
Modern businesses rely on web applications to serve customers, manage operations, and grow faster. From online stores to SaaS platforms, web apps power everyday digital experiences. Web application development has changed significantly over the years. Users now expect speed, security, and seamless interaction. Businesses expect scalability and easy maintenance. As these applications become more advanced, developers need smarter ways to build them.
Web application frameworks help teams meet these demands with organised code, built-in security practices, and reusable components. It provides ready-made tools, libraries, and structure for building applications efficiently.
Understanding web application frameworks is essential for anyone planning a modern digital product. The right choice can reduce development time, improve performance, and support long-term growth. We’re here with a list of the popular front-end and back-end frameworks, explaining how they work, their usage scenarios, benefits, and limitations.
1. What is a Web Development Framework?
A web application framework gives developers a readymade structure to build websites, web apps, and APIs. It offers built-in tools that handle routine tasks such as routing, database connection, authentication, and security. Developers do not need to create everything from the beginning. The framework provides reusable components and clear patterns that keep the project organised. This structure improves code quality and makes future updates easier. It also supports scalability, so applications can grow without major changes in architecture.
Many frameworks include testing tools, debugging support, and protection against common security risks. Developers can choose front-end frameworks to design user interfaces and back-end frameworks to manage servers and business logic. By using a framework, teams reduce errors, save time, and maintain consistency across projects. It allows them to focus more on solving real business problems instead of managing low-level technical details.
2. Front-End Web Application Frameworks
They are the client-side frameworks that focus on user experience. A front-end web developer designs interactive elements such as forms, buttons, images, graphs, and navigation menus. HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are the fundamental languages for building user interfaces (UI), refining the look and feel of a web app. All the front-end web development frameworks are built on these three languages. With the help of these web frameworks, you can design attractive layouts by dragging and dropping various elements and using predefined code and components.
Many web frameworks deal with the client-side of web applications. At present, we’ll look at the five most popular front-end web frameworks.
2.1 Angular
Angular is now a globally used JavaScript web framework introduced by Google. It’s written in TypeScript. It’s highly used to develop dynamic and single-page applications.
How Angular Works?
Angular follows the MVC architecture.
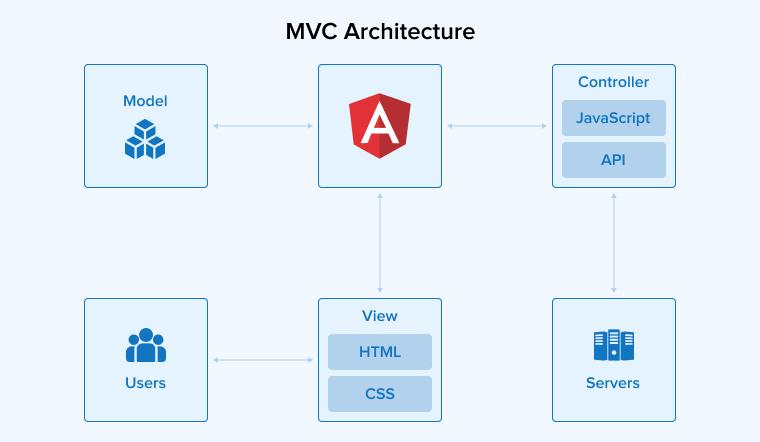
Here, the website is partitioned into three components:
- Model: It represents the data and business logic of your web application.
- View: It’s the user interface of web applications. It renders the data from the model to the user.
- Controller: It handles the communication between the Model and the View.
An Angular application is built with these eight blocks:
- Modules: A module groups related components, services, and directives into one unit. The root module starts the app, while feature modules manage specific functionality.
- Components: Angular component controls a section of the user interface. It combines template, style, and logic in one place. Developers use it to create reusable, interactive parts of the application.
- Services: Angular service stores shared logic and data for the application. Developers inject it into components to handle tasks like API calls and authentication.
- Templates: Angular template shapes the component’s user interface using HTML. It displays data and responds to user actions through bindings and directives. Developers use it to control what appears on the screen.
- Metadata: It guides how a class behaves in the application. Developers add it through decorators to define selectors, templates, and styles. Metadata helps Angular understand structure, appearance, and relationships.
- Data Binding: It links the component with the view. It updates the screen when data changes and reacts to user actions. Angular supports one-way, two-way, property, and event binding.
- Directives: Directives in Angular control how elements behave or appear in the interface. Developers use them to add, remove, or modify content dynamically. Angular includes structural, attribute, and component-based directives.
- Dependency Injection: Dependency Injection supplies required services to components automatically. Developers declare dependencies in the constructor, and Angular provides them.
When to Use Angular?
- For building a progressive web application (PWA) or a single-page application (SPA).
- For building scalable, large-scale enterprise applications with intricate user interfaces.
- To build content management systems (CMS).
- For real-time data visualisation using interactive dashboards.
Further Reading on: Why Use Angular
Pros of Angular
- Platform-independent: You can build web apps, mobile apps, native mobile, and native desktop applications.
- Reusable components: Angular provides the flexibility for building web apps with customised and reusable components.
- Smooth testing: You can easily perform unit and end-to-end web app testing.
Cons of Angular
- Limited SEO: With Angular, you have restricted SEO options. It’s because your Angular application mostly renders content on the client side.
- Learning Curve: It’s quite difficult to learn Angular and TypeScript, unlike other JavaScript frameworks and libraries.
- Extensive Boilerplate code: Even a simple Angular application contains a lot of unnecessary boilerplate code.
2.2 Vue.js
Vue.js is a lightweight, open-source, and progressive JavaScript framework for building web, desktop, and mobile applications. It’s mainly employed for developing one-page applications and web interfaces.
How Vue.js Works?
Vue.js primarily handles the View part of your web application. It draws inspiration from the Model View ViewModel (MVVM) architectural pattern. Vue.js, using its data binding characteristic, integrates the Model-View part (view instance) with the DOM (view part). Ultimately, the data you’ll observe in the View instance is nothing but the Model part.
A Vue application is a set of reusable Vue instances known as components. Components in Vue consist of a template and logic, with data flowing from the logic to the template and events directed from the template to the logic. There are two types of components: local and global.
When to Use Vue.js?
- To build single-page applications (SPAs) with complex functionality.
- You can easily build PWAs with a native app-like experience.
- You can go for building real-time tracking and monitoring systems with Vue.js.
- Taking advantage of Vue’s flexibility and modularity, one can create web applications dealing with financial data visualisation and investment analysis.
Further Reading on: What is Vue.js?
Pros of Vue.js
- Documentation Support: There are abundant learning resources for Vue.js.
- Lightweight: Easily load and install libraries like Ember (2.2.0 – 435k), Angular (2 566k), Preact (7.2.0 – 16k). etc, due to their sizes.
- Two-Way Communication Architecture: The MVVM architecture promotes two-way communication.
Cons of Vue.js
- Limited Plugins: Vue has a comparatively lower number of frequently used plugins than React or Angular.
- Community Support: Vue is a relatively new, popular, and evolving technology; hence, the number of experienced developers is limited.
- High Flexibility: Vue is a more than required flexible framework, leading to errors and irregularities in the code.
2.3 React
React is a component-based frontend JavaScript library developed by Facebook. It’s popular for building web applications with interactive and reusable user interfaces.
How React Works?
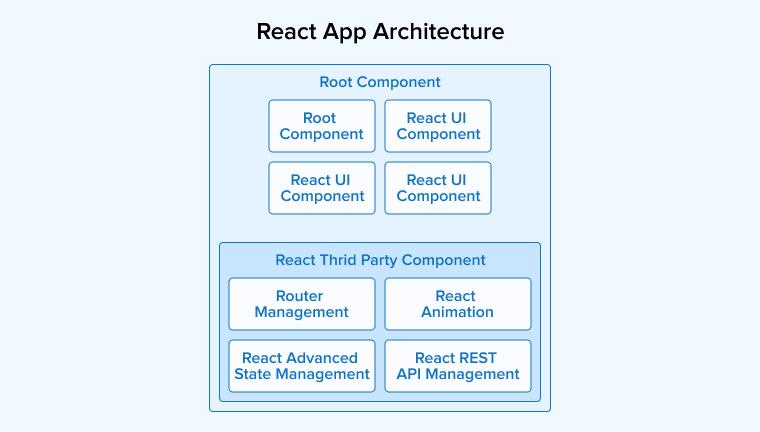
React employs a component-based architecture where your user interface gets divided into smaller, self-contained, and reusable components. For performing any modification, it does not directly manipulate the actual DOM. It then applies the necessary updates to the browser’s DOM based on the differences detected in the virtual DOM.
When to Use React?
- While developing web applications that require a high level of user interaction. React lets you focus on your interface’s view model.
- It is used to develop responsive web pages that reduce load time.
- If you want to make changes in any of the components without affecting others, React is the best choice because all the components are isolated from each other.
- You can develop native mobile applications with the help of React Native.
Further Reading on: Why Use React?
Pros of React
- SEO Friendly: React applications can run on the server, making them easily discoverable by search engines.
- State Management: Redux allows the storage and management of different application states, facilitating testing, debugging, and user experience.
- Reusable Components: You can reuse any component multiple times, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Cons of React
- No Standard Approach: React allows developers to select the methodologies according to their choice, as it lacks a proper application development strategy.
- Rapid development: React updates very frequently, thus introducing new changes and features that developers must adapt to quickly.
- JSX: Many developers find the JavaScript Extension (JSX) to be an obstacle to learning the framework.
2.4 Next.js
Next.js is an open-source React framework with excellent server-side rendering (SSR) and static site generation (SSG) capabilities.
How Next.js Works?
- Use create-next-app for developing your application.
- Next, run the development server with npm run dev or yarn dev.
- Choose between SSR or SSG based on your application’s content and needs.
- To create an optimised production build, use npm run build or yarn build.
- Deploy your application to any hosting provider that supports Node.js, like Netlify or Vercel.
When to Use Next.js?
- To build a web page dependent on organic search traffic.
- For creating content-rich websites.
- To create robust web applications like SPAs and PWAs.
- For developing SaaS products and Jamstack websites.
Pros of Next.js
- Performance: SSR reduces the page load time, resulting in a good user experience.
- SEO Friendly: Due to server-side rendering, search engines can easily locate and index your website.
- Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR): Next.js combines the benefits of static and dynamic rendering by allowing pages to be updated after deployment without a full rebuild.
Cons of Next.js
- Learning Complexity: Beginners in React may initially find it difficult to understand concepts such as server-side rendering (SSR).
- Devoid of built-in State Management: You will have to take the help of a third-party library like Redux for state storage and management, which can increase code complexity.
- Slow Dynamic Routing: Dynamic routing in Next.js may be slower due to its reliance on static routing features.
2.5 Ember.js
Ember.js is an open-source, client-side JavaScript web development framework. In present times, it is a thriving front-end web application framework.
How Ember.js works?
Ember.js, like Angular, follows the MVC architecture. It supports a built-in router for managing client-side navigation. It uses the Handlebars templating engine to define the structure and layout of your web page. The combination of JavaScript and Handlebars templates defines the reusable components in Ember.js.
When to Use Ember.js?
- You can build SPAs using Ember.js, thanks to its routing and data management capabilities.
- For developing large enterprise applications with complicated workflows and processes.
- To build real-time collaboration tools.
- To design high-performance web applications containing intricate routing.
Pros of Ember.js
- Community Support: Ember.js has an extensive and flourishing community of experienced developers for assistance.
- Quick Development Cycle: Ember.js works on a convention-over-configuration approach. Its organised structure commissions developers to completely focus on the core application development.
- Minimal Boilerplate code: You do not need to code for routing and state management, thus focusing on the main functionality.
Cons of Ember.js
- Steep Learning Curve: It’s time-consuming to learn and implement the framework.
- Performance Overhead: It can be slower for small-scale web applications due to its high complexity.
- Rigid Structure: Its convention-over-configuration principle restricts developers in their choice of coding style.
3. Back-End Web Application Frameworks
Backend frameworks are the server-side frameworks that deal with database interaction, API development, server-side rendering, etc. Many backend web development frameworks contain built-in security features to protect web apps from cyberattacks. They enhance the productivity of a backend developer, thus resulting in robust web applications.
There are many web frameworks focused on the server-side of web apps. We’ll look at the best web development frameworks that refine the backend development process in the section below.
3.1 ASP.NET Core
ASP.NET Core is an open-source cloud-based framework developed by Microsoft. It runs on the .NET Core and .NET frameworks and supports C# and F# programming languages. ASP.NET Core combines the MVC (Model View Controller) and Web API.
How ASP.NET Core Works?
ASP.NET Core is built of some major components, as visible in the diagram below.
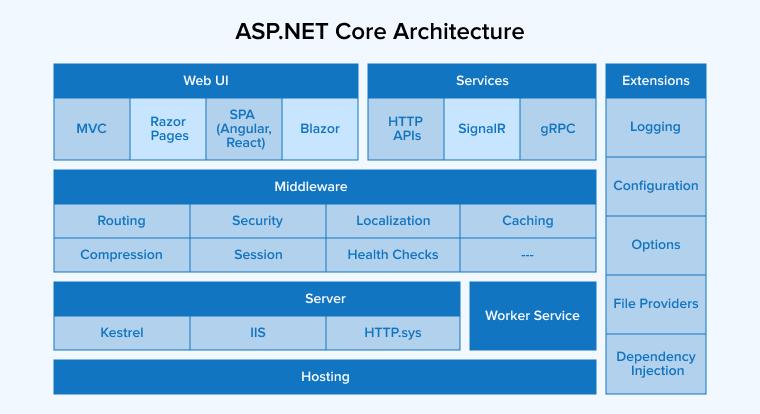
- Middleware: These components handle requests and responses.
- Dependency Injection: ASP.NET Coresupports dependency injection to enable loose coupling between objects and their collaborators.
- Hosting: It consists of a Generic host for non-HTTP workloads and a Web Host for HTTP workloads.
- Routing: Your web application can deliver actions according to the requested URL.
- Blazor: It lets you design user-engaging client-side web UI with NET.
When to Use ASP.NET Core?
- To develop RESTful services or web APIs using C#.
- When building web apps with all the modern technologies.
- To devise real-time applications like chat applications using SignalIR.
- While using Angular, React, or Vue.js, you can go for ASP.NET Core for the backend API.
Pros of ASP.NET Core
- Cross-Platform Support: ASP.NET Core can run on multiple OS.
- Backed by Microsoft: Microsoft is a well-established organisation to trust for its .NET contribution.
- Dockerization: Your web application can easily run on containers like Docker and Kubernetes.
Cons of ASP.NET Core
- Learning Curve: It requires investing your time and effort to learn this framework, even though you’re good with ASP.NET.
- Small Community: The ASP.NET Core community comprises fewer experienced developers than the .NET community.
- Limited support for older libraries: ASP .NET Core does not support all .NET libraries.
3.2 Ruby on Rails
Rails is an open-source web development framework made with the Ruby programming language. It’s among the celebrated server-side frameworks also used for front-end development.
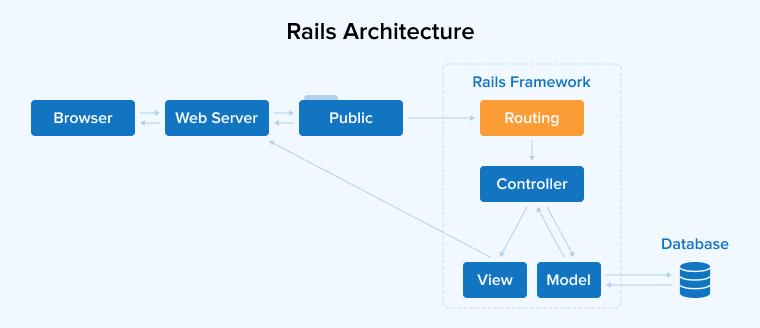
How does Ruby on Rails Work?
Ruby on Rails works according to the MVC architectural pattern.
- Model: Ruby classes interact with the database through an Active Record or dynamic Object Relational Mapping(ORM).
- View: They are the HTML files with embedded Ruby code (.erb).
- Controller: Handles the communication between Model and View.
When to Use Ruby on Rails?
- To build scalable web applications with the potential to manage high traffic and data volume.
- You can build stock marketing platforms like Coinbase and Fundrise.
- To develop prototypes and Minimum Viable Products (MVPs).
- To build APIs like RESTful APIs.
Pros of Ruby on Rails
- Secure: Rails has default security features to protect against threats like XSS, CSRF, and SQL injection.
- Free plugins: Rails has plenty of plugins, called gems, for adding additional functionalities.
- Consistent: Code is organized due to the convention over configuration principle.
Cons of Ruby on Rails
- Speed: RoR has a slower runtime speed than Node.js or Django.
- Low Flexibility: RoR has pre-built modules and dependencies, providing less space for a unique approach.
- Evolution: Overwhelming updates to the framework, including its tools and libraries, can become difficult to adapt to.
3.3 Django
Django is a prominent open-source full-stack web development framework written in Python for rapid application development.
How does Django Work?
Django’s working principle is Model-View-Template (MVT) architecture.
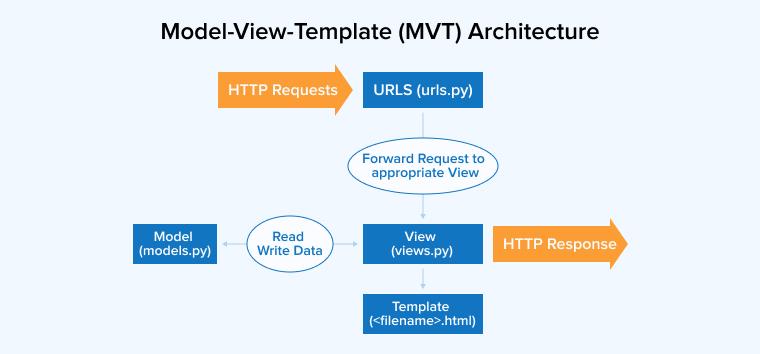
- Model: Python classes map to database tables using Object Relational Mapping (ORM).
- View: Works as a bridge between Model and Template.
- Template: It consists of Django template language and a template engine to process the final output.
When to Use Django?
- When you need a web app and an API backend within the same codebase to conform to the DRY principle.
- Your web app requires scale-up/down at any time.
- If you plan to integrate AI/ML with your app.
- Avoid database queries for working with databases.
Pros of Django
- Development Speed: Django is known as the “web framework for perfectionists with deadlines.”
- Versatility: It’s compatible with almost all front-end frameworks.
- Maintainability: It follows the DRY principle to get rid of unnecessary duplication.
Cons of Django
- Monolithic: It has huge built-in functionalities, resulting in low flexibility.
- Complexity: It does not qualify for building small applications due to performance overhead.
- Learning Curve: A beginner in development without a Python background may find its structure difficult to understand
3.4 Laravel
Laravel is an open-source backend development framework written in PHP. If you’re well-versed in HTML, Core PHP, and Advanced PHP, Laravel is easy to learn. It incorporates underlying characteristics of CodeIgniter, Yii, and programming languages like Ruby.
How Laravel Works?
Laravel works according to the Model View Controller architecture. The working of the Laravel framework is illustrated below through the functional diagram.
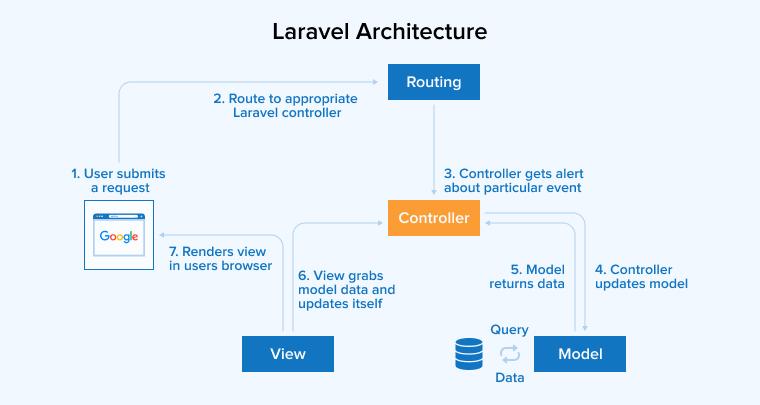
Middleware filters HTTP requests before passing them to the Model. The Blade Templating Engine facilitates seamless integration of PHP code into views. The ORM tool Eloquent facilitates smooth database access with object-oriented syntax.
When to Use Laravel?
- You can create a lightweight app with a microservices architecture using Laravel.
- You can build customized content management systems or readymade CMS using Laravel CMS packages like Winter CMS.
- You can build animated gaming applications like Open Dominion.
- The Swiftmailer library helps you build email and chat-based web applications.
Pros of Laravel
- Security: Laravel provides data encryption and CSRF tokens to boost application security.
- Artisan: This command-line comes with built-in commands and allows you to create your own custom commands.
- Migrations: It helps in tracking modifications in the database.
Cons of Laravel
- Frequent Updates The development process are challenging for the development teams.
- Dependency Management: Laravel depends on third-party packages for adding supplementary functionalities.
- Performance: The features of the framework reduce the performance of web applications.
3.5 Node.js
Node.js is the top web development framework for building server-side web applications utilizing JavaScript. It executes JavaScript code beyond the web browser.
How does Node.js Work?
Node.js employs the “Single-Threaded Event-Driven” architecture. The working principles behind the above architecture are:
- Asynchronous
- Non-blocking I/O
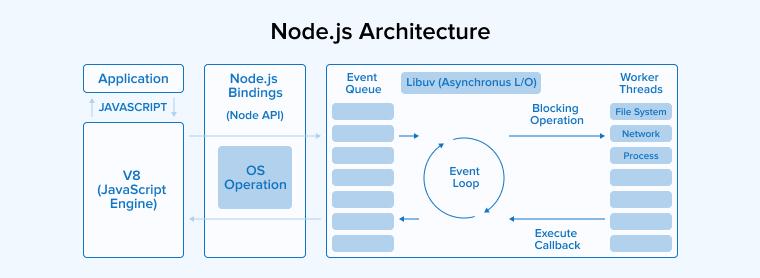
- The blocking or non-blocking client request goes to the server.
- The request is retrieved and appended to the event queue.
- From there, the requests go to the event loop one by one.
- If the request is small, the event loop executes it. Otherwise, it passes that request to the thread loop.
- The thread pool, on receiving the request, executes it and passes the response back to the event loop.
When to Use Node.js?
- You can build real-time collaboration tools harnessing the framework’s asynchronous and event-driven architecture.
- Node.js facilitates building complete SPAs.
- Due to less memory and resource consumption, private and public IoT systems can be built.
- For developing microservices and APIs.
Pros of Node.js
- High Performance: Node.js processes multiple requests simultaneously and performs non-blocking I/O operations, resulting in significant performance.
- Active Community Support: You can access plenty of documentation and tutorials related to Node.js through open-source projects.
- Cost-Effective: Node.js can be used for both frontend and backend development, saving time and money.
Cons of Node.js
- Unstable API: APIs in Node.js are frequently updated, resulting in incompatibility with the backend.
- Limited Library Support: Node.js has fewer libraries compared to other frameworks, and some existing libraries lack certain features.
- Callback-based Programming Model: The extensive use of callback functions can lead to callback hell.
3.6 Nest.js
Nest.js is a progressive and lightweight framework built on the Node.js runtime environment. Developers use this framework to make server-side web apps with the help of JavaScript or TypeScript.
How Nest.js Works?
A Nest.js web application is composed of modules. Nest.js works according to three principles:
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
- Functional Programming (FP)
- Functional Reactive Programming (FRP)
The three-tier architecture is as follows:
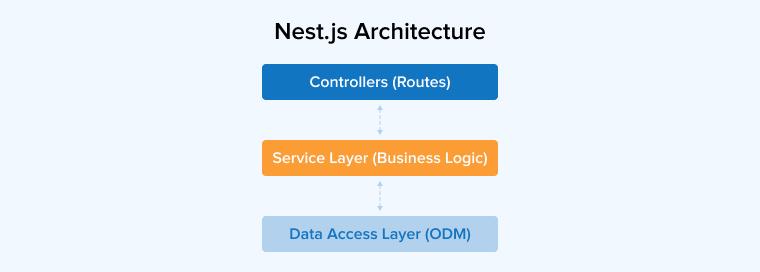
- Controllers: They receive incoming requests and define the routes.
- Service Layer: The service layer corresponds to the application’s business logic, for example, all the database management operations.
- Data Access Layer: It provides access to data stored in persistent storage.
When to Use Nest.js?
- When implementing a microservices architecture. Nest.js facilitates smooth communication using transport layers.
- For building complex GraphQL schemas.
- To develop real-time applications leveraging its event-oriented architecture.
- To enforce intricate authentication and authorisation by taking the help of the Passport.js library.
Pros of Nest.js
- Extensible: You are free to use other libraries in your development.
- Versatility: You can develop all kinds of server-side applications.
- Easy Testing: Application testing becomes simple due to dependency injection and modular architecture.
Cons of Nest.js
- Boilerplate code: You may need to write boilerplate code due to TypeScript.
- Unfit for Small Applications: The modularity of Nest.js can raise unnecessary complications.
- Learning Curve: Developers with no Angular background may find Nest.js difficult.
3.7 Express.js
Express.js is a minimal and lightweight Node.js framework. It is a free and open-source backend development framework.
How Express.js Works?
Like Node.js, Express.js employs an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model. When a user sends a request to the HTTP server, you define routes regarding the response from the server. The server handles all incoming requests in the callback. Different types of Middleware act as middlemen between the request and the response. The templating engine renders HTML pages from the server side.
When to Use Express.js?
- To build APIs connecting SPAs.
- Express.js’ event-driven characteristic is a best fit for real-time applications.
- For developing content management systems like Calipso.
- To build social media platforms where the middleware authenticates the users.
Pros of Express.js
- Speedy: Its minimalistic nature accelerates the application development.
- Platform Independence: Express.js applications can run on all Node environments.
- Rich Ecosystem: Express.js has a huge support of third-party middleware and plugins.
Cons of Express.js
- Learning Curve: Understanding Middleware can be difficult as it’s quite complex.
- No Strong Typing: No compile-time checks result in errors in your code.
- Restricted Built-in Features: Express is behind in terms of many more advanced features than other frameworks.
3.8 Spring
Spring is an open-source Java framework for building modern enterprise Java applications.
How Spring Works?
Spring operates on two principles:
- Dependency Injection(DI)
- Aspect-Oriented Programming(AOP)
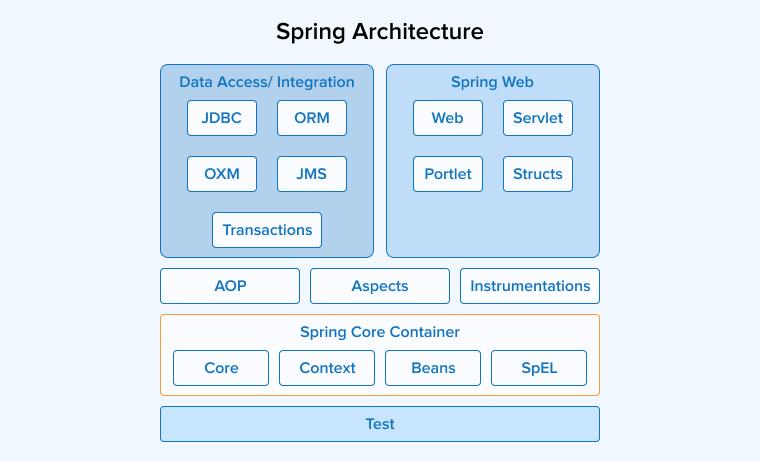
There are four types of modules involved in the working of Spring:
- Core Container: Provides the fundamental Inversion of Control (IoC) container functionality through interfaces like BeanFactory and its more advanced implementation, ApplicationContext.
- Data Access/Integration: Supports integration with databases and various data access technologies.
- Web: Supports web application development, including RESTful services.
- Miscellaneous: Includes additional modules that provide extra features, such as Spring Security, Spring Batch, and others.
When to Use Spring?
- Spring MVC and Spring Boot allow you to develop web apps with minimal or no configuration.
- API development with the help of RESTful web services.
- You can use Spring Batch for making batch-processing applications.
- For implementing microservices architecture using Spring Boot and Spring Cloud.
Pros of Spring
- Highly Adopted: It is the most popular framework for developing feature-rich Java applications.
- Testing: Dependency Injection promotes unobtrusive testing.
- Portable: You can select server-side in the web/EJB app and client-side in the Swing app business logic.
Cons of Spring
- Complexity: To operate Spring, you need to be highly skilled and experienced, especially in Java.
- Configuration Overhead: You need to configure things like dependencies, beans, transactions, etc.
- Overloaded Features: You can get confused in irrelevant modules, which can make development complex.
4. Final Words
Web frameworks provide tools for developers to build web applications across different platforms with ease. With the advent of Artificial Intelligence, all the frameworks are continuously evolving to integrate the arising technologies like blockchain, AR, VR, etc. Choosing any framework requires a careful evaluation of numerous parameters. Though they significantly help in the development process, a good amount of skill is required to implement them properly.





Comments
Leave a message...