
The health of online businesses depends on their ability to implement effective e-commerce security measures. According to statista, after accounting for 24% of all recorded scams in 2019, 38% of all scams in 2020 were related to online shopping. Hackers may enter a company in a matter of hours, and threats can come from anywhere. Mitigate the real threat of unauthorized access to your company’s information to prevent potential severe reputational harm and economic interruptions.
Therefore, companies should opt for the best eCommerce development services and security practices to ensure security. It will protect the business and consumers from hacking attacks. This blog discusses the best eCommerce security approach.
1. What is E-commerce Security?
To protect financial data during online purchases, eCommerce businesses must adhere to security standards. Online businesses require protection from cyberattacks in the same way that brick-and-mortar stores use safety officers or cameras to deter shoplifting. In such cases, retailers are the primary target of cybercrime.
E-commerce security is something you should learn about if you want to keep your online business safe. Here are a few security elements, shop owners need to check:
- Privacy: People who work online for businesses need to protect private customer information from people inside and outside the company. If you break your customers’ trust by violating their right to privacy, you could do a lot of damage to their personal information and your business’s image. Some things that protect privacy are antivirus software, firewalls, and encryption.
- Integrity: Judging the honesty of an online store relies on its accuracy in maintaining customer information. An online store that does well needs to keep its customer data set up to date and clean. Customers will lose faith in your business and your ability to keep their private data safe if you use the wrong information about them, like their address, contact information, or sales from the past.
- Authentication: Authentication lets you check that a customer is who they say they are and backs up what your business says. There should be proof on your eCommerce site that you sell the things you say you do. Some things you can do to make people more likely to trust your business are to post case studies and use client quotes on your e-commerce website. Before making a purchase online, customers should be asked to provide information that proves they are who they say they are. Consumer authentication can be done by using two-factor authentication or magic URLs to log people into their accounts.
- Non-repudiation: When people do business together, non-repudiation makes sure that no one can back out of their promises. The idea of “non-repudiation” is present in both in-person and online deals. Digital signatures and other methods of non-repudiation make sure that once a deal is made, neither party can back out of it.
2. Why E-commerce Website Security is a Most Important?
Online stores can’t ignore consumer fears about safety when they shop online. An important thing for most online stores should be to make sure their customers are safe and happy. Your customers will like the extra steps you’ve taken to keep your online store safe from hackers and scams. Customers are more likely to trust your business if your website has strong protection.
3. Common E-Commerce Security Threats
Following are the common e-commerce security threats:
3.1 Phishing Attacks
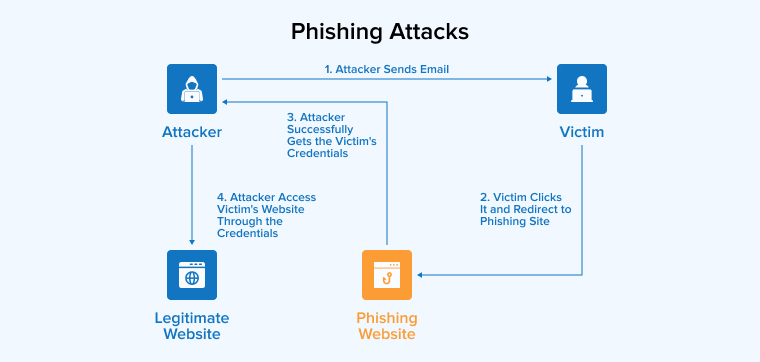
Cyber attackers use phishing as a method to trick targets into revealing sensitive information through email, text messages, or phone calls, including login credentials, credit card details, or social security numbers. Typically, phishing emails or calls may seem urgent and originate from an address or number that looks like one the victim frequently uses. Hackers, in their quest to appear affiliated with reputable organizations, go to great lengths. They even include connections to seemingly legitimate websites to deceive and mislead.
However, phishing is only successful if victims give the attackers the information they need. Users will be more on guard against identity theft if they know you’ll never contact them by email or text message to request sensitive information.
3.2 Malware & Ransomware
Malicious software, sometimes known as malware, is software with violent intentions. Email attachments or links to fraudulent websites are common drivers for its spread. Malware is software designed to steal information, obtain unauthorized access to a system, or monitor a user’s online activities once it has been triggered by a user’s action, such as clicking on a link or opening a file.
However, ransomware is malicious software that encrypts a user’s data and demands payment before decrypting them. Even if you pay the demanded ransom, there is no guarantee that you will regain access after ransomware locks you out.
3.3 E-Skimming
The practice of “e-skimming” has become commonplace on e-commerce websites as a means of collecting sensitive information such as credit card numbers and personal details. Cybercriminals steal payment details in real-time as users enter them on compromised checkout sites.
E-skimming can be mitigated by maintaining up-to-date third-party APIs and pushing security fixes to your web server frequently. Whether your e-commerce site has already been hit by e-skimming, determine whether your cyber insurance protects the damages and take away the checkout page to look into and prevent the source.
3.4 SQL Injection Attack
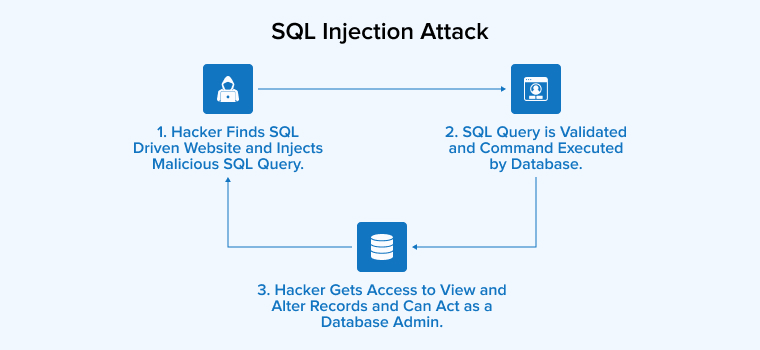
Most online stores sensitive customer data in databases, including emails, postal addresses, phone numbers, and more.
A malicious person can get information to these databases by launching a SQL injection attack. A malicious piece of code allows unauthorized users to access the whole back-end database, bypassing the authentication page in the process. The information can be stolen, changed, or deleted from that point on.
3.5 Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
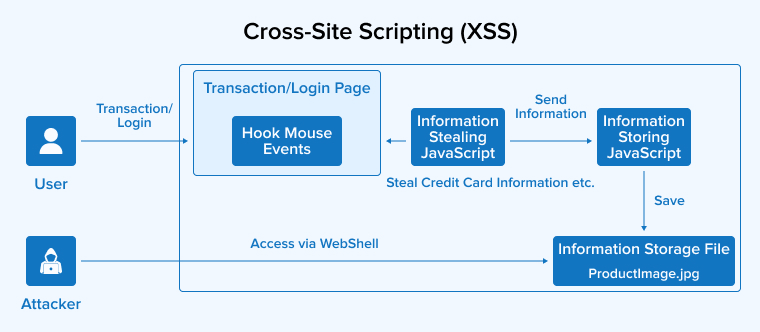
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a vulnerability that can be exploited to inject malicious code into an otherwise safe eCommerce site, posing a hazard to online retailers. When a visitor visits the compromised website, this code will launch an attack.
Client portrayal, keystroke recording, access to files, webcams, and microphones, and even identity theft are all possible outcomes of XSS.
3.6 DoS and DDoS Attacks
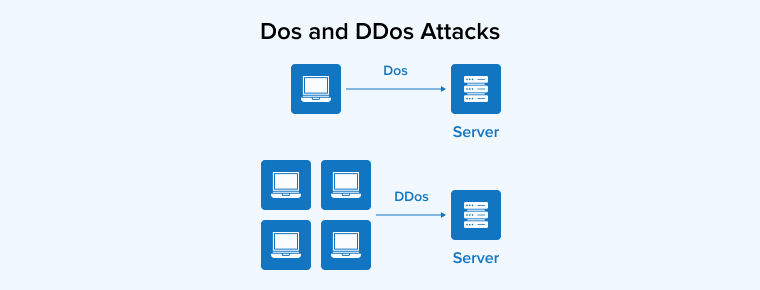
DoS attacks are an effort to crash your eCommerce store by overloading it with spam traffic, making it inaccessible to legitimate customers. A DDoS (Distributed DoS Attack) is an attack launched by a network of compromised computers. Infected machines working together as a network are called a botnet. Both attacks are hostile and designed to slow down your online store.
3.7 Brute Force Attacks
Brute-force techniques include simply figuring out the login details needed to enter the administration panel of your e-commerce site. To crack a password, hackers utilize brute-force techniques, repeatedly trying millions of permutations of characters, figures, and symbols.
If hackers can get into your internet presence, they will be able to gain entry to your website’s database, which contains sensitive information. Customers’ private and financial details and other classified data can be easily hacked and transferred.
3.8 Financial Fraud

The financial assets of both customers and stores are fair game for these types of attacks. Two frequent tactics used by cybercriminals include making purchases using stolen credit card information and then requesting fraudulent refunds.
Online fraud is especially prevalent at Buy Now, Pay Later e-commerce companies. By utilizing compromised accounts or creating new mule accounts, fraudsters can make unlawful transactions using BNPL.
3.9 Spam
Spam is an unrelated message that induces consumers to click on harmful websites. Spammers commonly utilize email to disseminate these links, but they can also do so by posting them in comments under social media posts or even through contact forms. Spam reduces a website’s safety and speeds up load times.
To avoid spam attacks, set reCAPTCHA on forms and remove irrelevant comments. To counteract spambots, ReCAPTCHAs ask visitors to enter a somewhat garbled string of numbers and characters.
Keeping your form response data clean by removing any spam comments that make it through and conducting a root-cause investigation to understand where they came from will help you find a solution.
3.10 User error
Everyone here can relate to such errors. We accidentally press a button. We modify a part of the structure that was never supposed to be modified. As soon as you try to access the site, nothing happens until you realize your data is no more there. Hence, keeping a regular backup works well here as a solution.
4. Best Practices for E-commerce Security
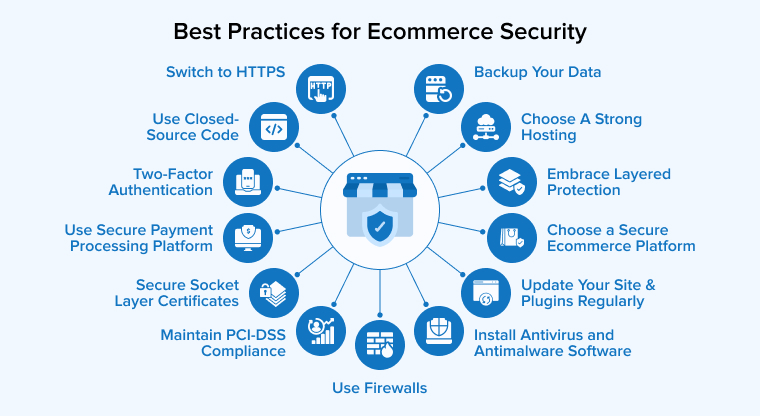
Following are the best practices for e-commerce security:
4.1 Embrace Layered Protection
Adding extra layers of protection might help you feel more secure from online threats. Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks and infected inbound traffic can be prevented by using a global Content Delivery Network (CDN). They employ machine learning to keep harmful traffic at bay.
An additional layer of protection, like Multi-Factor Authentication, can be implemented. One such instance is the use of a two-factor authentication. When a person logs in, they immediately get a text message or email with instructions on what to do next. If you take this step, scammers won’t be able to get into real users’ accounts because they will need more than just login information and passwords. Hacking can still happen, though, even with two-factor security.
4.2 Use Closed-Source Code
To decide whether to use open-source or closed-source software when upgrading your software is the first thing you should think about. People working together in public create open-source software. Anyone can help make the code better as it grows. In comparison, open source code is public, while closed source code is secret, and only a few people can see or change it.
Fewer people look at closed-source software, but the ones that do have been carefully chosen. Cutting down on the amount of programmers and other pros working on the project will help it get done faster and with fewer bugs.
With their help, you can:
- Manage the codebase’s settings.
- Limit the scope of your project and keep records of who worked on what.
- Ensure you do not overlook any problems.
- Analyze the team’s and the product’s level of quality.
4.3 Switch to HTTPS
If you’re still using HTTP old versions, you’re leaving yourself up to attackers. If you want consumers to see the green lock and the word “secured” in their browsers, you need to use HTTPS. HTTPS technologies safeguard users’ private data and the critical information they enter.
Since HTTP protocols have mostly been phased out, most up-to-date browsers will warn the user that continuing on the site might compromise their security. Some browsers even forbid the user from visiting the site entirely.
Another advantage that you gain from changing to HTTPS is greater ranking on Google’s search page as Google regards HTTPS as a ranking element. Purchase an SSL certificate from your host before initiating the change. Getting an up-to-date SSL certificate and switching to the HTTPS protocol is essential if you want to attract a significant amount of visitors.
4.4 Secure Socket Layer Certificates
Trusted authorities known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) issue certificates widely used in online commerce. These certificates establish an encrypted link between a user’s web browser and the server.
Cryptocurrency technology guarantees that any data exchanged across the browser and the server stays confidential and unintelligible, while the SSL certificate confirms the legitimacy of the eCommerce site.
4.5 Choose A Strong Hosting
You need a hosting service to keep your website’s files safe and easy to find online so that people can visit it. So, it’s very important to pick a service that can keep your eCommerce info safe and secure.
You should make sure that the hosting service you choose has security features like SSL certificates, DDoS protection, encoding, and the ability to find malware. Also, make sure that it offers backups so that you can quickly get your site back up and running if there is a security breach.
4.6 Update Your Site & Plugins Regularly
A very important thing to know about online store safety is that it is a process that never ends. To keep your online store safe, you need to be on guard all the time, make saves often, and use the latest versions of all the programs, add-ons, and themes you need.
Patch your site as soon as it comes out if you intend to leave it open to threats. But you shouldn’t run any programs you don’t know because they could make your website less safe. If you want to get your WordPress version, themes, and plugins, you should use the official WordPress installation and update pages.
4.7 Use Firewalls
A firewall and the plugins that go with it let only approved traffic into an e-commerce site. The system actively blocks any other potentially harmful links. It’s easier to find and stop attempts to break into a network when you can control the flow of data. Firewalls are very good at stopping SQL leaks, spam, and cross-site scripting threats because of this.
4.8 Install Antivirus and Antimalware Software
It is important to have a program or app that can find malware and stop it from getting into your devices, computers, and online accounts. Anti-malware software is another name for this kind of bug software. Anti-malware software should get rid of any virus that has been able to hide on your site.
4.9 Two-Factor Authentication
A user’s login attempts are verified when they input a one-time passcode (OTP), respond to a security question, or use biometric data. Microsoft claims that MFA proves great accuracy in preventing cyberattacks. Thus, implementing MFA in e-commerce platform is an excellent technique to increase e-commerce security. Use a plugin like Wordfence Login Security and a mobile app like Google Authenticator to enable multi-factor authentication.
4.10 Maintain PCI-DSS Compliance
The PCI Data Security Standard (DSS) is a set of guidelines according to GDPR(General Data Protection Regulation) for protecting credit card data from data breaches. Only use a PCI-compliant e-commerce platform to store your credit card information.
4.11 Backup Your Data
Data loss commonly occurs due to hardware failures or cyber-attacks. Periodically backing up your data is crucial to prevent permanent loss. Nobody should do your work for you. If you forget to back up your files manually, use a service that does it for you.
4.12 Use Secure Payment Processing Platform
If hackers infiltrate your company’s systems and access private information, such as customers’ credit card numbers, they can doom your business.
To keep this from happening, your business should never store a customer’s credit card information on its computers and should always make sure its payment methods are safe. You can also use a third-party system to handle funds from afar. Paying online with PayPal, Stripe, Skrill, or Wordplay is one of the most common ways to do it.
Set up your entire store to cater to the requirements of online sales. Everything in your IT stack should be completely secure, from deals to keeping records to processes.
4.13 Choose a Secure E-commerce Platform
There are many sites that work jointly to send requests to the server that is closest to the user’s location. A content delivery network (CDN) refers to this infrastructure. This is a great choice for a web store that ships all over the world. People from every corner of the world may visit and ask questions on an eCommerce site. But if the site takes too long to load, people may not come back. A content delivery network (CDN) can help speed up page loading by doing things like scaling pictures. This is because you’ll be keeping a lot of media files.
5. Conclusion
Businesses should implement several security protocols and laws pertaining to eCommerce in order to continuously prevent security concerns. Customers have to trust e-commerce to work, and that trust depends on how safe their transactions are.
Customers trust that online retailers can securely store their personal information when they knowingly and voluntarily provide it to them. We hope that these tips are useful to you.
FAQs
What are the major e-commerce security issues?
Various types of eCommerce security issues can be identified such as cybersecurity, encompassing harmful codes, unwelcome applications such as adware and spyware, phishing attacks, hacking incidents, and instances of cyber vandalism.
What are the e-commerce security strategies?
One may opt for many e-commerce security strategies by following the best security practices such as choosing a strong host, adding multi-layered security, using firewalls and SSL certificates, updating sites regularly, and more.
What are the elements of e-commerce security?
E-commerce security should have six fundamental elements, namely integrity, nonrepudiation, authenticity, confidentiality, privacy, and availability.






Comments
Leave a message...