challenge can be addressed by performing secure migrations to compatible systems.
Before beginning data migration, ensure that your storage system is secure to prevent data loss due to corruption. So, plan your data migration thoroughly and always keep a backup. First, check the transmission security, and then migrate the critical or essential information. Don’t try to migrate everything all at once. It may cause unexpected errors.
3. Complexity and Variability of Standards
Compliance laws can be difficult to understand because of their complex nature and frequent updates driven by evolving market conditions and the technological landscape. Due to such complexities and variabilities, every healthcare system might interpret the standards differently. As a result, inconsistencies become frequent in data communication.
The variabilities might be the reason why existing compliant systems may no longer adhere to the standards. Additionally, the complexities of HL7 can cause inconsistencies in data exchange, which can disrupt patient care.
1.3 HL7 Versions
HL7 is an international standard used in multiple healthcare domains such as EHRs, laboratory, and billing systems. HL7 comes in various versions, where HL7 v2 is the most widely used version with a structured format to share messages. Meanwhile, HL7 v3 and HL7 CDA show clinical data within a structure.
1. HL7 v2
HL7 v2 is a widely adopted messaging standard created to enable different systems within a healthcare organization to communicate. It provides the ability to share or exchange different types of data, such as observation results, medical prescriptions, patient admissions and discharges, transfers, and financial transactions. This grants systems with large-scale interoperability.
On the downside, HL7 v2 can’t store any data in the database, and its data transmission operations are limited to a single organization. As a result, if you need a scalable solution that allows communication between systems from different healthcare organizations, HL7 v2 is not the right choice.
2. HL7 v3
When HL7 v2 had limitations in handling complex data exchange well, HL7 v3 was built to address those gaps. This solution is designed upon a Reference Information Model (RIM), which serves as a universal reference model for representing healthcare data. HL7 v3 offers a more robust data exchange framework compared to v2, which provides better interoperability between systems. However, complying with HL7 v3 can be expensive and complex because it requires a full implementation of the RIM model.
3. HL7 CDA
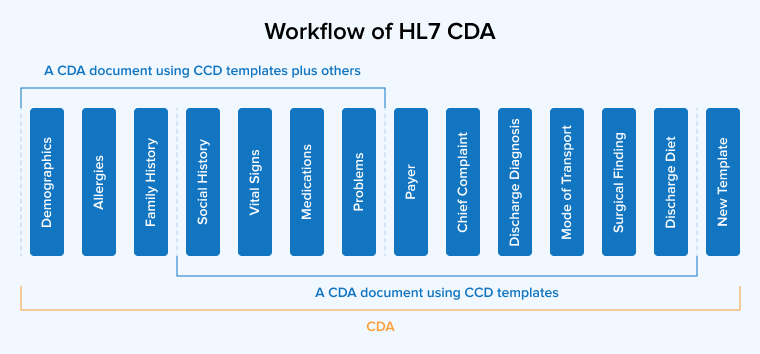
As the name suggests, HL7 Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) uses standardized document structures for clinical data exchange. It specifies both the format and the content requirements of a clinical document, allowing patients and healthcare providers to share them effortlessly.
Therefore, HL7 CDA has several key attributes, including human readability, context relevance, stewardship, wholeness, potential for authentication, and persistence. CDA is mainly applicable in facilities like hospitals and clinics that store or manage patient health information.
HL7 CDA covers a large range of patient-related data, including lab results, medications, medical history, insurance details, etc, in different file formats from texts and images to sounds.
2. What is FHIR?
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) is an advanced set of rules and standards for the exchange of electronic medical records and other healthcare information. Developed by HL7, FHIR was introduced in 2014 to improve interoperability among healthcare systems.
FHIR is designed with a modular architecture and uses RESTful web services as its foundation. It supports data exchange in both XML and JSON formats. Users can access specific resources through a discrete URL that enables operations like retrieving, sending, and manipulating through API requests. The FHIR structure is very different from other message structures.
Many top companies are using these API standards for data exchange, as it not only helps them maintain protocols but also boosts their momentum. The Centers for Medicare& Medicaid Services (CMS) has also mandated that every healthcare organization is required to adopt the FHIR standards.
2.1 Advantages of FHIR Adoption
The adoption of FHIR standards offers greater flexibility compared to conventional models, among many other advantages. Let’s take a peek at some of the common benefits of FHIR implementation.
1. High Security
FHIR prioritizes data privacy and security by supporting robust security features like OpenID Connect and OAuth 2.0. These protocols ensure secure authentication and authorization for data sharing between different healthcare apps and other systems. FHIR implementation also includes adherence to security best practices like access controls and encryption for both data at rest and in transit
2. Focus on Patient Experience
FHIR puts the patients in control of their records. They get to decide what data they want to keep private, what to share, and more. This fosters trust and transparency in the healthcare services. Moreover, asking for the patient’s permission before accessing or sharing their details is easy to implement across all apps and devices. Additionally, patients are immediately notified about any changes in their health information or if any risk or significant events occur.
3. Faster Data Exchange
In comparison to traditional methods, FHIR allows for faster exchange and upload of patient data. Implementing a standard set of rules allows doctors and medical staff to quickly access health records from various sources and generate a unified view.
Implementing a standard set of rules across all systems helps healthcare professionals make informed clinical decisions. Moreover, you no longer have to spend more money on custom integrations to transmit huge data files.
FHIR uses a RESTful API approach with modern architecture to provide a streamlined and efficient data exchange solution, simplifying the data access and utilization process.
4. Rapid Implementation and Scalability
FHIR is a resource-oriented standard that allows healthcare organizations to quickly adapt to changing requirements. Implementing FHIR-based solutions, organizations can save a significant amount of time and resources, leading to rapid implementation. The advantages accrued from reduced costs enhance the organization’s ability to scale.
2.2 FHIR Integration Challenges
FHIR standards are relatively new, so there are limited studies and experiences available that highlight potential issues and how to address them. But here, we have compiled FHIR challenges that can help you prepare for effective implementation and overcome these obstacles.
1. Performance Issues
Designed for granular data access, FHIR often requires making multiple API calls to fetch required information. When dealing with large datasets or complex queries, this approach can lead to slower response times and increased server load compared to bulk data exchange formats.
2. Versioning Challenges
Like every other regulation, FHIR also evolves over time. As a result, new versions are continuously introduced at regular intervals when changes are made to the resource structures. Managing and maintaining these versions across multiple systems while ensuring backward compatibility is challenging and can lead to integration issues during system upgrades.
3. Limited Support for Legacy Systems
Most of the healthcare organizations are still empowered by traditional systems that are not compatible with modern standards like FHIR. These legacy healthcare systems often lack the interfaces capable of seamless communication with apps adhering to FHIR protocols. As a result, the data exchange becomes more complex and prone to errors. This lack of support makes FHIR integration extremely challenging. To make this work, developers have to utilize extensive system upgrades, custom adapters, and additional middleware, leading to increased development costs.
3. Core HL7 and FHIR Protocols
Both HL7 and FHIR standards share information across the system components within the boundaries of certain rules, following specific protocols.
3.1 HL7
The core protocols for HL7 standards are discussed below:
1. OSI Layer 7 Protocol
Layer 7 of the OSI model, also known as the application layer, provides app services to network software by using protocols like SMTP and HTTP. It keeps the same format and content that healthcare applications share, without connecting the systems through any mode of transmission. Messages are commonly delivered via a TCP/IP connection.
2. Event-Driven Protocol
When the need to define a data exchange between apps or systems arises due to any healthcare-related event, it is defined as an event-level protocol. This event can be anything from a patient’s admission to ordering medicines from a pharmacy. Whenever an app or system identifies an event, it shares the information with other systems that need it.
3. Application to Application Protocol
This protocol is used to establish communication or data exchange directly between two independent systems, rather than following a client-server model. The message in such cases is of extreme importance. The role of the application doesn’t matter here.
4. Standard Protocol
When an application wants to share a message or when two apps need to exchange a specific set of information, they require a standardized communication method. The HL7 protocol facilitates this standard, mitigating the risks occurring from integration with a third-party system.
5. Exchange Protocol
This HL7 protocol defines a standard format and rules for transmitting or exchanging data with each other. Data processing and storage hold no importance here, and while database structure requires matching HL7 message definition, it isn’t mandatory.
3.2 FHIR
FHIR is a relatively new standard, and hence it uses different protocols from HL7. Some protocols of FHIR acting as the foundation for its interoperability include:
1. RESTful API
For data exchange between different healthcare apps, FHIR utilizes RESTful principles. Standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, DELETE, and PUT help you perform necessary operations in the FHIR resources.
2. HTTP(S)
HTTP serves as an essential transport protocol in FHIR, enabling data sharing and messaging over the internet across various apps, systems, and organizations.
3. OAuth (Open Authorization)
Authentication and authorization in FHIR are commonly managed using OAuth. It only allows authorized parties with access tokens to access and use FHIR resources.
4. WebSocket
The WebSocket protocol is largely used in FHIT applications to enable real-time communication and data exchange between servers and client-side apps. This allows for back-and-forth communication and updates the FHIR resources efficiently.
5. SMART on FHIR
This protocol was designed by integrating the FHIR standards with the Substitutable Medical Apps Reusable Technologies (SMART) platform. It allows the development of healthcare apps that can securely integrate with EHR systems and access required FHIR resources.
4. Similarities Between FHIR vs. HL7
Both HL7 standards and FHIR standards were developed by the same non-profit entity called Health Level Seven International. So, it’s not like comparing and pitting them against each other will give us a clear winner. Both standards are necessary for healthcare systems to perform interoperability tasks securely.
One can say that FHIR is the latest standard of all, launched with the best features from all its predecessors. And that is the reason why it has many similarities with HL7 v2, v3, and CDA. Here are a few:
4.1 Built Around Reusable “Chunks” of Code
Health Level Seven International creates standards designed to enable interoperability between healthcare applications. Therefore, the developers have reused the same pieces of code to build the new and improved systems.
4.2 Forward/backward Compatibility
Both HL7 and FHIR regulations are backward/forward compatible. A standard is considered backward compatible if systems using newer schemas can correctly interpret data formatted with older schemas without experiencing any issues. Meanwhile, forward compatibility means that systems using older schemas can process data created with a new schema.
Having forward/backward compatibility allows these standards to work successfully with data and interfaces from different versions. This compatibility helps minimize the costs associated with upgrading hardware, software, and engineering efforts.
4.3 Extensibility Mechanism
Both standards enable you to extend the capabilities of your system by either modifying the existing features or adding new ones. Healthcare systems must be kept updated, and hence, they require frequent changes. This mechanism allows you to update your system without affecting existing operations or user experience.
5. HL7 vs FHIR: A Comparison Table
We discussed the similarities between HL7 and FHIR, but there are many notable differences as well. Let’s take a quick look at the table below, highlighting the critical factors for better understanding.
| Features | HL7 | FHIR |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Uses traditional messages, formats, and syntaxes. | Uses REST APIs and open web technologies for data exchange. |
| Flexibility | Flexible | More flexible |
| Accessibility | Restricted access | Free access |
| Security | Transport Layer Security | Transport Layer Security (and SSL) is an authorization protocol. |
| Human Readability | Doesn’t support readability. | Supports human-readability. |
| Platform Support | EHR, HIS, EMR, LIMS | EHR, HIS, EMR, LIMS, telemedicine, mobile apps |
| Reliability | Multiple options columns make it unreliable. | Reliable because of specific resources. |
| Use Cases | Medical Records Management | Universal data exchange across IoMT devices and healthcare applications. |
| Messaging Format | Only supports XML | Supports XML and JSON |
| Interoperability Type | Syntactic | Syntactic and semantic |
| Integration | Can’t connect with cloud healthcare systems. | Seamless integration with mobile and cloud healthcare systems. |
| Implementation | Need significant efforts for customization and integration. | Easy implementation with modern web technologies. |
| Adoption | Widely used across the world. Almost 95% of US healthcare organizations use it. | Relatively new but slowly gaining traction. |
| Extensibility | Non-extensible | Feature extensible resources |
6. Why is FHIR Better Than HL7?
Being the latest standard in the series of HL7 standards, FHIR is built using the best of all its predecessors. It offers significant improvements in interoperability compared to all previous HL7 standards. Every feature FHIR offers to ensure interoperability has already been tested in real-world healthcare environments using previous HL7 standards.
Whatever flaws those previous offerings had were removed by Health Level Seven International when adding those features into FHIR. Moreover, FHIR introduces advanced features that can easily meet the requirements of the modern healthcare market. Here is how FHIR out-bests the previous HL7 standards:
- Easy execution compared to predecessors: FHIR helps developers attain interoperability without any difficulties. It has better compatibility than v2 and covers several technologies.
- Suitable for most common scenarios: FHIR resources offer components to help developers build a custom software solution that can easily adapt to changing business and users’ administrative requirements.
- Freely available: FHIR is available free for implementation. As a result, you can save a lot of money on implementation costs.
- Supports multiple paradigms and architectures: To obtain interoperability in a multi-component and complex system, developers need flexibility in terms of the technological solutions and decisions they make. FHIR promises flexibility by supporting multiple architectures, paradigms, and data formats.
- Provides advanced data governance: FHIR ensures that patients have more control over their data and how it is shared. The implementation of these regulations simplified data exchange but enhanced data security.
7. Conclusion
HL7 and FHIR standards are critical to achieving interoperability between healthcare systems for secure and efficient data exchange. HL7 follows a traditional approach by offering a fixed framework for messaging and sharing information. On the other hand, FHIR provides a more flexible and interoperable solution to meet the modern requirements.
There are several benefits of adhering to these standards, including faster decision-making, reduced operational costs, and enhanced patient care. But it is important to note that the successful implementation of healthcare regulations demands careful planning, adherence to best security practices, and continuous monitoring and maintenance.
FAQs
What are the benefits of FHIR in healthcare?
The advantages of using FHIR include giving patients more control over their data and decisions about who can access it. It also allows seamless integration between different healthcare systems for direct access and use.
What are the disadvantages of HL7?
HL7 is a complex healthcare standard. So it is challenging to understand and implement all of it. Moreover, achieving compliance with HL7 standards is costly and time-consuming.






Comments
Leave a message...