
ML.NET is an open-source machine learning framework created by Microsoft. It enables .NET developers to build machine learning applications and custom models without leaving the .NET ecosystem. Previously, developers often relied on conventional machine learning languages and frameworks to build computational and ML solutions. Now, a leading .NET development company can deliver high-performing machine learning models with accurate predictions across multiple platforms.
Using C# and F#, you can build ML.NET apps that not only support Windows but also run on Linux and macOS. Now, integrating AI tools and software into your existing .NET applications has become easier. Read this blog to learn what ML.NET is and how to use it to build machine learning models with a real-life example.
1. What is ML.NET?
ML.NET is an open-source, cross-platform machine learning framework in the .NET ecosystem. It provides a comprehensive set of APIs to build, train, and deploy custom ML models. ML.NET also supports importing models from other platforms using Infer.NET, TensorFlow, and Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) format.
They offer a variety of models trained for tasks such as speech recognition, object detection, and image classification. Optimizing an existing machine learning model is challenging, but using ML.NET can simplify the process.
Having high compatibility, ML.NET is useful with C# and F# applications across multiple host environments like web, desktop, and mobile. The framework provides a utility called AutoML, which offers a command-line interface and built-in dataset support. It lets you quickly select an intent, train the ML model, and evaluate predictive outcomes. Using AutoML is important for your existing app to consume the new ML model.
Take a look at what a Reddit user says about ML.NET
Comment
byu/Individual-Trip-1447 from discussion
incsharp
1.1 Benefits of ML.NET
Using ML.NET to build, train, and launch .NET applications can offer many benefits. Some of the key advantages are described below:
1. Seamless Integration
The biggest advantage of working with ML.NET is its deep integration with the .NET ecosystem. It provides tools and libraries to build everything from mobile apps to enterprise-grade systems, allowing ML.NET to fit seamlessly into existing workflows. With the .NET ecosystem at your disposal, you do not need to learn new languages or frameworks to build or train machine learning models. Instead, .NET developers can use their C# and F# skills directly.
2. Scalability and Performance
Managing large volumes of data and maintaining high-performance computation can be challenging for enterprises. ML.NET addresses these challenges by providing the IDataView data structure, which enforces efficient memory usage and enables multi-threaded model execution. For these reasons, ML.NET is a strong choice for building high-traffic, high-performance solutions such as finance and e-commerce applications.
3. Model Building and Training
The ML.NET framework provides an API for training machine learning models tailored to a specific purpose or business requirements. During training, an algorithm processes existing data to discover hidden patterns. After identifying these patterns, the algorithm makes decisions or predicts future outcomes without explicit programming.
4. Robust Security Features
Similar to other applications, security is paramount in ML apps as well. ML.NET offers a wide range of security features through its connection to the .NET ecosystem. Developers can use .NET Core to implement data safety features, such as access control and data encryption, preventing unauthorized access to application data. Moreover, the Azure Active Directory and other identity providers from integrations of the .NET Core make it easy to adhere to authorization and authentication policies.
5. Flexibility and Customization
ML.NET comes with a large array of algorithms and techniques, giving developers the flexibility to choose the option that best fits their project needs. With a comprehensive set of pre-built components and APIs, ML.NET supports every operation, from classification to clustering and regression to anomaly detection, required to run during machine learning model development. To fulfill their specific needs, .NET developers are allowed to extend the ML.NET capabilities using customized ML components. It helps add domain-specific knowledge to the framework to build custom models for unique use cases.
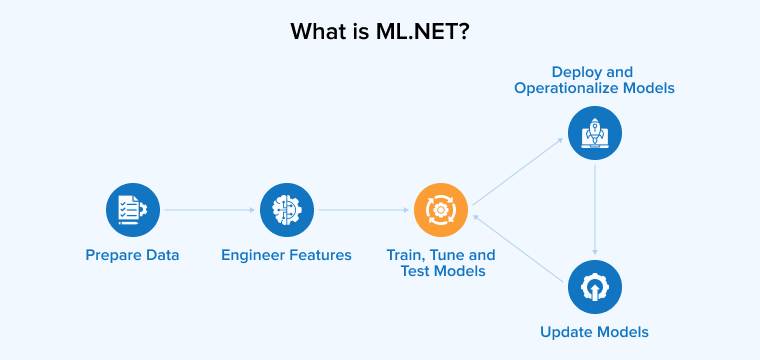
1.2 Things to Know Before Getting Started with ML.NET (Architecture)
Before initiating ML.NET development, it is necessary to understand how to build machine learning models and train them to deliver accurate results. This process is commonly divided into four stages as discussed below:
1. Initialize the Model
Multiple modules are available for machine learning, such as anomaly detection, classification, regression, and clustering. Choose the module that best suits your machine learning model development requirements.
2. Train
After choosing a suitable module, it is time to train the ML model. Provide the model with input data so it can learn to analyze information and discover hidden patterns. One simple way to do this is to create JSON files that represent daily inventory snapshots. Each JSON file contains forecasting records using fields such as:
- productId
- date
- location
- onHand
- incomingQuantity
- outgoingQuantity
- leadTimeDays
- reorderThreshold
Save one file every day and then upload the folder to your AI model so it can learn temporal patterns across locations and days. This will help the model learn relationships between incoming/outgoing flows, lead times, and thresholds. After training on this data, the model can predict future stock levels and recommend reorder quantities. If the model can understand the input data and has the capabilities to predict the results, then it can be called a trained model.
3. Prediction
Also termed as Score, prediction requires a column that matches the one used to train the model. As the name suggests, the prediction helps produce relevant results utilizing the trained model.
4. Evaluate
After training the model, comes evaluation. Assess hope your trained model performs on real-world data compared with its performance on the test set when predicting the final results.
2. Getting Started with ML.NET (Example)
You can create, train, evaluate, and consume ML models directly within .NET apps by integrating the ML.NET Model Builder into Visual Studio. In this section, we provide a step-by-step process for building an ML model. So, let’s get started by looking at what you need to start the project.
2.1 Prerequisites
- Visual Studio 2022 or a higher version
- Install the .NET desktop development workload
- Install the ML.NET Model Builder extension
You can install the ML.NET Model Builder by navigating to
Extensions > Manage Extensions > Search “ML.NET Model Builder
In this guide, we will learn to build an ML model that predicts the prices of houses based on factors like:
- Size in square feet
- Number of bedrooms
- Location (Urban, Suburban, Rural)
2.2 Step-by-Step Guide
Here, we discuss how to use the machine learning dot net framework to build, train, evaluate, and consume the ML models.
Step 1: Create a New .NET Console App
Start a new window in Visual Studio 2022 and create a new project. Next, choose the C# Console App project template.
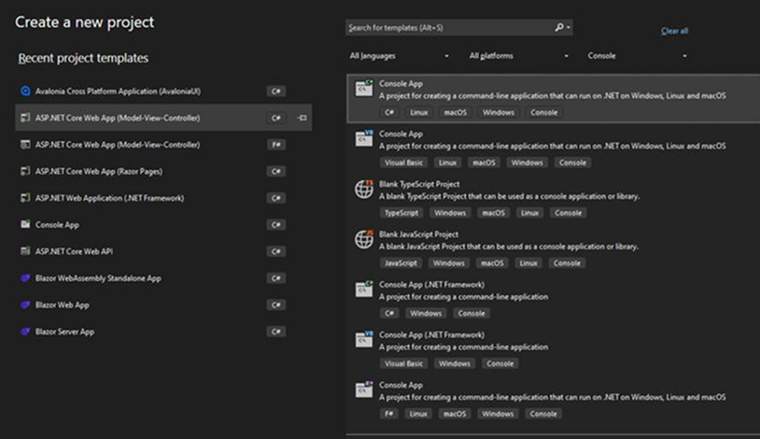
Now, change the project name to MyFirstMLApp and ensure that the “Place solution and project in the same directory” remains unchecked. Click on the “Next” button.
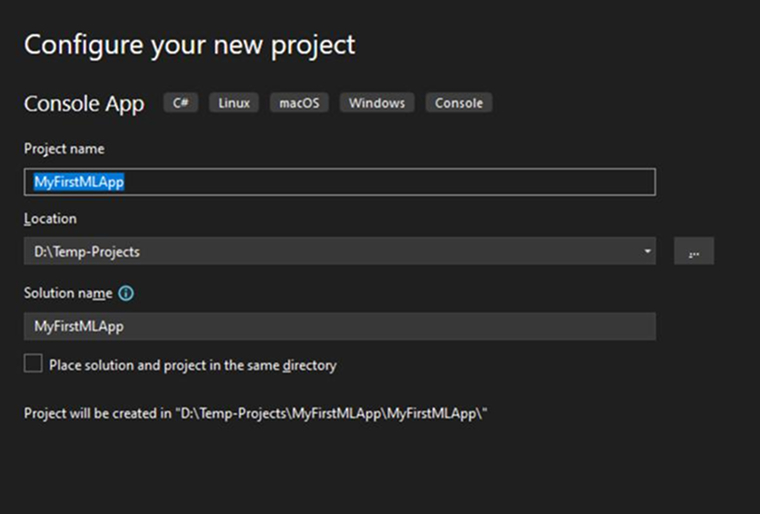
Pick the .NET 8.0 version framework (the long-term support version) and click the “Create” button. It will trigger the Visual Studio IDE to generate your ML project and load the Program.cs file into it.
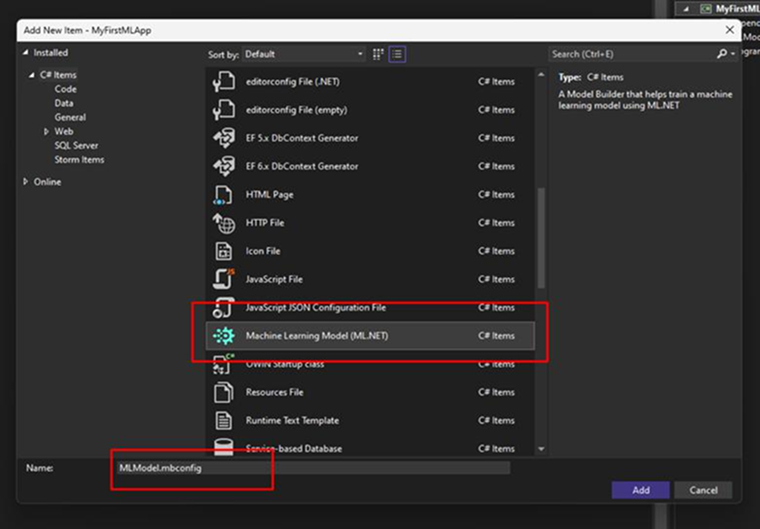
Step 2: Add a Machine Learning Model
Go to the Solution Explorer and right-click on the MyFirstMLApp project. Then,
Select Add > Machine Learning Model.
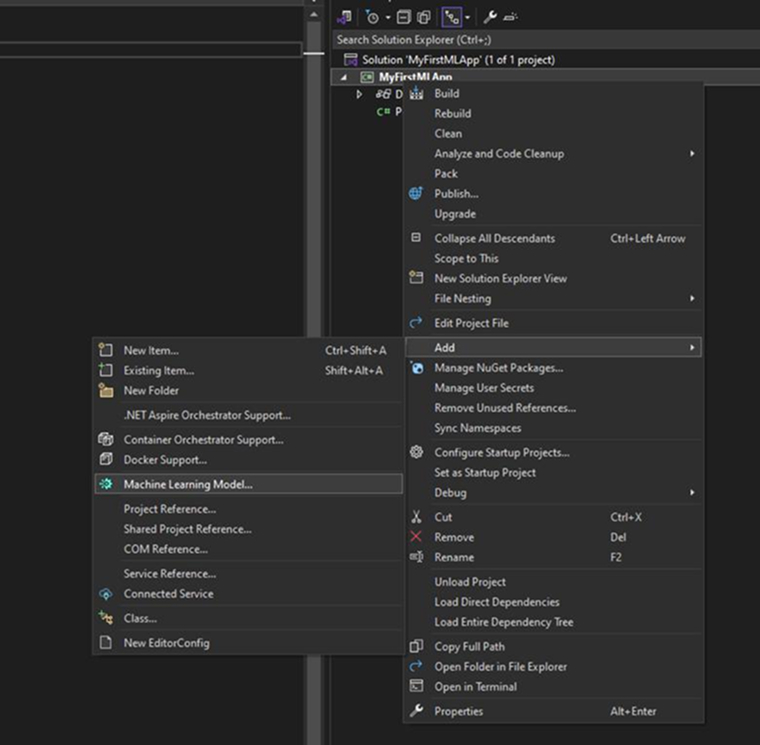
In the dialog:
- Ensure that the ML.NET option is selected.
- Rename the file to MLModel.mbcomfig.
- Click on the Add button.
Clicking the Add button adds the MLModel.mbconfig to your ML.NET solution, opening the Model Builder UI in a new docked tool window in Visual Studio.
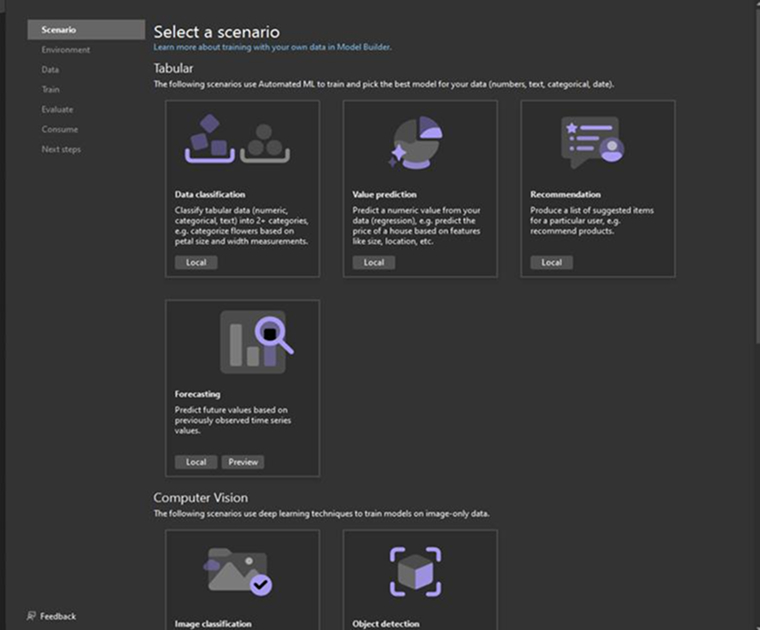
Step 3: Pick a Scenario
Select a scenario for your machine learning model, such as predicting a numerical value. Whenever there is a need to predict a numerical value like temperature or price, it is recommended to use the Regression technique. Click on the Next button, select the Local environment option, and go to the Data step.
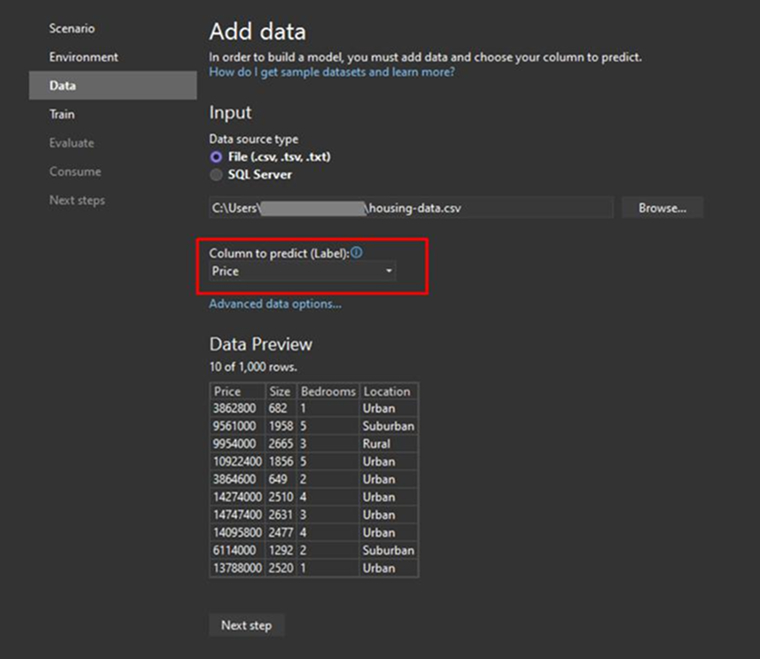
Step 4: Load Training Data
Upload the data from your local file into Model Builder. Add the housing-data.csv file. Select the “Price” as the label to predict, and click on the Next button.
Step 5: Train the Model
Set the model training time, for example, 10 seconds or 60 seconds, and then click Start Training.
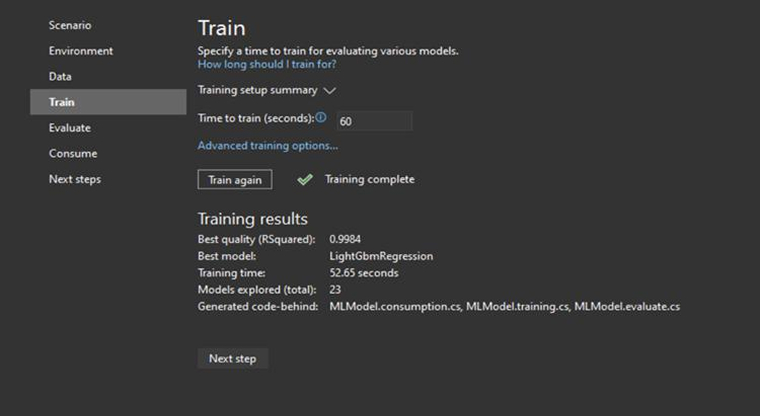
After completing the training, Model Builder will show the following:
- Algorithms with the best performance.
- R-squared and other evaluation metrics.
- The number of modules tested and the training time.
Click on the Next button.
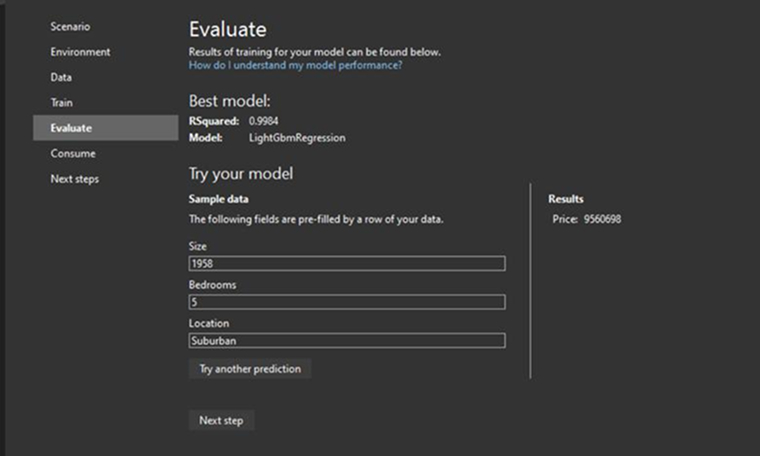
Step 6: Evaluate Your Model and Try It Out
You will be shown the best-performing algorithms and their accuracy metrics. It’s now time to assess how well your machine learning model performs. Go to the “Try our Model” section to enter the values and test the predictions. For example:
- Size: 1958
- Bedrooms: 5
- Location: Suburban
- Predicted Price: 9560698
The evaluation can be repeated by modifying the input values and testing the model prediction throughout various cases.
Step 7: Consume the Model in Your App
In the consume step, the screen displays an auto-generated code snippet for creating a sample input and obtaining a prediction. Copy this code to use it in your app.
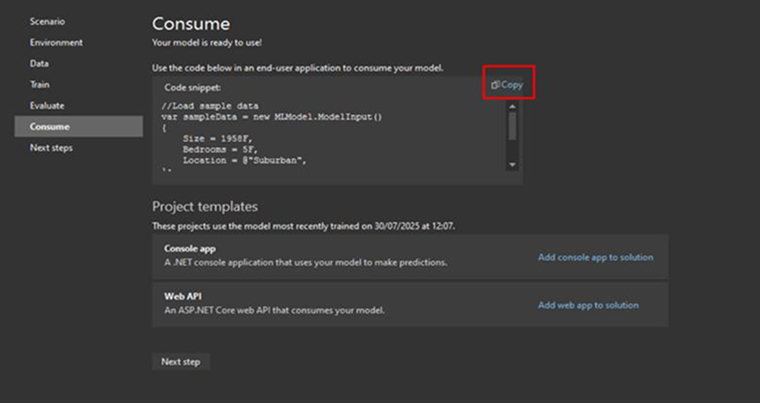
Now you have two options:
- Test the Model by adding the Console App.
- Add a Web API to integrate with the frontend apps.
Finish the Consume step by clicking on the Next button. Then open the MyFirstMLApp project and replace its Program.cs code with the copied code snippet.
Use any of the following methods to run your MyFirstMLApp project:
- Ctrl + F5
- Debug > Start Without Debugging
Depending on the given input values, you will start seeing the predictions in the model’s output.
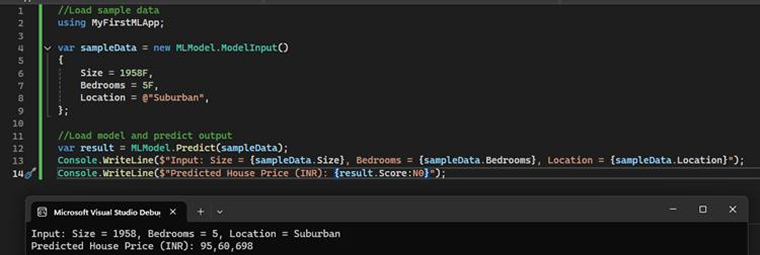
This is how we can use ML.NET in Visual Studio to create a housing price prediction model.
3. Conclusion
The ML.NET framework enables .NET developers to use their existing skills and resources to work with machine learning. There is no need to learn new languages or frameworks. ML.NET provides everything you need to add an ML model to your .NET applications. In this blog, we looked at a practical use case of the ML.NET framework. However, building, training, and deploying the ML model is not enough. After deployment, you need to continuously evaluate and retrain the model to ensure accurate results. Thanks for reading. Feel free to contact our experts in case of any query.
FAQs
Is .NET used in machine learning?
The ML.NET framework enables .NET developers to build, train, and add tailored machine learning models into their applications.
Can you do ML in C#?
ML.NET allows the use of C# and F# languages to build customized ML models without leaving the .NET ecosystem. .NET developers can reuse existing libraries, code, and tools when working with ML.NET.
What is the difference between ML.NET and LLM?
ML.NET and LLM are distinct machine learning approaches with different use cases. Classic machine learning models require domain expertise and specialized data to fulfill specific business needs. Meanwhile, LLMs are more suitable for handling routine tasks that involve unstructured data, like analyzing job applications.




Comments
Leave a message...