
The healthcare industry continuously faces serious threats and challenges with data security, experiencing numerous breaches that put patient privacy and care at serious risk. This only confirms the need for strong healthcare compliance, like HIPAA and HITECH.
With the rapid growth of healthcare software, the need for robust security becomes imminent. Healthcare organizations require technology to handle such a huge and complicated task. This is where a specialized healthcare software development company becomes helpful. They can develop and deliver compliant software that helps hospitals and providers set up proper procedures, boost security, and stop data breaches.
This article acts as a complete guide to healthcare software compliance, discussing various regulations, their importance, challenges, and how to achieve them.
1. What is Healthcare Compliance Software?
A healthcare compliance software is a digital solution that helps healthcare organizations comply with several standards and complex regulations when governing operations.
This system streamlines the management of compliance-related activities, tracks incidents, and automates the generation and maintenance of necessary documents. It increases operational efficiency and mitigates risks of non-compliance. Additionally, it encourages and promotes a culture of compliance within the organization, which supports better patient care and data privacy.
Healthcare compliance software stores all the necessary information and keeps it updated, which helps address compliance issues. From healthcare startups and research facilities to individual practitioners and collaborative administrative or IT staff, everyone who deals with the patient’s health information needs this solution.
1.1 Importance of Healthcare Software Compliance
Healthcare institutions and businesses can improve their operational performance while reducing the risks of errors and non-compliance. This solution not only strengthens data security but also helps deliver quality patient care. Here are a few reasons why it is important to adopt a compliance solution in the healthcare industry.
1. Enhanced Risk Management
Healthcare compliance software enables hospitals and clinics to handle the risks of non-compliance or data breaches. It allows for frequent assessment of policies, and if your operation aligns with relevant regulations and industry standards.
Data breaches and cyberattacks threaten both patients’ health information and healthcare organizations’ financial data. Healthcare compliance software enables hospitals and clinics to handle the risks associated with regulatory non-compliance and potential data breaches.
To ensure compliance with relevant industry standards and regulations, organizations are forced to perform risk assessments frequently. It allows for frequent assessment of policies and operations that align with the relevant regulations and industry standards.
2. Improved Patient Safety
Compliance software solutions provide healthcare professionals with the necessary tools to identify areas of improvement in their daily operations. By resolving these concerns, healthcare providers can reduce the risks of errors, avoid adverse incidents, and deliver the best possible care to patients. Information compliance programs place robust safeguards on patients’ information and medical records, making it secure and available when required for treatment in the present or future.
3. Interoperability and Standardization
Adhering to industry standards such as Clinical Document Architecture (CDA), Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM), Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR), and Health Level Seven (HL7) enables seamless communication between different healthcare IT systems. This allows for easy exchange of patient information, medical records, lab results, and other data across systems to ensure coordinated care.
4. Quality Assurance Measures
A compliance program ensures that healthcare operations meet industry standards as well as national and international regulations. For that, healthcare compliance software closely monitors the quality of the system and implements QA measures where necessary. Only a quality software solution can help healthcare providers offer better patient care.
The software continuously verifies that the latest code changes and updates to online information adhere to established policies. Continuous quality monitoring and regular security audits help identify defects or bugs in the system. Modifications are made to the areas requiring improvement. As a result, the code execution is performed smoothly.
5. Mitigation of Cybersecurity Threats
To ensure compliance, healthcare organizations must also implement cybersecurity best practices. Additionally, these practices are customized to meet the specific operational needs and patients’ requirements. This helps mitigate the risks of various types of cyberattacks, including internal and external threats.
1.2 Key Regulations and Standards
Healthcare regulations and compliance laws must be followed by all organizations, ranging from hospitals to medical device manufacturers and cloud service providers that have access to the patient’s health information. Now, the regulations may vary from region to region and have different compliance rules depending on the sensitivity of information the entity is handling. Let’s take a look at the top healthcare standards.
1. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA establishes national standards to protect the privacy and the security of individuals’ health information in the United States. It is a set of rules and compliance standards to regulate the use, exchange, and storage of health data. The Office of Civil Rights (OCR) oversees and manages HIPAA enforcement.
HIPAA regulations give patients the right to access, request amendments to, and obtain an accounting of their protected health information (PHI). These rules place technical, administrative, and physical safeguards on the PHI to ensure its safety. HIPAA also emphasizes secure transactions via unique identifiers and standardized code sets.
HIPAA compliance is essential because it ensures data confidentiality, mitigates the risks of unauthorized access, and promotes trust between healthcare providers and patients.
2. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Regulations
On top of taking care of basic compliance tasks, the FDA also covers rules for keeping medical devices, medicines, and biologics safe and effective. The FDA is an agency enforcing a set of over 200 regulations, laws, and standards. However, with the lack of a universal framework for implementing FDA in healthcare, each healthcare organization has to decide which standards and regulations apply to its operations and then take the necessary steps for compliance.
The Office of Regulatory Affairs (ORA) within the FDA is responsible for assessing regulatory compliance, investigating fraud or criminal activities, overseeing laboratory testing, and inspecting drug facilities. This ORA has the power to enforce laws by pursuing criminal prosecutions, obtaining injunctions against healthcare organizations that operate unlawfully, and seizing unregulated goods and products.
3. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR is responsible for controlling healthcare information in the European Union. This regulation applies to every organization working within the boundaries of the EU and those who target or manage data for people residing in the EU. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) was created by taking inspiration from the GDPR. Following this, many US-based states came up with their healthcare regulations.
The GDPR grants patients the right to know and control how their data is processed. Patients can also ask the healthcare organizations to correct or remove their information from the database. This helps ensure patients’ privacy, and in case it is violated, organizations have to notify about the breach to the Information Commissioner’s Office within 72 hours.
4. Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH)
Passed in 2009, the HITECH Act encourages adoption and meaningful use of health information technology (Health IT). It provides financial incentives to healthcare organizations that use certified health records (EHR) and other Health IT solutions. This Act strengthens the security and privacy rules of HIPAA. For example, if a data breach happens, it requires health organizations to report it to the Department of Health and Human Services as well as to the affected patients. HITECH has a direct impact on healthcare practices, helping to improve the quality and efficiency of the care.
5. Stark Law
The Stark Law prevents physicians from referring patients to certain Medicare or Medicaid services with which they have a direct or indirect financial relationship, unless there is a specific need for it.
The designated health services (DHS) under the Stark Law include occupational therapy services, physical therapy, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory services. By violating the Stark law, physicians may incur fines of up to $15,000 per service and exclusion from federal healthcare programs.
The Stark Law has a great impact on healthcare practices. Hence, it helps minimize the risks of self-referral abuse. This ensures that DHS and referrals are provided to patients based on their medical requirements and not on the physicians’ financial interests.
6. HL7
Health Level Seven is an international non-profit organization responsible for setting industry standards for exchanging, sharing, integrating, retrieving, and storing patients’ health information.
Electronic Health Records operate as a distributed system that depends on seamless interactions between multiple subsystems to create certain healthcare operations. HL7 works here as a link between these subsystems. So, it’s the backbone of EHR. It not only sets standards for EHR but also helps smooth its functioning.
2. Steps to Achieve Healthcare Software Compliance
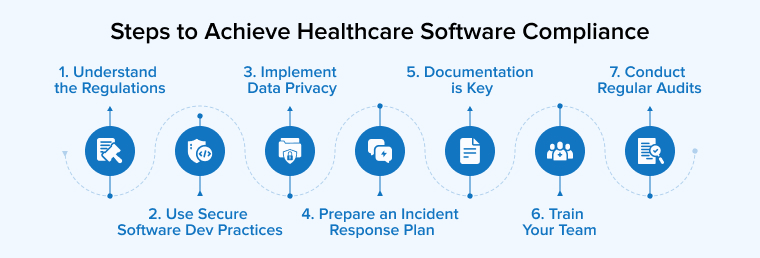
Although there is no foolproof guide to achieving healthcare software compliance, we can implement a few best practices to ensure that regulatory standards are upheld.
2.1 Understand the Regulations
The first thing to understand is the regulations applicable to your software. Determining them is easy based on the services offered or used by your software. For example, if your software handles healthcare information, it must comply with standards such as HIPAA. The FDA applies to medical devices that use that software.
Depending on the region, you may need to follow the GDPR for data protection and the MDR for medical devices. Therefore, conduct thorough research to identify the legal requirements applicable in your region as well as in the regions where your software will be used. If it is deployed globally, then your healthcare solution must comply with multiple regulatory bodies.
2.2 Use Secure Software Development Practices
The best way to ensure that a healthcare system adheres to legal compliance is by adopting it right from the design phase. Developers must implement best coding practices and secure methodologies. Using frameworks like OWASP Top Ten helps identify and reduce system vulnerabilities.
Additionally, you need continuous monitoring and vulnerability scanning to make sure your healthcare solution remains healthy. Look out for common cyber threats in every phase of the development life cycle, ranging from planning to post-release support, to prioritizing security.
2.3 Implement Data Privacy and Security Measures
PHI is highly sensitive and valuable on the black market. Therefore, hackers often target hospitals and clinics to steal this data. Such breaches can lead to disruptions in healthcare services, significant financial losses, and even endanger patient lives. This can be prevented by following robust data privacy and security practices.
Compliant systems are required to be equipped with various features such as role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication to ensure security. The users are also given the right to data portability and to delete their personal information.
2.4 Prepare an Incident Response Plan
Despite thorough legal compliance and robust security measures, there are days when hackers can easily breach your system. Therefore, it is essential to prepare disaster recovery plans in advance to respond effectively during such threats. In case of an attack, healthcare providers have to react promptly to prevent any type of data loss and make sure that the facility remains operational. You need fail-safe measures for almost every scenario and data backups in case of breaches.
2.5 Documentation is Key
Documenting is essential for healthcare software compliance. These records serve as proof for regulators regarding everything you have done to adhere to relevant standards. Every change made to the code goes as a report in the documentation, along with each risk management procedure and incident response plan.
2.6 Train Your Team
Despite implementing robust technologies and security best practices, errors caused by human factors can still occur. That is why the healthcare providers, including the doctors, nurses, medical and administrative staff, should receive training on adhering to data privacy and healthcare compliance laws.
2.7 Conduct Regular Audits
Over time, healthcare regulations may be changed or updated. So, it is recommended that you continuously assess your healthcare software to identify the areas of improvement that can meet the ongoing regulatory needs.
3. Challenges in Healthcare Software Compliance
Adhering to healthcare compliance is not easy. There come many challenges along the way. Here are a few challenges that you need to prepare for to ensure compliance.
3.1 Privacy and Data Security
Cyberattacks and data breaches are on the rise, even in organizations equipped with robust security measures. Protecting the patient’s health information and user privacy is the biggest challenge in the digital age. Since EHRs are now used widely across the globe, compliance with relevant regulations like HIPAA and GDPR is more critical than ever before. It means strengthening the system against both external and internal threats.
3.2 Staff Training and Education
Train all staff members to make them understand compliance policies and how to implement the best possible measures to ensure adherence. This is not an easy task, but quite overwhelming and time-consuming. Compliance policies themselves are complex to understand. Many compliance programs come with integrated training modules that each employee is required to complete. These modules support self-learning and provide regulatory bodies with evidence that the organization meets compliance requirements.
3.3 Third-Party Risk Management
Healthcare organizations often have to integrate their systems with third-party service providers, such as cloud service platforms and payment gateways associated with medical devices. Many of these third-party vendors have access to sensitive patient information and healthcare data. As a result, each of these third parties becomes vulnerable.
Hackers don’t need to target hospitals directly, which are protected through robust security, but can easily attack third-party vendors that have less security. Though these third-party vendors are required to follow compliance laws, they often lack the essential measures to keep the data completely safe. In such cases, the healthcare organizations must provide them with the necessary resources to ensure data security.
3.4 Changing Technology Landscape
The technological landscape is evolving rapidly, which brings both opportunities and challenges across all sectors, including healthcare. Emerging technologies like AI and ML help in providing accurate diagnoses and enhanced medical services. Adopting these new technological developments in the healthcare sector is important for staff to offer better quality patient care. However, keeping up with the rapidly evolving technological field is tough. They not only need to invest a large sum of capital to acquire these technologies but also spend an enormous amount of time and money to train the staff on how to use them. It’s quite bothersome and expensive if it’s a frequent occurrence.
3.5 Keeping Up with Changing Regulations
Healthcare regulations frequently change to address emerging risks and advancements in technology. So, what was considered an essential legal requirement last year may no longer be necessary today. Therefore, healthcare organizations must stay updated on the regional regulations, changes in the policies, and data security standards.
Sometimes, due to regulatory changes, medical devices and software are often recategorized, subjecting them to a whole new set of rules and standards. Therefore, developers and stakeholders must build a flexible system that can adapt to the changing technological landscape and regulations.
4. Conclusion
Maintaining compliance in healthcare software is crucial to safeguard patient data and ensure privacy. It also helps patients trust you, which is key in healthcare. By using a strong compliance solution, you’re not just following rules but also building robust data security. Choosing a good compliance automation platform can streamline this complex process and mitigate the risks.





Comments
Leave a message...