
AI plays a major role in banking by automating and streamlining various financial processes. Its predictive analytics capabilities improve risk management, while virtual assistants and chatbots enhance customer experience.
As AI advances, banks are expected to make the most out of AI. A reputable finance software development company assists banks in creating solutions that address current challenges and provide data-driven insights to inform future strategies.
In this blog, we will explore how AI benefits banking, its challenges, best practices, future trends, and real-life examples.
1. What is AI in Banking?
The practice of implementing advanced machine learning techniques, algorithms, and models to automate various banking operations is referred to as AI in banking. It enhances decision-making, streamlines complex workflows, improves customer engagement, and automates mundane, time-consuming tasks.
AI empowers banks to create customized financial services, implement effective risk management, and ensure faster approvals. Banking processes that once required manual oversight, operated within rigid frameworks, or relied on outdated software can be modernized by integrating them with AI/ML algorithms and data-driven systems.
AI in banking isn’t just about increasing operational efficiency or applying automation; it represents a shift in mindset and culture from reactive to proactive, predictive, and adaptive operations.
AI-powered systems are designed to learn from real-world interactions and evolve according to requirements. AI helps create innovative banking solutions that transform the end-users’ experience with digital financial services.
2. Benefits of AI in Banking
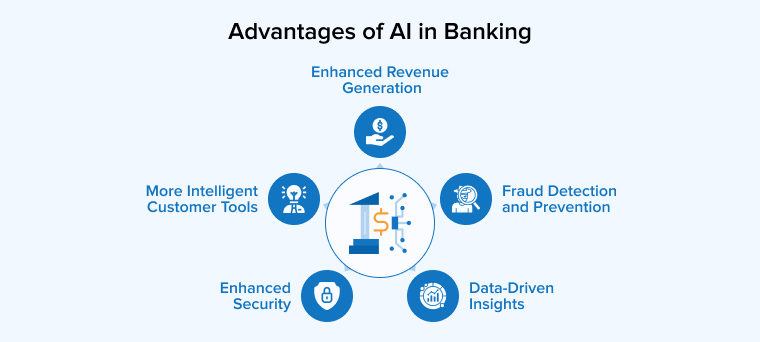
AI is revolutionizing the banking and finance industry with a long-lasting impact. Its adoption has already begun to demonstrate several notable benefits, including but not limited to:
2.1 Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI systems are significantly more accurate and efficient in quickly analyzing historical patterns and identifying anomalies that indicate fraudulent activity. Real-time threat detection also enables banks and financial organizations to respond to potential threats before they cause any damage to the system, thereby reducing the risks and losses.
Unlike humans, AI tools can remain vigilant 24/7, monitoring transactions using their pattern recognition capabilities. These tools are trained on a specific set of rules and instructed on standard operating procedures to follow if any anomaly or unusual activity is detected.
2.2 More Intelligent Customer Tools
Fueled by deep learning, agentic AI, and GenAI, banking and investment firms are creating sophisticated solutions that streamline customer service. AI chatbots and virtual assistants enable companies to offer 24/7 customer support, efficiently resolving customer queries. Moreover, AI is also used to build finance apps that help customers manage their finances and save money.
2.3 Data-Driven Insights
Banks must gain insights into market trends and customers’ behavior to offer better services and experiences. Analyzing large volumes of data helps identify patterns and support informed decision-making. These data-driven insights also prove effective in product development, marketing, and customer retention.
2.4 Enhanced Revenue Generation
Banks provide personalized financial services and products using AI, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, which in turn enhances revenue generation. AI models help identify new business opportunities, optimize marketing strategies, streamline sales funnel, and boost revenue growth.
2.5 Enhanced Security
AI enables banks to apply robust encryption mechanisms to strengthen data security. In the finance and banking industry, a significant proportion of AI solutions are designed to ensure the safety of banks and their data. These solutions utilize advanced encryption techniques to transform data into a machine-readable format, safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
As threats continue to evolve, encryption methods are regularly updated to ensure that attackers can’t breach the robust defenses of banking systems. When it comes to protecting sensitive financial information and maintaining customer trust, it is better to be proactive with AI.
3. AI Use Cases in Banking
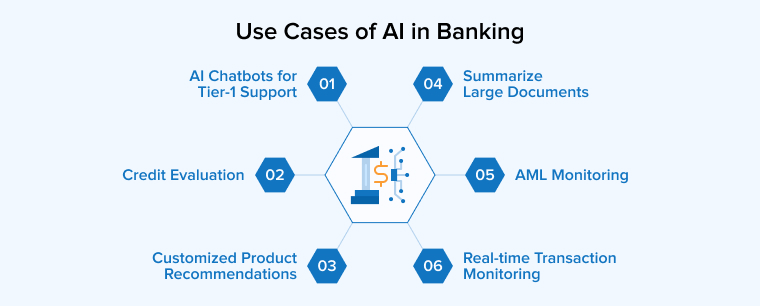
Given below are the top use cases of AI that are revolutionizing the banking sector.
3.1 AI Chatbots for Tier-1 Support
AI chatbots in the banking industry handle routine tasks and low-priority queries such as balance checks, FAQs, account updates, and more. These bots act as virtual agents to reduce the workload on the bank’s customer support team. They are continuously available virtually to answer customers’ queries and manage demand during surges in customer service requests.
AI chatbots or virtual assistants are trained to understand customer queries and provide specific, human-like responses that meet their needs. Most importantly, these bots learn and evolve with each customer interaction to deliver a better customer experience.
3.2 Credit Evaluation
Banks have a formal and often lengthy review process to determine whether an applicant is eligible for credit. A typical credit evaluation involves gathering important information about the applicant, assessing this data to determine creditworthiness, deciding if the applicant qualifies for additional credit, and determining the amount to be granted.
To ensure a thorough evaluation and prevent fraud or default, a significant amount of time, money, and effort is spent on each application. Despite these measures, banks and financial firms still risk losing money if they make a single incorrect step in the process.
However, no such risks exist when credit evaluation is powered by artificial intelligence technology. Of course, it requires large data sets including credit history, amount of debt, payment history, and more. AI can quickly process these datasets and has the capability to detect even the smallest of discrepancies and anomalies.
AI tools can evaluate credit scores using both historical and forecast data. This approach is especially helpful for new customers, startup founders, and students who have no credit history. Using AI in credit evaluation reduces risk while increasing the customer acquisition rate. Meanwhile, customers benefit from unbiased access to enhanced credit services.
3.3 Customized Product Recommendations
AI/ML algorithms are specifically used in banking to analyze large data sets such as demographics, browsing behavior, transaction history, and more to help banks offer personalized product recommendations to customers. By assessing data, AI enables banks to understand the financial needs and preferences of their customers. This allows them to offer products that align with customer expectations and create new cross-selling opportunities.
AI-driven recommendation engines not only help banks increase sales but also assist customers in discovering what they truly want through personalized product and service suggestions. These personalized offerings enable banks to build customer loyalty, generate more revenue, and deliver lifetime value to their clientele.
3.4 Summarize Large Documents
Banks handle vast amounts of paperwork daily. Sorting, analyzing, and signing these documents can take an excessive amount of time if done manually. Using AI to assess large financial documents can significantly save time and reduce operational costs. AI tools analyze the documents and provide summaries for manual review to identify important documents or determine their priority levels. For example, AI tools can summarize the communication between customers and support executives by analyzing the interaction history.
3.5 AML Monitoring
Monitoring and assessing every transaction is necessary to detect suspicious activities and prevent financial crimes. It is also a prerequisite for anti-money laundering compliance. AML monitoring is optimized through AI integration, which provides the capability to quickly analyze large datasets and identify anomalies or fraud patterns that traditional systems often miss. AI empowers banks to effectively counter actual money laundering threats while minimizing false positives.
3.6 Real-time Transaction Monitoring
AI tools analyze every financial transaction with great scrutiny to detect suspicious activities that may indicate fraudulent patterns. Now, anomaly detection and threat pattern recognition are possible in real-time, thanks to AI algorithms. For example, if the AI detects multiple transactions using the same credit card but from different locations, it will flag the card as stolen.
AI tools in banking monitor customers’ spending behavior. Any sudden change in behavior, a surge in purchases, or transactions in unusual categories, will be flagged. These tools also consider temporal factors of financial transactions, such as time, location, and frequency, to determine whether the activity appears suspicious or genuine.
4. AI in Banking Examples
In this section, we will explore leading financial firms to understand how they leveraged AI to simplify operations, deliver better services, and stay ahead of their competitors. These examples demonstrate how AI integration can revolutionize the banking ecosystem.
4.1 PenFed Credit Union
Einstein is a virtual assistant that PenFed Credit Union plans to integrate into both its internal operations and customer-facing processes using GenAI. It functions as a service representative, responding to emails and online chats to address queries and questions. The organization will initially deploy the virtual assistant to provide internal support to employees, with a gradual extension of its use to customers.
4.2 Kasisto
Kasisto is a New York-based company that was among the first to offer digital banking services in the United States. It uses a conversational AI platform called KAI, which helps banks and financial organizations create their own chatbots and virtual assistants.
Empowered with NLP and AI reasoning, KAI is capable of answering finance management queries. Some of the top clients of Kasisto’s KAI platform include Standard Chartered Bank, DBS Bank, TD, and the UAE’s digital bank Liv. They use KAI bots to guide customers through various financial operations such as blocking credit card charges, making international transactions, and more.
4.3 JP Morgan Chase

JP Morgan uses AI on its platform called Contract Intelligence or COiN to review legal documents. It can analyze thousands of commercial credit agreements within seconds, a task that would have normally taken thousands of hours if done manually. JP Morgan leverages Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and machine learning algorithms to reduce complexity and human error in the legal review process while simultaneously increasing operational efficiency.
5. Challenges of AI in Banking
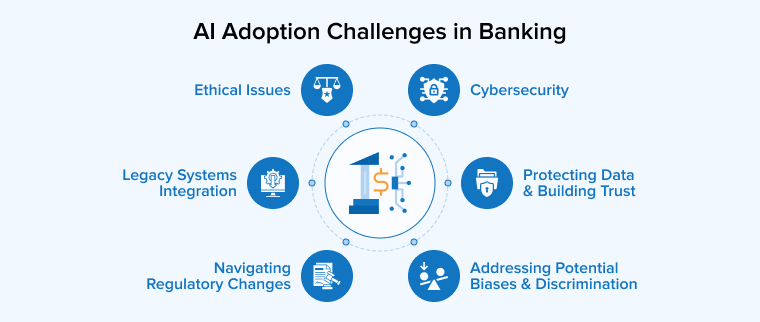
While using AI in banking certainly offers numerous benefits, there are a few challenges to its effective implementation. Understanding these challenges is essential to overcoming them and maximizing the advantages of AI in banking.
5.1 Addressing Potential Biases and Discrimination
Make sure the data you feed to the AI model is unbiased. Otherwise, the system may propagate biased outcomes in crucial processes such as risk assessments and loan approvals. Therefore, before training AI models on large datasets, banks must actively identify and remove biases to ensure that the models make equitable decisions and do not disadvantage any group.
5.2 Protecting Data and Building Trust
Banks hold sensitive information, and if it is exposed, it can be easily misused. This can result in both financial loss and a loss of trust, along with potential legal consequences. Therefore, banks must implement systems designed to protect their customers’ data and privacy. Secure storage, anonymized samples, and data encryption are some methods to safeguard when training the AI models. Additionally, frequent and thorough audits of AI tools help maintain trust among customers and regulators.
5.3 Cybersecurity
Banks use GenAI for compliance management and fraud prevention, but certain risks remain. Attackers often target AI models because these models have access to sensitive internal data from both the system and the banks. This raises serious security concerns. Therefore, it is essential to implement efficient AI governance to maintain a balance between innovation and risk management.
5.4 Legacy Systems Integration
Many banks around the world operate on decades-old infrastructure. When ushered into the age of AI and compelled to keep up, they try to integrate the legacy systems with modern AI tools. This is where the nightmare begins. Outdated legacy systems can’t handle the new AI/ML models or safeguard their data effectively. In such a case, a comprehensive strategic plan is required to update the outdated system first, making it compatible with modern AI models.
5.5 Navigating Regulatory Changes
Regulations for AI in banking are still evolving, so considerable challenges are expected as regulators strive to keep pace with technological advancements. Banks must actively engage with the regulatory bodies to establish an effective and transparent framework that ensures the ethical and responsible use of AI in banking activities.
This helps overcome biases in AI algorithms and enhances the ability to explain their decision-making process, which is essential for banks to maintain public trust and transparency.
5.6 Ethical Issues
There are ethical concerns about using AI in banking related to decision-making, transparency, and accountability. Addressing these concerns should be a priority for banks. For that, they can define and establish clear guidelines for ethical development and use of AI. Fostering a culture of transparency and improving the explainability of AI models will ensure accountability.
Do not leave critical decisions for AI; instead, assign them to trained employees or subject-matter experts. Additionally, ensure human oversight of every decision made by AI models.
Seamless collaboration among internal teams can help address ethical dilemmas and mitigate the social impact arising from the use of AI in finance.
6. The Future of AI in Banking
AI is widely used across every sector to revolutionize the way services are offered to users and enhance their experience. In the banking industry, AI has brought innovations that have proven to be transformative in many ways. It is expected that, in the future, AI will help banks offer more efficient and personalized banking services. Let us discuss some future trends.
6.1 Ethical AI Development
The emphasis on ethical AI development will only grow as AI technology evolves. It is essential for AI models to avoid biases and remain transparent and fair. Banks and financial institutions will increasingly invest in guidelines and frameworks that ensure the responsible use of AI and maintain customer trust.
6.2 Advanced Predictive Analytics
As AI technology advances, its predictive capabilities will continue to improve. Future AI systems may be able to forecast credit risks, market changes, and customer behavior with increasing accuracy and speed.
Banks can easily leverage these insights to make informed decisions that help avoid potential problems and create financial products and services tailored to individual needs. Advanced predictive analytics also support the development of resilient risk models that enhance compliance and enable smart investment strategies.
6.3 Autonomous Finance
Currently, we use AI that requires prompts to perform programmed tasks. In the future, the AI models will be adaptive and advanced enough to take appropriate actions autonomously.
Such systems automatically adjust investments, tweak budgets, and shift funds on behalf of the users. This enables banks to offer a set-and-forget experience, as AI models continuously adapt to changes in objectives and spending behavior.
7. Conclusion
Artificial intelligence technology is transforming how banks operate, making financial processes faster, safer, and smarter. AI has also proven useful in detecting fraudulent patterns in real-time. It enhances customer service through chatbots and quickly analyzes vast amounts of data, providing banks with the insights needed to make informed business decisions and offer personalized products.
While obstacles such as algorithmic bias, cybersecurity threats, and compliance complexities exist, banks can overcome them through clear rules and careful oversight. In the future, as AI evolves, even more advanced tools will emerge that can predict market changes and manage finances automatically. By embracing these changes responsibly, banks are set to deliver a better, more secure experience for their customers and stay ahead of the competition.
FAQs
Will AI Replace Humans in Banking?
AI is not here to replace humans but to assist them in banking. It automates various mundane and repetitive banking operations, effectively assessing large datasets to quickly offer insights for informed decision-making. Currently, AI solutions are primarily implemented to increase operational efficiency, freeing human capital to focus more on high-value tasks.
What AI tools are Banks Using?
Banks are using a myriad of AI tools. AI-enabled chatbots and voice assistants have become common in every major bank and financial institution. Additionally, AI is used to enhance biometric authorization.
What are the Risks of Using AI in Banking?
Banks can face regulatory compliance challenges, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and algorithmic bias when using AI in banking. If these risks are not properly addressed through AI governance and monitoring, they may lead to legal penalties, data breaches, and unfair decision-making.
How Will AI Disrupt Banking?
AI helps automate data collection and processing, leading to faster and more informed decision-making. The emerging technology also ensures that organizations are fully prepared to meet regulatory requirements and avoid cyber threats.






Comments
Leave a message...