
FinTech plays a vital role in the global economy. It not only makes the financial services easy to access worldwide, regardless of the geographic location or socioeconomic status, but also drives innovations such as electronic payments, mobile transfers, cryptocurrency trading, and more.
Top finance software development companies help businesses build FinTech solutions that streamline financial processes, improve operational efficiency, reduce costs, boost revenues, and enhance the end-user experience. However, such rapid growth also introduces certain security risks.
FinTech companies can leverage cybersecurity to tackle threats. This article explores why cybersecurity is important in fintech, common challenges, best practices, and future trends.
1. Why is Cybersecurity Important in FinTech?
Financial technology has simplified and made financial operations more flexible worldwide, making them easily accessible to everyday users. However, these same FinTech solutions that streamline financial processes also face significant security risks.
Improper implementation of security measures can make a FinTech solution vulnerable to cyber threats. These vulnerabilities must be effectively addressed and mitigated during testing and QA or at the compliance stage. Failure to do so can expose your FinTech solution to cybercriminals through data breaches, DoS, DDoS, malware, and more.
A research report from IBM suggests that FinTech service providers are the primary targets of cybercriminals. In 2024 alone, the global average cost of a data breach was $4.88 million. This indicates that, despite being more efficient and flexible than traditional services, FinTech solutions face significant security risks.
Any cyberattack or data breach can result in financial losses, legal actions, privacy violations, and loss of customer trust. Fintech institutions are not subject to the strict regulations that govern traditional banks, making it even more important for them to implement robust cybersecurity measures.
2. FinTech Cybersecurity Risks and Challenges
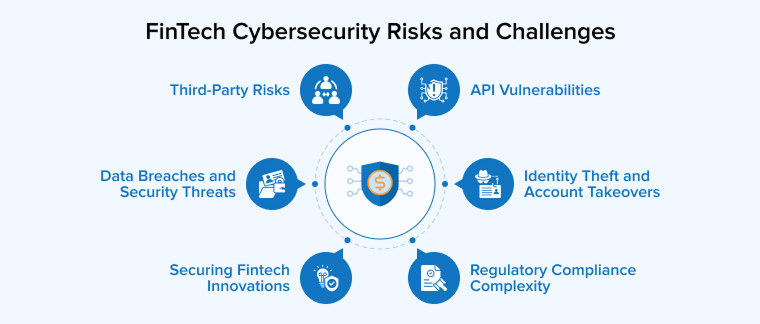
Working in FinTech cybersecurity is challenging and risky, not only because the systems are highly sophisticated but also because the evolution of threats is outpacing both technological advancements and compliance requirements.
2.1 Regulatory Compliance Complexity
The regulations for FinTech are still in the development phase. They are continuously updated as the technology keeps evolving, and their impact is analyzed. So, these regulations are not only constantly changing but also complex. FinTech solutions must adhere to various policies and local financial laws, such as GDPR and PCI DSS.
The constant back-and-forth caused by changes and updates makes these regulations a complex puzzle, increasing requirements and overhead without ensuring solid implementation or compliance. Additionally, FinTech solutions are often deployed across multiple markets, forcing companies to diversify their resources to keep up with the market trends, which further disperses their security efforts.
2.2 Third-Party Risks
FinTech solutions offer innovative features and improved efficiency by integrating several third-party services. However, granting these third parties access to your system raises significant security concerns. Therefore, you must implement additional security measures to protect your app and data from breaches and attacks.
FinTech companies often rely on third parties for external services such as payment processing, cloud computing, and data analytics. These services require access to customer information and systems to deliver better performance. If these services or their providers are compromised in any way, both the FinTech company and its end-users will likely experience the impact.
Even if a FinTech company and its solution are protected by the highest security standards, it matters little if third-party providers implement only a fraction of those protocols. Cybercriminals often exploit third-party vendors as gateways to breach or attack FinTech systems.
2.3 Identity Theft and Account Takeovers
To attack or breach a FinTech system, cybercriminals often use hacked credentials or stolen identities. By impersonating users, they gain easy access to FinTech apps and user accounts to steal money or sensitive financial information.
Identity theft is one of the most common types of cyberattacks. It often involves exploiting APIs to obtain authentication tokens and compromise verification methods. In these attacks, cybercriminals target numerous usernames and passwords to gain unauthorized access to systems. Often, attackers impersonate customer representatives or financial advisors to trick users into sharing their passwords and tokens.
Another method attackers use is SIM swapping, where they bypass SMS-based two-factor authentication by convincing mobile carriers that they are the legitimate users, prompting the system to deliver the verification code directly to attackers. Robust authorization and authentication mechanisms are essential to prevent such identity theft attacks.
2.4 Securing Fintech Innovations
The same innovations that help FinTech offer better services, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, cryptocurrencies, and decentralized finance, also pose a significant challenge to its cybersecurity. Although blockchain is widely known for its security, any vulnerability in the smart contract can provide attackers with an opportunity to steal millions of dollars from a DeFi platform.
There are exchange risks associated with cryptocurrency, and wallets are susceptible to hacking. Al-driven algorithms are not completely secure. Attackers can easily manipulate the training data to trick the very AI models designed to protect the system, thereby disrupting its services. Therefore, banks and financial institutions must maintain a balance between growth and security, ensuring that innovative solutions do not introduce new risks.
2.5 API Vulnerabilities
Application Programming Interfaces are widely used in FinTech systems to share data and integrate with other solutions. However, if these operations are not performed securely, the vulnerabilities can be easily exploited by cybercriminals.
Using APIs to access the data in a FinTech system is possible if the system has a weak authentication method in place. Such a system can’t withstand cybersecurity threats like injection attacks and others. This serious security lapse can lead to unauthorized access, data theft, and service disruptions.
2.6 Data Breaches and Security Threats
Attackers exploit app functionalities to take advantage of vulnerabilities or flaws in business logic, gaining access to sensitive data. This often results from insufficient security testing. Furthermore, the rapid deployment of APIs, especially at a large scale, leads to the addition of new functionalities without proper security checks. Such unsecured API endpoints become gateways for data breaches.
Meanwhile, to prevent advanced security threats such as DDoS attacks, you must use mechanisms that provide continuous monitoring of the system. Using AI to simulate attacks can help identify vulnerabilities and potential attack vectors in your system.
Phishing attacks are not only psychological manipulation but also technically sophisticated. Make sure your employees are aware of possible phishing traps, such as fraudulent business emails and other vectors, to prevent security breaches originating from within the organization.
3. Best Practices for CyberSecurity in Fintech
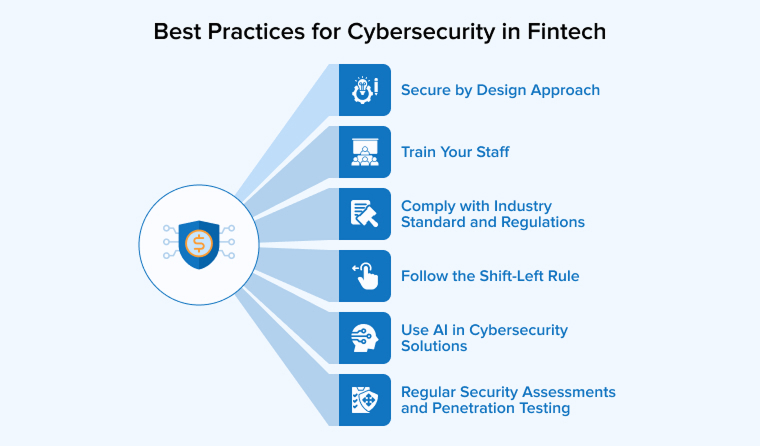
FinTech companies operate within a complex ecosystem where they are entrusted not only with their customers’ money but also with sensitive financial and personal information. It is their responsibility to protect this data and funds from numerous cyber threats. To achieve this, adhering to the best practices is essential. It helps strengthen their defense, ensures compliance, and maintains customer trust.
3.1 Secure by Design Approach
Adapting a security-by-design approach is the best way to build a FinTech solution with minimal or no flaws. In this development process, from requirement analysis to maintenance, the FinTech app is designed to meet the highest and most appropriate security standards.
3.2 Train Your Staff
When there aren’t any easily exploitable flaws in your system, hackers turn their attention to your employees. Train your staff to prevent unauthorized access and to recognize malicious attempts from within the organization. Phishing emails, fraudulent requests, and scams are the most common methods cybercriminals use to breach FinTech systems. These tactics have proven to be highly effective and easy to execute.
Training your staff will help raise awareness of social engineering attacks. Employees fall victim to these traps because they do not follow security protocols properly, cannot spot red flags, and fail to recognize suspicious activity. Foster a security-first culture by training your staff to identify such disguised threats, which will reduce human errors and eliminate the chances of a breach.
3.3 Comply with Industry Standard and Regulations
To ensure the safety of the consumer’s money, data, and privacy, the financial services industry is heavily regulated. Each region has established different laws to protect its citizens’ rights. Any FinTech company planning to enter a market must first align its products with the region’s regulatory standards, such as GDPR, PCI-DSS, KYC, and AML, to ensure compliance and build trust.
3.4 Follow the Shift-Left Rule
The shift-left rule refers to the practice of implementing security measures early in the software development lifecycle. It aims to minimize the costs associated with identifying and addressing issues during development. This practice also positively impacts maintenance costs, reducing them by 30%.
3.5 Use AI in Cybersecurity Solutions
Cybersecurity can be enhanced by integrating artificial intelligence technology. AI improves the ability to detect data irregularities and ensures precise actions to protect the system and its data.
- Uncovering Threats: AI can detect malicious behaviors that lead to attacks like malware and phishing with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
- Fraud Prevention: To protect personal and financial data, AI identifies irregularities in transactions and immediately blocks unauthorized access.
- Endpoint Protection: AI ensures the security of your FinTech systems against potential breaches by continuously monitoring devices across networks.
- Threat Intelligence: Analyzing global data enables AI to derive actionable insights into emerging vulnerabilities and attack methods.
- Risk Mitigation: In the event of a breach or cyberattack, AI immediately isolates the compromised systems and neutralizes all malicious actions.
AI is not a substitute for human expertise, but leveraging it can certainly strengthen your defences against various cyberattacks. It offers the speed, precision, and adaptability necessary to confront and address the increasing sophistication of cyber threats. AI serves as a proactive measure that helps prevent threats and disasters.
3.6 Regular Security Assessments and Penetration Testing
Conducting regular assessments helps identify vulnerable areas that attackers might exploit to infiltrate the system, steal data, or disrupt services. FinTech companies are required by regulations to perform comprehensive vulnerability scans to detect weaknesses in their systems. Ensure that your security testing covers the entire attack surface, including web interfaces, mobile apps, and APIs. The results of these tests should inform the security strategy moving forward.
4. Future Cybersecurity Trends in the FinTech Industry
FinTech companies need cutting-edge solutions to tackle evolving cyber threats and protect their data. Leveraging emerging technologies to develop modern, adaptable solutions can ensure both resilience and security.
4.1 AI-Driven Threat Detection
AI models play a crucial role in real-time threat detection. Advanced models help strengthen system security to prevent potential threats. Automating threat detection also enables FinTech companies to implement automated responses to possible attacks, allowing for quicker mitigation.
4.2 Zero Trust Architecture Becomes Standard
A zero-trust architecture is essential for a secure FinTech future. Adopting a “Never Trust, Always Verify” model ensures that every request, whether coming from inside or outside the organization, is thoroughly verified. This individual verification of each request reduces the risks of attacks from both internal and external sources.
4.3 Quantum-Resistant Encryption
Using an encryption mechanism is one of the best security practices to protect your data. However, using an outdated encryption technique can make your data more vulnerable. Adopting quantum-resistant algorithms will strengthen the security of sensitive information and provide long-term protection.
4.4 Biometric Authentication Expansion
Biometric authentication techniques such as voice authentication, facial recognition, and fingerprint scanning are rapidly replacing traditional passwords. FinTech firms can use these methods either as alternatives to passwords or as an additional layer of security. A multi-layered biometric security system provides robust data protection and is widely implemented by many leading firms.
4.5 Blockchain for Enhanced Data Security
Blockchain isn’t just about payments. It has cybersecurity applications as well. The tamper-proof and decentralized structure of blockchain ensures that your data, contracts, and transactions are protected against unauthorized access and alterations.
5. Conclusion
Cybersecurity is a priority in FinTech to ensure the safety of financial transactions and data. It is important to address challenges such as technological vulnerabilities, compliance issues, and data breaches to maintain customer trust. FinTech companies are primarily targeted because of the sensitive financial data stored in their systems, more so than the money stored in their digital vaults. Implementing cybersecurity best practices such as employee training, multi-factor authentication, incident response plans, encryption, and regular testing is essential to safeguarding both sensitive customer information and crucial company operations.
FAQs
What are the 5 Key Technologies in Fintech?
The most critical cutting-edge technologies that have proven to be highly useful in the FinTech sector are:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
- Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
- Big Data and Data Analytics
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Cloud Computing
What is Cybersecurity in FinTech?
Cybersecurity in FinTech refers to the practices of implementing appropriate measures to protect the sensitive personal and financial information stored within the FinTech ecosystem. By offering a range of financial services on their digital platforms, FinTech companies become prime targets for cyberattacks.






Comments
Leave a message...