
In the last ten years, the healthcare software and app development business has been propelled by technological advancements that have led to new methods of illness detection, prevention, and treatment. This would not have been possible without the rapid development of AI-driven technology and the digitalization of healthcare operations in reaction to harsher global challenges and the growing demand for more readily available and high-quality medical treatment.
This whole post is for you, if you’re interested in examining the technological advancements driving the healthcare industry towards digitalization. Let’s take a peek at the essential healthcare technology trends that have the ability to revolutionize healthcare systems.
1. Top Digital Healthcare Technology Trends to Watch
Here we discuss the most emerging healthcare technology trends in the industry. Keep reading.
1.1 Impact of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Let’s see how artificial intelligence contributes Healthcare.
1. AI in Diagnosis & Drug Development
Outside of pandemic treatment and response, AI has many other potential uses. Artificial intelligence is tremendously useful for speeding up the decision-making and data-processing phases. Machine learning is incredibly useful in the healthcare sector, particularly for improving the speed and accuracy with which new drugs may be discovered and diagnoses can be made.
AI is assisting in the analysis of CT images for the detection of pneumonia in patients being treated for COVID-19. Microsoft’s Project InnerEye is an AI system designed for use in radiotherapy. Due to this, 3D patient contouring may be done in a matter of minutes rather than hours. It’s possible to view the source code for the project on GitHub. Microsoft’s Project Hanover is an artificial intelligence system built to organize the content of PubMed’s biomedical research publications. Because of this, cancer diagnoses may be made faster, and the right treatments can be chosen for each individual patient.
2. AI in Mental Health
Advances in artificial intelligence have ramifications outside the realm of medicine. In order to monitor trends and monitor mental health in relation to the COVID-19 epidemic, researchers from MIT and Harvard have used machine learning. Using an AI model, scientists combed through hundreds of Reddit posts and discovered that discussions of depression, anxiety, and suicide thoughts had nearly quadrupled over a given time frame. This might drastically improve our knowledge of the emotional well-being of broad groups of people.
It is possible to utilize AI to uncover the signs of diseases that are brought on by chemical shifts in the brain and which manifest themselves in a variety of psychological symptoms. Dementia is one example of such a condition. Alzheimer ‘s illness is one of the most prevalent kinds of dementia, and it is marked by difficulties in communication, thinking, and remembering. There is a wide variety of mental symptoms associated with these disorders, and oftentimes they progress for decades before anybody notices anything is wrong. But, one of the most successful strategies to treat dementia, and even reverse the underlying cause in certain circumstances, is through early identification.
Recent developments in deep learning and AI audio processing have made it feasible to analyze human speech for indicators of dementia. To put it another way, a speech processing AI model can be programmed to distinguish between normal speech and the speech of a dementia patient. Alzheimer’s disease can be detected years before the onset of severe symptoms using such models for screening or self-checking.
3. AI Improves Cancer Diagnostics
Extracting tissue for examination (as in a biopsy) was the only surefire way to diagnose cancer for decades. On the other hand, this doesn’t offer all of the details of the organ tissue. To detect cell mutations, modern histopathology techniques use computerized imaging of the afflicted region. Utilizing WSI, or Whole Slide Imaging, pathologists may look at considerably greater sections of human bodies all at once.
The huge image resolution makes working with WSI seem difficult. Although WSI scans provide a wealth of information, inspecting them thoroughly requires a lot of time spent carefully zooming in and out and scrolling from region to area. Artificial intelligence programs that can analyze WSI by use of camera input and specialized neural networks have therefore emerged. The diagnosis process may be sped up by using this method, which helps medical experts by identifying the area of interest where probable cancer cells can reside.
It would appear that the AI method for WSI analysis is not only effective, but also requires little in the way of setup prior to actual analysis. This helps spread its use throughout the healthcare sector as WSI scanners become commonplace in hospitals and clinics.
The increase in computing power spurred on by artificial intelligence has a profound effect on healthcare. Automatic help in the workplace, medical operation optimization, statistical imaging, etc., have all contributed to greater diagnostic accuracy, making it likely that AI will continue to dominate emerging trends in healthcare.
Global Healthcare Services Market size was valued at USD 10.30 Trillion in 2021 and is projected to reach USD 21.06 Trillion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 8.27% from 2023 to 2030. – Verified Market Research
At a CAGR of 20.41% between 2022 and 2030, the worldwide internet of things (IoT) in health industry is projected to increase from its 2021 valuation of USD 180.5 bn to approach roughly USD 960.2 bn by 2030.
By integrating virtual reality (VR) technology with artificial intelligence (AI) diagnostics, various wearable devices with the help of AI have the ability to improve the accuracy of a variety of diseases, including speech disorders, cerebrovascular disease, downs syndrome, Parkinson’s disease treatment, neurological conditions, cancer, and myasthenia gravis, can be diagnosed and treated.
1.2 Internet of Medical Things
In terms of health technology developments in 2022, the widespread use of IoMT devices would be the simplest to anticipate.
At a CAGR of 20.41% between 2022 and 2030, the worldwide internet of things (IoT) in the health industry is projected to increase from its 2021 valuation of USD 180.5 bn to approach roughly USD 960.2 bn by 2030. – Published in Globenewswire.
Higher costs in healthcare are another area where IoMT might help in cost savings. IoT healthcare may reduce healthcare spending by $300 billion annually, according to a Goldman Sachs analysis.
Telemedicine is cost-effective because it allows for consultations to take place outside of healthcare organizations, where they are not needed. Healthcare IoT can also improve organizational effectiveness. Workflows may be streamlined and automated just like in any other computerized industry. For instance, having access to up-to-the-minute information about all medical supplies and machinery improves the effectiveness of healthcare management. Digitally tagging medications for tracking purposes can aid in the battle against the sale of fake medications.
Yet, IoMT gadgets are important in healthcare administration. They are able to provide medical attention to outlying communities that typically lack access to specialists because of financial constraints. Consistent in-home visits are a boon to patients who are unable to leave their houses for appointments. These days, practically every routine test may be performed on a portable point-of-care device, with the findings being sent wirelessly to healthcare organizations.
As per the report by Fortune Business Insights, The internet of medical things (IoMT) market size was USD 41.17 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow from USD 30.79 billion in 2021 to USD 187.60 billion in 2028, at a CAGR of 29.5% during the 2021-2028 period. – Published in Globenewswire
1.3 Cybersecurity
The healthcare sector was targeted by hackers at a time when it was more vulnerable than it has been in decades. There have been many attempts by hackers to compromise the COVID-19 vaccination.
There have been many reports of assaults on vaccination databases, including at Pfizer, BioNTech, and the European Medicine Agencies. Ransomware attacks have increased healthcare provider awareness of cybersecurity architecture in the United States.
VMware Carbon Black, a cybersecurity firm, revealed that in 2020, its healthcare clients were the target of 239.4 million potential cyberattacks.
Among the different types of healthcare software, cybersecurity and data protection software stand out as the most closely watched. After a slew of assaults and data thefts in the healthcare industry, it’s clear that spending more on data security is essential.
A growing digital healthcare business naturally needs a secure architecture to safeguard patient data and other sensitive information. This bodes well for the cybersecurity industry in healthcare, as a growing number of healthcare facilities are anticipated to hire outside help.
1.4 Telehealth
In order to provide medical treatment to patients, telehealth services make use of electronic devices, including laptops, cellular phones, and tablets.
Medical professionals were forced to adapt swiftly as the number of patients seen in person dropped as a result of the epidemic. More than 43% of Medicare primary care appointments were made through telehealth in April 2020.
Despite the worldwide distribution of COVID-19 vaccinations, telemedicine appears to be here to stay. Fortune Business Analytics projects that the telehealth industry will be worth more than $185 billion by 2026.
1.5 Focus on Mental Health
Mental health issues have escalated worldwide due to the COVID-19 pandemic. According to the World Health Organization, around 1 billion people live with a mental health condition, with over 75% of them living in low-income countries without access to treatment. Every 40 seconds, someone dies by suicide, and half of all mental illnesses begin by age 14.
Remote Patient Monitoring(RPM) advancements in telemedicine have made it possible for people to receive professional mental health care without putting their physical health at risk.
McKinsey and company report that since February 2020, telemedicine use has increased 38-fold and is now stable. Mental health treatment makes up the vast majority of distant visits. Thus, this cutting-edge medical innovation of 2022 has risen to prominence.
In addition, persons with chronic diseases, allergies, and other psychological disorders now have access to patient care because of the advancements in healthcare technology. Prior to this, they were unable to visit a doctor because of a lack of funds, a reluctance to seek treatment in public, and racial discrimination. But now, all they require is access to the Internet and to set up a means of communication.
1.6 Regulations and Risks
When it concerns legislation and requirements, the on-demand economic system presents unique challenges. Most notably, the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom determined that Uber drivers should not be deemed “self-employed” but rather Uber workers. This increases Uber’s costs significantly because drivers are now eligible for perks like subsistence wages and paid vacation.
Like the United States, the European Union is having trouble drafting effective laws to monitor the on-demand healthcare market. According to the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work, most digital platforms have prioritized expansion over adherence. As a result, on-demand services have to wait in the dark until laws are hammered out.
Operating an on-demand business comes with substantial legal dangers. The introduction of new rules might destabilize an otherwise successful business model by necessitating the incurrence of unexpected costs. However, protecting the rights of employees is crucial.
1.7 Remote Patient Monitoring and Wearables
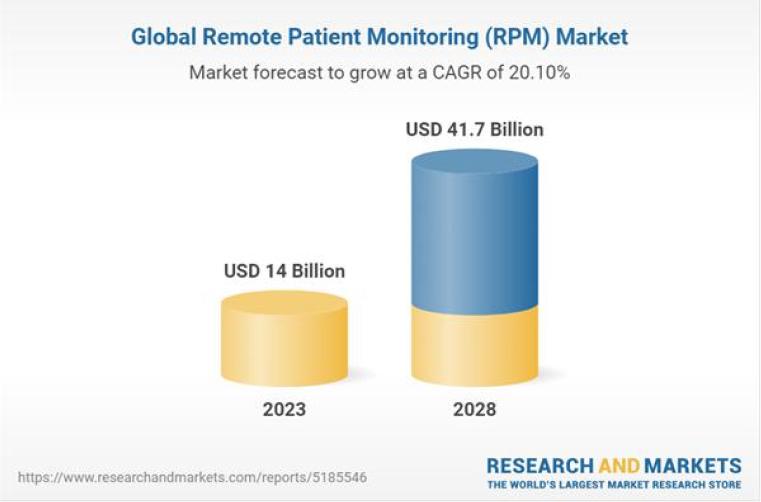
A stronger healthcare system may be achieved when healthcare providers are able to observe patients without depending on the healthcare facility. It is possible that the implementation of remote patient monitoring as a type of IoMT will have far-reaching consequences for the healthcare system. Remote monitoring has the potential to revolutionize the management of chronic conditions including hyperglycemia, cardiovascular disease, and asthma.
Accessibility to real-time data from interconnected health instruments on a routine basis has the potential to be utilized in preventative healthcare settings. For instance, a clinician can be notified of a suspected cardiac arrest by use of wearable electrocardiogram equipment. Furthermore, having access to this kind of real-time data might aid in the management of chronic illnesses by encouraging the adoption of healthier practices.
Wearable devices that may be worn as part of a user’s everyday routine are more widespread than you would expect. In recent years, consumer-grade sensors have improved to the point that they may be relied upon for serious medical applications. If you suffer from atrial fibrillation, for particular, you may use Apple Watch’s electrocardiogram (ECG) capability to keep tabs on your health. Wearables that collect data useful for scientific research are becoming increasingly popular.
With the usage of an electronic blood pressure cuff, one may continually and reliably transmit measurements of their hypertension and pulse to their healthcare provider. Edible detectors in smart pills report back to physicians or caretakers on whether or not a patient is taking their prescription as directed. Since research has revealed that barely half of the chronic illness medicine is taken as advised, the importance of this problem increases.
1.8 Billing and Claims
The epidemic accelerated the necessity to automate healthcare operations and also ushered in telemedicine. When dealing with organizational duties, this is crucial.
Just about everything, including billing, Medicaid, and so on, must be done online, regardless of whether an in-person consultation with a doctor is required. There is a significant role played by IoMT gadgets and compatible systems.
Consider an e-Prescription system, which is a type of interoperable electronic health record (EHR) or electronic medical record (EMR). Medical professionals and other medical staff can view patient insurance information using a streamlined e-Prescription system. Drugs provided to patients can be checked against the system to see if they are authorized by their insurer. Everything is done mechanically now. The patient should only take up the medication once all the necessary documentation, especially medical coverage, has been digitally validated.
1.9 Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Emerging healthcare technologies include the use of virtual reality and augmented reality. Surgical residency programs are a prime example. Virtual reality (VR) education eliminates the need for hospitals as a teaching venue for medical practitioners.
Virti, located in the United Kingdom, collaborated with the National Health Service (NHS) to provide training for frontline workers throughout the epidemic. There was an urgent need to recruit additional staff to work in ICUs, and these individuals needed rapid education on how to utilize personal protective medical equipment, how to go around the ICU, how to operate ventilators, and how to communicate with patients and their relatives. Dr. Alex Young, the company’s founder and CEO, claims that the platform employed tailored prediction technologies as well as gamification and various content forms to captivate users and embed information.
Virtual reality technology has also been shown to be an effective means of medical staff training. Retention is purportedly increased by 75% (compared to 10% with more conventional approaches), and skill fading is reportedly reduced by 52%. Virtual reality software has the potential for usage in healthcare settings. Virtual reality (VR) software and healthcare technology may be used in a variety of exercise rehabilitation settings, for instance.
With so many potential uses, virtual and augmented reality are quickly growing in popularity. Investing in it makes economic sense for a precise medical industry, which may greatly benefit from increased productivity.
1.10 Big Data and Analytics
Recent years have seen an incredible explosion in the volume of healthcare data collected as a result of the ongoing technology revolution. Massive (anonymized) data sets may be used to determine medical patterns and digital health solutions, opening the door for researchers to find previously unknown connections between, say, population demography and health and the state of the economy or the environment.
When researchers get access to a large enough dataset, they may transform it into Big Data, which can then be used by artificial intelligence and machine learning systems to gain insights into human health that have previously been unavailable. Analyses of this kind can pave the way toward better strategies for preventing and treating chronic diseases. The use of analytics to combat the spread of COVID-19 is a particularly ingenious application of big data’s potential in preventing global pandemics.
Obviously, millions of patients’ records aren’t necessary to draw any useful results. An electronic health records (EHR) system is the most common piece of healthcare software used for data collection and analysis.
1.11 Wearables and Mobile Apps
The popularity of wellness applications and remote health monitoring will continue to grow. There are a number of high-quality (and countless amateurish) health and fitness applications available for download from the GooglePlay and iTunes stores.
Some of these smartphone applications may coordinate with wearables like pulsometers and fitness bands to report or evaluate health problems like heartbeat, body temperature, hypertension, and other metrics obtained by the detectors implanted on the bodies.
1.12 Cloud Computing
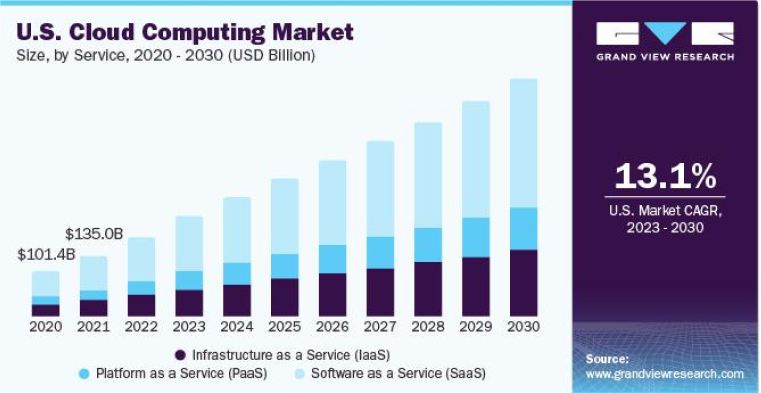
In healthcare, cloud computing reduces capital and operating costs by providing on-demand disk space. It improves productivity while decreasing wasteful spending.
Sharing medical information, automating back-end processes, developing and maintaining telehealth software are all made much simpler with cloud computing.
By 2025, the healthcare cloud computing market is projected to grow from its 2020 level of USD 28.1 billion to a whopping USD 64.7 billion by 2025 at a CAGR of 18.1%. – Health Cloud Solutions.
To better tailor patient care plans, electronic medical records (EMRs) may now be stored on the cloud and analyzed with cloud computing’s robust analytic capabilities.
1.13 Cloud Migration
The transition to healthcare cloud services has begun in earnest, and it will continue to expand. MarketsandMarkets predicts that the worldwide healthcare cloud computing industry will grow from an anticipated $34.9 billion in 2022 to a total of USD 84.9 billion by 2027, a CAGR of 17.8%.
It is the answer to many of the most pressing problems in service delivery, such as patient record keeping, telemedicine, and access for those with limited financial resources. Global healthcare professionals are increasingly turning to cloud computing to streamline the storage and distribution of electronic messages and patient data in real-time.
If your call centre is still using antiquated technology, migrating to the cloud may be the best way to boost customer engagement and simplify problem resolution. The capacity of many organizations to provide high-quality treatment at low cost and keep patients engaged is hampered by antiquated healthcare infrastructures. By migrating to the cloud, businesses can build a cognitive AI and automation-powered omnichannel contact centre system that is both safe and regulatory and can be used in tandem with other components of a cohesive ecosystem to provide a superior experience for customers.
According to the HIMSS (Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society) report, Cloud services are an expansion of a healthcare agency’s network infrastructure. There shouldn’t be any trouble with connectivity scaling up when more programs are migrated to the cloud.
1.14 Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
As per the Pan American Health Organization, The world will be short of 12.9 million healthcare workers by 2035, few individuals can afford to travel for in-person medical visits, as reported by the World Health Organization (WHO). The COVID-19 epidemic has made matters much worse. Robotic process automation (RPA) technologies have the potential to address healthcare’s inefficiency problems if they are used on a large scale.
The advent of RPA-enabled bots is a major step forward for healthcare IT. Precise automation, reduced costs, optimized workforce, and even transformative changes are all possible for healthcare providers thanks to the technology available today. If a patient inputs their clinical signs into an AI system, they will get a more precise diagnosis than they would from a regular search engine.
In short, RPA technology advancement has brought human-like robots into the healthcare industry. They can recognize screenwriting, accept data input, and carry out previously established tasks, among many other things. Data management, consultation booking, insurance claims, optimal treatment delivery, and hospital administration are just a few of the many modern healthcare applications for robotic process automation.
1.15 Social Determinants of Health (SDOH)
While there are many exciting developments in healthcare that deserve attention from both patients and medical professionals, these trends cannot address the root causes of health disparities in America.
As a result of SDOH, there are significant gaps in health care provision between socioeconomic groups. If there isn’t a supermarket in a neighborhood, for instance, residents may have trouble obtaining nutritious foods, and if there aren’t any hospitals nearby, those in need may be untreated. These sorts of situations raise the danger of being sick, but also the danger of dying as a result of disease.
1.16 Organ Care Technology & Bioprinting
The technology underpinning bioprinting is 3D printing, which we discussed at length in the article Explore the Industrial Uses of 3D Printing. External prosthesis, cranial or orthopedic implants, and individualized airway stents are all examples of medical products that might be made using 3D printing technology. Yet it has also proven useful in surgical planning, and has been used for anything from routine open-heart operations to the groundbreaking Cleveland Clinic face transplant.
The Wexner Medical Center at The Ohio State University is developing a method that they hope may one day enable robotic surgery technology to print human cells, bones, and possibly even organs within individuals’ bodies. An opportunity to save the lives of those who are battling cancer. In this way, we get to the realm of bioprinting, which includes the possibility of 3D-printed human organs. Although it may not seem possible at first, testing of the concept has begun. Ears, eyes, bones, and skin are some of the organs now being studied for 3D bioprinting in medical settings.
2. Future of Healthcare Technology
The medical sector as we know it will be completely transformed by future trends. Advancement, data, and patient-centered care are converging to pave the way for a shift that will shake the foundations of healthcare as we know it. Top healthcare technology trends are carving a road toward improved quality, productivity, and adaptability in patient care via the use of cutting-edge tools like predictive analytics, customized medication, digital twins, and mental health applications.
While security will get better generally, new threats will emerge, necessitating proactive measures rather than reactive ones. Machine learning, AI, and extended reality are just a few of the cutting-edge technologies that are enhancing the standard of medical treatment.
Healthcare organizations must weigh the costs and benefits of several options for modernization. Finding the proper group of software engineers that can cater to your specific requirements and help you achieve your goals is crucial.
3. Final Words
We have had the tools to implement telemedicine, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and healthcare apps for years, long before the epidemic. Although the covid 19 pandemic was the impetus for the healthcare industry to advance and for individuals, providers, and hospitals to adopt digital health practices, it was necessary.
Doctors and patients alike are beginning to appreciate the benefits of technological healthcare services, including remote access, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and expedited research and development methods. The fact that digital health trends are receiving support and investment suggests that others agree with the value they provide.
There is still a lot of room for development. The healthcare sector, on the other hand, is adopting technology actively, with an eye on improving the future of healthcare and expanding access to quality medical treatment.






Comments
Leave a message...