
The choice of a programming language is a crucial factor that significantly influences the efficiency and the outcomes of web development. A programming language also determines the performance, security, adaptability, and load-bearing capacity of the application. However, selecting an appropriate programming language is not an easy task.
With numerous options available in the market, only a few have proved to be relevant and reliable over time. So, one must consider their project requirements and the language’s ability to fulfill them. To help you make that decision, we provide a list of the most popular and widely used web development languages with a brief discussion of their features, pros, and cons.
1. Top Programming Languages For Web Development
Let’s explore various programming languages in detail to identify their features and determine which one is to best for your project.
1.1 JavaScript

According to the survey conducted by Stack Overflow, JavaScript remains the most popular language. JavaScript is a top programming language that is adopted by many developers to provide interactive elements, automate processes on certain pages, and add animations that enhance the user experience.
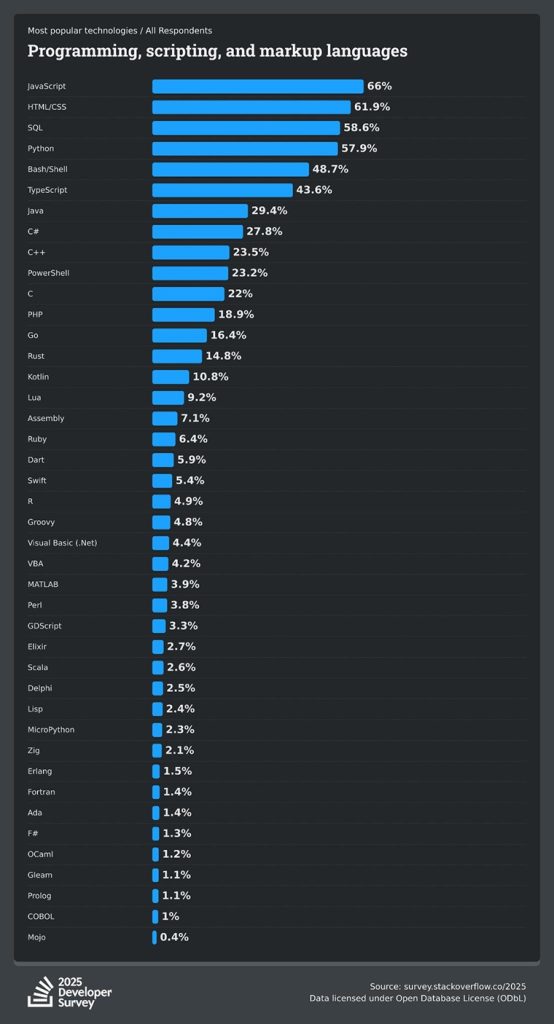
JavaScript is evolving rapidly and is currently the most popular web development language in use. It is now a back-end coding language thanks to Node.js. When it comes to web development, there are “big three” pillars: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which are utilized by nearly every website that makes use of them in some way. Although many others exist, including server-side languages like Java, C++, Python, and SQL, mastering these three is essential for web development.
JavaScript proves its flexibility by seamlessly handling tasks on both the front-end and back-end of development. Here’s the image that showcases the versatility of JavaScript.
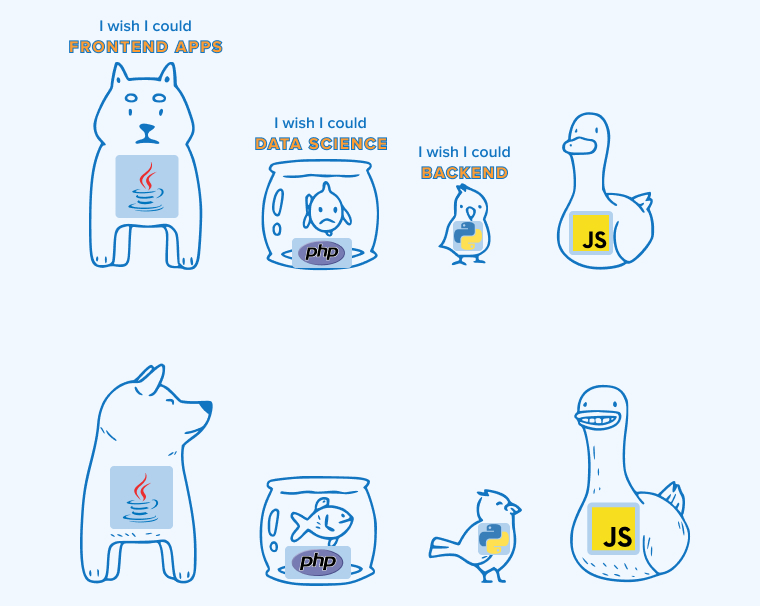
Features of JavaScript
- DOM manipulation: It offers several methods to access DOM elements through various attributes, allowing developers to customize and manipulate webpage elements.
- Functional programming: This language utilizes functions as the main building blocks to create solutions. Functional programming helps define function expressions, higher-order functions, pure functions, first-class functions, etc.
- Event-driven Architecture: With this architectural pattern, JavaScript developers can build responsive and interactive web apps and manage a large user base simultaneously.
Pros of JavaScript
- XMLHttpRequest Web API: This object is crucial part of JavaScript for communicating data to both parties without the need to refresh the page. By making asynchronous HTTP requests to the server, the object facilitates seamless interaction.
- High Compatibility: One of its biggest benefits is that major browsers can incorporate JavaScript, providing consistent output across platforms. JavaScript can also be used for both client and server-side components.
- Beginner-friendly: JavaScript is a popular programming language with several online courses to help you learn it quickly and easily.
Cons of JavaScript
- Security Risks: One major drawback of JavaScript is that its source code is constantly accessible to the public.
- Faults are only found in the production environment: A website’s rendering could be halted if a JavaScript problem occurred. Browsers are quite forgiving when it comes to faulty JavaScript.
- Not consistent: The behavior of JavaScript may vary from browser to browser, making it challenging to develop code that works consistently across multiple browsers.
Further Reading on: JavaScript vs TypeScript
1.2 TypeScript

Microsoft released and supports TypeScript, an open-source, object-oriented programming language, under the Apache 2 license. Anders Hejlsberg, a pivotal figure in the development of the C# language, developed TypeScript. The TypeScript programming language is a statically typed extension of JavaScript that produces standard JavaScript upon compilation. It is a scripting language for creating large-scale applications in JavaScript that can run on any web browser, server, or OS. The browser isn’t used to execute TypeScript code. For compilation and output, a compiler is used. It’s fair to say that TypeScript is an enhanced version of JavaScript from ES6.
According to GitHub, TypeScript is one of the popular programming languages.

Features of TypeScript
- Generics: Developers use this feature to develop different classes, functions, and components that can work with numerous types and still maintain strict type safety. Using this feature unlocks the robustness and reusability of your code.
- Data types: By offering an array of built-in primitive types, TypeScript allows developers to work with various kinds of data. It helps them define variables, function parameters, return values, and more.
- Static Typing: With static typing, developers can easily catch type-related errors during compilation only. As a result, the errors in runtime reduce significantly. As it helps you find errors early, you can write reliable code.
Pros of TypeScript
- Type Safety: Clearly declaring variable types helps catch type errors during compilation, reducing runtime errors and enhancing code quality.
- Strict Null Checking: With strict Null checking, TypeScript avoids possible issues caused by undefined and null values. This helps save time during debugging and makes the code more reliable.
- Interfaces and Generics: By introducing interfaces and generics, TypeScript helped improve modularity and reusability of its code. Because with these features, developers can build more expressive type annotations and reusable components.
Cons of TypeScript
- Compatibility: Integrating this language with existing builds and tools is challenging. When you use TypeScript to work on legacy systems with languages like JavaScript, you need some serious refactoring.
- Steep learning curve: Learning the concepts of interfaces, annotations, and other TypeScript features is a little difficult, especially if you are making a transition from JavaScript. Moreover, the typing system is a little complicated, so you have to execute it properly.
- Requires compilation: Before running the TypeScript program in browsers, it needs compilation, which increases your development time.
1.3 NodeJS

Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform runtime environment largely used for creating networking and server-side applications. Developers prefer this JS-based platform for web development. It is efficient and lightweight, which helps with the rapid development and deployment of web applications.
It was initially launched in 2009 with a focus on performance and scalability. That is the reason why many companies opt for Node.js to develop enterprise-grade applications.
Some of the leading brands that use Node.js for their high-traffic websites and real-time apps include Netflix, IBM, Microsoft, LinkedIn, and PayPal.
Features of NodeJS
- Non-blocking I/O and asynchronous request handling: This feature allows NodeJS to run next requests while fetching data for the previous ones, all on a single thread. As a result, the wait time reduces, and the app functions seamlessly.
- Callbacks and promises: These functions are used in NodeJS for I/O operations without complicating the code. They ensure smooth functioning of the app, promising to return the data once it is retrieved and then run the necessary operations.
- Event loops: They are used to collect new callbacks and poll for new requests from the event queue. It repeats the loop once all the operations are completed.
Pros of NodeJS
- High speed: Node.js offers a faster runtime compared to other web development frameworks. It is reliable, flexible, and high-performing.
- Scalability: Node.js is highly scalable, so it allows it to respond quickly to the data layers. It makes building applications easy.
- Reduces development cost: NodeJS saves a considerable amount of time and costs during development. And that’s why many companies prefer Node.js over other frameworks.
Cons of NodeJS
- Unstable API: The NodeJS APIs change continuously, making them backward incompatible. This lack of consistency keeps the developers occupied in making necessary code changes to keep it compatible with the latest API versions.
- More Development Time: NodeJS is unopinionated, which might often confuse developers about the suitable approach to development. This leads to reduced productivity and increases the development time.
- Not for heavy computing applications: While NodeJS is perfect for complex apps, it is not built for performing CPU-intensive tasks. Heavy computations need the app to block incoming requests, but NodeJS allows I/O operations through callbacks and promises. This can seriously degrade the performance.
1.4 C#

Microsoft created C#, an up-to-date general-purpose object-oriented .NET programming language. To facilitate the usage of many different high-level languages across a wide range of computer systems and architectures, C# is optimized for Common Language Infrastructure (CLI), which includes both the executable code and the necessary runtime environment.
Features of C#
- Supports modern web services: C# provides built-in features that can transform any given component into a web service that can be accessed on the internet from any application or platform.
- Native support: C# allows restricted use of native pointers to offer native support for Windows and COM apps.
- Automatic memory management: Inheriting the features from .NET, C# provides features allowing automatic garbage collection and memory management.
Pros of C#
- Debugging: Since C# is a strongly typed language, it aids in the early detection of bugs.
- Rich ecosystem: Its extensive library and framework simplify the development of complex applications. The .NET Framework is a suite of development tools and services that is compatible with C#.
- Flexibility: C# is a flexible language with many potential uses, including the development of desktop, online, and mobile apps.
Cons of C#
- Limited cross-platform capabilities: C# is a popular language for Windows, which might put a limitation on its cross-platform functionality.
- Slower: Some days, C# might lead to slower and problematic execution speed when compared to languages like C or C++.
- Steep learning curve: C# is a difficult language to learn because it utilizes some complicated concepts and functionalities.
1.5 PHP

The name PHP stands for Hypertext Preprocessor. It is a server-side scripting language. Scripts in PHP are interpreted by the PHP engine on the server, which generates the HTML for the client’s browser.
PHP is a server-side scripting language best utilized for server-side functionality because of its deployment tools and capabilities. The server-side language PHP simplifies deploying, submitting, and confirming your code considerably due to its deployment tools and capabilities. PHP is helpful in many development domains since HTML, a common front-end tool for creating online apps and pages, can contain PHP code.
Another advantage of PHP is that it’s an excellent way for beginners to see results with their back-end coding because it frequently ignores minor faults that don’t impact the ultimate result. PHP web development is one of those languages for web development that works for both front-end web development and back-end web development.
Features of PHP
- JIT Compilation: Your PHP scripts can now run faster with JIT compilation, as it allows you to compile parts of code during runtime.
- Server-Side Scripting: By running scripts on the web server, PHP helps developers manage users’ sessions across multiple requests, along with other tasks like form submission.
- Security Features: PHP comes with built-in security features for data encryption, the establishment of secure communication protocols, and maintaining a secure environment for users.
Pros of PHP
- Free and easy to use: PHP is an open-source and widely used scripting language. It’s free and can be used for anything from events to web apps. Due to its ease of usage, there is a shorter learning curve. If you know C, you’ll feel right at home working with PHP.
- Flexibility: PHP-based software is cross-platform and may be used with any operating system.
- Faster loading speed: PHP-based database-connected applications are easily deployable. The major reason it’s popular is that it loads pages quickly, even on sluggish connections.
Cons of PHP
- Security risks: For PHP apps, Common security vulnerabilities include cross-site scripting, SQL injection, and CSRF (Cross-site request forgery).
- Not suitable for enterprise app development: Large, data-intensive online apps are not a good fit. Users may receive misleading information or insights due to its fragile character.
- Performance limitations: Online application performance degrades when additional functionalities are used from the PHP framework and related tools.
1.6 HTML

Hypertext Markup Language, or HTML, is a programming language used to create electronic texts known as pages that are displayed on websites. Every page has multiple connections to hyperlinks or links to other pages. Every web page on the Internet has been created using HTML in some capacity. Understanding how to display texts or carry out the loading of various elements is a must for browsers.
The majority of developers consider HTML to be one of the simplest programming languages to learn and utilize. HTML is frequently taught to web developers before any other programming language, and it is an essential component of all development courses. It is straightforward to learn since it uses basic tags, and case insensitivity is not a problem.
HTML is an open-source language. Programmers can use it without having to invest in any additional software. Users can access major aspects of the language without using any other plugins or software. This is why a large number of companies utilize HTML to meet their website design needs. It is possible to have full websites developed in HTML.
Features of HTML
- Audio and Video Support: When using HTML, no need to rely on third-party media services. It provides tags that allow you to embed images and videos into your HTML document easily.
- Local Storage: HTML allows for storing data in the client browser through JavaScript APIs. This helps developers build offline apps that require local data storage.
- WebSockets: They establish a two-way communication between the client and the server, reducing the latency in responses. It also provides capabilities to manage large numbers of connections simultaneously.
Pros of HTML
- Compatibility: All browsers support the HTML language, and it is built into every operating system.
- Speed and simplicity: HTML documents are easily readable and load quickly.
- Large memory storage: Due to the program’s caching capabilities, large files can be stored.
Cons of HTML
- Lack of dynamic capabilities: Being a static language, it is incapable of producing dynamic results on its own.
- Verbose: To make even a basic website, we have to write lots of code. Making lists, tables, and forms is just as time-consuming as keeping track of a page’s color scheme.
- Deprecated tags: We need to double-check the deprecated tags and make sure we’re not using them elsewhere, as another language that interacts with HTML has taken over the tag’s original function.
1.7 CSS

The layout and presentation of documents to users are specified using the computer language CSS. In general, the term “document” refers to a text file format that uses a markup language, such as the popular HTML and others like XML.
CSS helps create a customer version of a document. This is especially important for browsers designed to graphically present documents onto screens, printers, and projectors, like Chrome, Firefox, and Edge.
The usage of CSS selectors gives users the ability to choose and manage various web page elements. They can be thought of as structural elements used to match attributes and attribute values.
CSS saves time because only one CSS file needs to be created and can be applied to several HTML pages. Each HTML element has a defined style that a user can utilize to apply to other web pages as needed.
CSS code is simple to maintain, and users can easily modify the style globally. All web pages are automatically updated after modifications are made.
Web standards are evolving; fewer and fewer people are using HTML attributes while more and more people are choosing to utilize CSS. It is advised that web developers utilize it across HTML pages to guarantee compatibility with upcoming browser updates. It supports the creation of visuals.
Features of CSS
- Scroll snapping: This feature helps make transitions and draw users’ attention to key web page elements. Such scrolling was already in effect in mobile apps, but this feature implements the same on websites without using JavaScript.
- Transitions and Animations: These properties allow you to add interactive elements and animations on the website, giving dynamic effects to give users a more engaging experience.
- Container Queries: It is used for reusable components where each component needs a distinct layout in its occupied space. The feature helps components adapt their layout to the space available in their parent container.
Pros of CSS
- Reusable: CSS is crucial because it allows you to define a single set of rules for styling an element that can then be reused in various contexts.
- Uniform styling: The primary benefit of CSS is that it applies styles uniformly across many different websites. It’s helpful that a single command may affect numerous variables.
- Simplified programming: To boost site performance, web developers need to employ fewer lines of code on each page. Because of this, much less work is required even when building large or complex features.
Cons of CSS
- Inconsistency: When it comes to cascading style sheets (CSS), what works in one browser may not work in another. Web developers must do browser compatibility testing by opening the code in several different browsers.
- Security risks: The CSS programming language doesn’t offer sufficient security features to protect the web solution and its data.
- Code changes affect functionalities: We need to check for incompatibilities after making the modifications. All browsers will notice a similar adjustment.
1.8 Ruby

Ruby on Rails (RoR), a popular framework, is designed especially to use Ruby, a programming language, to construct and carry out web development tasks with less code. Software developers use frameworks, programming languages, and tools to create software products, custom features, and modules, making the software development process more efficient.
For novices, learning web development and practicing back-end development is frequently an excellent option because the Ruby on Rails framework and Ruby language are so straightforward. RoR makes it simple to create tasks and functions, which streamlines the creation of software.
The majority of other programming computer languages, such as JavaScript, HTML, CSS, and SQL, don’t provide both back-end and front-end functionality. Ruby, on the other hand, combines both ends and enables programmers to create a full-fledged web application. Every feature you may need for web app development is available with Ruby on Rails, and you can easily extract what you need to move forward.
Features of Ruby
- RESTful Design: Leveraging these design principles, ROR creates APIs to offer a standardized method to structure routes and controllers for CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations.
- ActiveRecord: This feature was introduced in Rails 8 to minimize the query overhead. It also improves the database interactions to increase app speed and ensure efficient resource utilization.
- Assets Pipeline: RoR utilizes the Asset pipeline to handle and optimize the app’s assets, like images, CSS stylesheets, and JavaScript files, to serve them to the user in the best possible manner and enhance overall app performance.
Pros of Ruby
- Shallow learning curve: It is easy to learn this language, even for first-timers. Ruby is an easy computer language that you can start with if you’re new to the field.
- Not opinionated: Ruby has an all-inclusive structure, which means that programmers can compose code in any style they choose. Some languages, like Java, have rules about how to organize code. Ruby, on the other hand, lets writers write code in any way they want.
- Highest standard of safety: RoR provides a variety of built-in security functionalities to safeguard the app and its data from external attacks like SQL injection, CSRF, and cross-site scripting.
Cons of Ruby
- Lacks mobile development capabilities: Ruby isn’t the best language for making apps for mobile devices.
- Small community: The community of people who work with Ruby is not as big as the other computer language communities. Ruby might not be the ideal language for exploring if you want extensive guidance and assistance.
- Slow Runtime Performance and Speed: RoR registers very low speed and performance compared to other web development frameworks like NodeJS and Django. It completely falls upon the development team to ensure optimal performance by optimizing the database and server environment.
1.9 Java

Java is the most preferred language for programmers who wish to create robust, large-scale online applications that need high levels of security to protect data. It’s a platform-independent, flexible language that you may use to construct online, mobile, and desktop apps and tools on different platforms, such as computers and mobile devices. Java operates on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), standardizing the computer on which programmers run code instead of enabling it to operate successfully on each programming machine, which accounts for its scalability and dependability.
Because Java has so many potential implementations, many programmers utilize it for web and software development. However, this also means that there are numerous third-party companies available to assist novice programmers in learning how to implement Java code for back-end projects.
Features of Java
- Architecture-neutral: Java compiler compiles the code into an architecture-neutral object file format, allowing developers to run it on multiple processors that have the Java runtime system.
- Multithreaded: Java developers can run multiple tasks concurrently with this feature. It optimizes resource usage and also enables you to create interactive applications.
- Mobile and web development: Through technologies like Servlets and JSP, along with frameworks like Spring, Java supports web app development. It offers Android SDK and other tools to support Android app development.
Pros of Java
- Easy and affordable: Java is one of the easiest programming languages to learn and use due to its clear and simple code. Java’s straightforward design makes it inexpensive to create and hassle-free to keep up to date.
- Simplifies development process: OOPs ideas aid Java in its ability to address practical issues. In addition, it simplifies the maintenance of complex code by separating it into manageable parts.
- Versatility: The Java programming language is very adaptable. That’s because Java can operate on any computer without any additional software or hardware.
Cons of Java
- Performance Limitations: The performance of Java for native apps is considerably lower than that of languages like C++. Thread deadlocks, insufficient caching configurations, and garbage collections are the prime reasons for it.
- Commercial license required: Initially, Java was free to use for all. But now you need to obtain commercial licenses if you want to use the programming language for commercial purposes and access its commercial-level tools and features for app development.
- GUI building: During app development, creating a GUI helps developers offer a native look and feel. However, Java lacks that capability. You have to use GUI builders compatible with Java to provide the same level of GUI quality that languages like Python and C# offer by default.
Further Reading On:
Java vs C#
Why do We Need Java Reactive Programming?
1.10 Python

Python is one of the most potent and effective multi-purpose languages for web development and data science analysis. It is an open-source language that is very simple to deploy as well as to learn and use. Given that scalable web pages and applications are frequently developed using it, it is regarded as one of the best programming languages to learn for web development. The design of Python’s language, which is straightforward, elegant, effective, and strong, is its unique selling point (USP). It is the benchmark for developer proficiency and has influenced several programming languages like Go.
It is among the top backend programming languages for web development and offers first-rate integration. In addition, it has the capability of seamlessly offloading to C/C++ the CPU’s taxing jobs. There are many available frameworks in Python and extensive toolkits for computational science, statistics, and mathematics. The desktop, web, and web apps based on GUI, data science, machine learning, and network servers are all created using the Python programming language.
Here’s a Google trend report that clearly explains that, over the years, demand for Python has been increasing
Features of Python
- GUI Programming Support: This feature enables you to interact with the program through windows, menus, and buttons. With this, developers can also build graphical interfaces for their apps.
- Interactive Mode: With this feature, developers can see the results of their commands immediately. They only need to type the commands once. It helps test out a new small piece of code or to learn the language.
- Extensibility: You can easily extend the capabilities of the Python programming language using C or C++ code. It helps you fill the gaps in the Python programs using scripts or code written in other languages.
Pros of Python
- Easy to learn and understand: Python, a high-level programming language, has a syntax quite similar to that of the English language. The code is more readable and understandable as a result.
- Highly efficient: The clean design of the Python programming language provides process control and amazing text capabilities to deliver desired outcomes.
- Automatic Memory Allocation: There is no manual allocation of free space in Python because the process is automated. Moreover, the memory from the discarded objects in Python is recycled by the garbage collector.
Cons of Python
- Memory concerns: Python makes a few compromises to simplify things for the programmer; hence, it becomes a very memory-intensive programming language.
- Not for faster web solutions: Python’s limited processing speed and inefficient use of memory make it a poor choice for applications that require speed.
- Global Interpreter Lock: It’s a mechanism in Python that prevents the code from executing multiple threads simultaneously. It limits the concurrency and parallelism of Python apps.
1.11 SQL

The standard database language known as SQL, or Structured Query Language, is used in conjunction with other programming languages. It is used to manipulate databases as a query language for databases. With more than 50% of developers using SQL for programming, it ranks third on Stack Overflow’s list of the most popular programming languages.
A form of computer language called SQL, or structured query language, employs queries, also referred to as data requests, to get data from databases. SQL can be used to retrieve valuable server-side information from databases and use that information to perform activities that guarantee the client-side functionality of the software.
Back-end developers usually use SQL to perform additional administrative tasks that help in the operation of a piece of software rather than creating the framework for its features. Because many databases use it to interact with data, it would be a good idea for you to learn this language if you want to understand how data is retrieved, updated, and stored.
Features of SQL
- Views: Providing an abstraction layer, this feature simplifies complex queries and offers virtual data representation. It restricts access to certain rows and columns to organize the database structure and enhance data security.
- Triggers: When specific database events occur, this feature initiates predetermined responsive actions. It helps implement complex business logic, automate mundane tasks, and ensure data integrity.
- Indexes: It comes with a quick lookup mechanism that helps enhance query performance. Indexes also allow quick data retrieval even from large datasets.
Pros of SQL
- Accessibility: It is possible to swiftly and easily access a large volume of data. Data manipulations such as inserting, removing, and rearranging take essentially no time at all.
- Scalability: SQL databases can grow horizontally and vertically to meet the needs of any size organization or workload.
- Security: SQL databases contain features like user authentication, encryption, and access control that help keep data safe from prying eyes. To minimize data duplication and ensure data correctness, SQL databases use restrictions such as unique keys, primary keys, and foreign keys.
Cons of SQL
- Highly complex: SQL’s complex user interface makes even experienced database administrators uneasy with complex tasks.
- Works well with structured data only: Since SQL databases demand that data be organized into tables and columns, they are less adaptable to processing unstructured or semi-structured data than NoSQL databases.
- Doesn’t support real-time processing: For applications that need instantaneous processing of data, SQL databases might be a hindrance due to their design for batch processing and lack of support for real-time analytics.
1.12 Swift

To create apps for iOS, macOS, tvOS, and watchOS, developers may use Swift, an open-source, multi-paradigm programming language. Apple developed the language in 2014 so that programmers would have a robust tool with which to construct iOS applications. Safe, quick, and expressive are only some of the reasons why this language was created, as stated on swift.org. It is meant to replace C-like languages. Likewise, the Swift community is expanding and improving all the time. The Swift programming language’s source code is publicly available on GitHub.
Features of Swift
- Robust generics: With this feature, developers can create versatile functions that work with any type. Generics also allow you to reuse these functions.
- Protocol extensions: Instead of overwhelming yourself with defining behavior in individual conformances or in global functions, you can do it in the protocols themselves.
- Flexible enumerations: Pattern matching is supported in Swift enums, and they are also allowed to carry payloads.
Pros of Swift
- Time Saving: Application memory management is handled automatically by Automatic Reference Counting (ARC), saving developers valuable time.
- Built for the future: As a future-proof language, Swift makes it simple to grow applications by adding new capabilities as they become necessary.
- Provides enhanced security: Swift’s robust typing and error-handling features make it a very secure programming language.
Cons of Swift
- Compatibility concerns: The common concern that has been raised by developers is that Swift comes with a lack of compatibility with each release. With each update, developers need to make sure that it has been rewritten to stay up-to-date.
- Lack of community support: One of the major issues with Swift because it’s still growing compared to other open-source languages.
- Lacks support for older versions of iOS: This means the projects that are running on older versions of iOS can not use Swift.
1.13 Go

Rob Pike, Robert Griesemer, and Ken Thompson created the free and open-source programming language Go. With the advent of clusters of servers, multicore processors, and large codebases, this statically typed language was released to the public in 2009 to increase developers’ efficiency.
Features of Go
- Built-in Concurrency: The language supports concurrency by allowing developers to write concurrent code with goroutines and channels. This is the reason why Go offers better concurrency than other languages.
- Error handling: Errors in Go are managed differently. It returns the type error’s value as the last return for a function. If the function works up to expectation, the error parameter is returned as nil. If not, then Go returns the error value. After that, the calling function checks the error return value, manages the error, or throws one of its own.
- Interface-Based Design: Having a robust and versatile interface system helps developers adhere to design practices and write modular and testable code.
Pros of Go
- Beginner-friendly: The syntax is basic and simple to understand for newbies, and there are not many complicated built-in functions. So, developers may not require complex libraries to perform common tasks.
- Statically typed language: Errors caused by the vast array of variable types in dynamic languages are simplified or eliminated in Go because it is a statically typed language.
- Provides features for testing: It has built-in testing support, so developers may not require external testing support for most projects.
Cons of Go
- Not flexible: While Go is simple to learn, it lacks flexibility and limits its usefulness.
- New language: Go has a lot of potential, but it’s still a young language; Therefore, it’s not yet on par with its more mature languages in several important respects.
- Less Expressive Syntax: Go’s syntax is simple and sincere, which also puts limitations on expressiveness. So to gain positive tasks, programmers need to write more code compared to other languages.
1.14 Scala

Unlike some other languages, Scala may be used for a wide variety of tasks. Martin Odersky conceived of and worked on the project to completion. In 2001, Martin began developing Scala as a student at the Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL). On January 20, 2004, we saw its formal release.
While Scala is not an extension of Java, it is compatible with it in every way. The composition of a Scala file results in Java bytecode, which may then be executed on a Java Virtual Machine.
Scala is an object-oriented language with a functional backbone. Every result is an object in this language, and every operation is a value, making it a true object-oriented language. The term “scala” comes from the word “scalable,” which describes the language’s ability to expand in response to user demand.
Features of Scala
- Pattern matching: Developers can use this advanced mechanism to match complex data structures and extract values expressively and concisely.
- Actor model: This feature allows Scala to support distributed and concurrent computations. Implementing this model helps build fault-tolerant and scalable solutions.
- Case Classes: Scala introduced these special classes for immutable data modeling. They can automatically create methods for equality, pattern matching, etc.
Pros of Scala
- Quick learn: If you have experience with object-oriented languages like Java, you may find the syntax of Scala to be comfortable. As a result, it is faster to learn than most others.
- Supports parallel processing: With Scala, we can create systems that can handle a large number of simultaneous requests without crashing.
- Seamless integration for data analysis: With the help of libraries like Apache Spark, among others, Scala may be an excellent option for data analytics.
Cons of Scala
- Complex programming: Type information in this hybrid functional/object-oriented language might be confusing at first.
- Small community: Scala has a small community of programmers. While it may be simpler to locate Java programmers, not all Java programmers have the skills necessary to write efficient Scala code.
- Difficult debugging: Scala code is highly verbose, due to which the error messages often become unclear, and that becomes a roadblock during the debugging process.
1.15 Perl

The initial purpose of the computer language Perl was to facilitate the manipulation of scripts. Nowadays, however, Perl is employed for a wide range of tasks, from web and GUI development to system management and beyond. It’s a reliable language that works on a variety of different computer systems. Web development with Perl CGI. The common gateway interface (CGI) is the interface between a web browser and Perl.
Common applications include generating reports for file conversions that need information to be extracted from text files, as well as performing such extractions. It was originally called “Practical Extraction and Report Language,” which explains how the name stuck.
The language Perl is based on is called an interpreted one. A Perl program is executed by first compiling it into a byte code and then converting that byte code into machine commands. Time can be saved by using Perl instead of C.
It’s included in the Oxford English Dictionary and works with a wide variety of OSes. It borrows ideas and syntax from a wide variety of languages, including English, awk, Bourne shell, C, sed, and more.
Features of Perl
- Open-source and extensible: It is open-source software licensed under the GNU Public License, and its capabilities can be extended with 250,000 open-source modules. Perl supports the Unicode character set.
- Cross-platform compatibility: It contains sophisticated capabilities for transforming text into markup languages such as HTML and XML. It also supports external databases such as Oracle, MySQL, and many others. Perl is easily embeddable into other systems, including web servers and database servers.
- Data management: It is capable of handling encrypted online data, such as e-commerce transactions.
Pros of Perl
- Rich offerings: Even with its reasonably developed library environment, Perl is potent due to its support for functional codes, objects, and procedural programming.
- Supports encryption and decryption of data: When it comes to data encryption, Perl is also well-equipped with a very sophisticated programming language.
- Free to use: Perl is freely available to everybody. Anyone is welcome to use and improve upon this programming language at no cost.
Cons of Perl
- Difficult to understand: Perl is a hard-to-read language.
- Debugging concerns: A major drawback of Perl is the difficulty of fixing bugs, especially in comparison to other languages.
- Not beginner-friendly: It is not geared toward students who are interested in learning how to build websites or programs. Hence, the rapidness, adaptability, and ease of the Perl programming language have never been improved.
1.16 Rust

Graydon Hoare, a Mozilla employee, started working on Rust, a system programming language, in 2006. In his words, this language is “safe, asynchronous, and practical,” and it adheres to the utilitarian and declarative paradigm. Rust is a programming language with syntax that is reminiscent of C++.
Because source code is publicly available online, anybody can use Rust and collaborate with its community to enhance its features and functionality. In 2016, 2017, and 2018, the Stack Overflow developer survey named Rust a “most favored programming language.”
Features of Rust
- Ownership System: This feature ensures the safety of Rust applications. Every single piece of information in Rust has a unique owner. The data is automatically cleaned when its owner goes beyond the scope. This helps avoid issues like memory leaks and dangling pointers.
- Borrowing and References: If different parts of your code want to access the same information without taking ownership, then it is known as borrowing. Rust allows this through safe data transfer and a pre-determined lifetime where the borrowed data doesn’t outlive its owner.
- Traits and Trait Objects: Rust has traits for defining shared behavior that allows polymorphism. Replacing this approach with traditional inheritance helps avoid complex inheritance chains. Moreover, Trait objects give dynamic dispatch for flexibility.
Pros of Rust
- Reliable and secure: Rust is built to be both quick and reliable. After the Rust execution engine, it is safe to transfer data between threads without worrying about damage.
- High performance: The embedded domain-specific language in Rust aims at machine learning and low-level systems programming, continuing the language’s emphasis on performance.
- Can support a variety of ideas: The expressiveness of software is another area where Rust excels. The language’s goal was to improve readability without sacrificing efficiency or security.
Cons of Rust
- Limited resources: Rust has a vibrant community, but it’s important to keep in mind that the language and its ecosystem are still in beta.
- Lack of automation: A high-level project can be converted into Rust source code manually, but there isn’t much backing for automatic code generation tools at present.
- Increased compilation time: It takes more time to compile Rust programs compared to other languages. This slows down the development process, delaying product launch.
1.17 Kotlin

Kotlin is a statically typed and open-source programming language. Although Kotlin is distinct from Java, it is fully interoperable with Java code. You can also access Kotlin code from Java using Kotlin-specific annotations and the JVM platform.
This modern and robust programming language is more than efficient in addressing various Java issues. It is more concise and expressive than Java. Kotlin supports functional programming. Its JS compiler helps developers build statically typed frontend browser apps.
JetBrains made Kotlin a fault-proof programming language, making its maintenance easy and affordable. Thanks to the coroutine from Kotlin, it has become easy for developers to work with asynchronous code.
Features of Kotlin
- Null Safety: Null pointer exceptions are a major reason behind crashes in legacy Java apps. This feature protects Kotlin apps against it. It uses a strict type system that can find potential null-related issues during compilation.
- Data Classes: It simplifies the development of model objects and automates the creation of utility methods, leading to enhanced efficiency.
- Concise and expressive syntax: This makes it easy to read and maintain the code, enabling developers to avoid repetitive patterns and focus on writing code logic.
Pros of Kotlin
- Increased productivity: Supporting various IDEs, Kotlin helps improve developer productivity by allowing them to use a familiar toolkit, increasing overall output.
- Easy to learn: Kotlin was created to enhance Java functionality. So, it is similar to Java. Being familiar with Java allows you to easily use and understand Kotlin.
- Less Buggy: Kotlin code is lighter and concise than Java to help developers deliver consistent output. Kotlin can detect bugs during compilation, which can be easily fixed before runtime.
Cons of Kotlin
- Limited learning resources compared to Java: Kotlin has fewer resources, such as documentation, tutorials, implementation patterns, and third-party libraries, for developers to learn how to use the language.
- Fluctuating compilation speed: Sometimes, the compilation speed of Java is fast, whereas in other projects, it is rather slow. In terms of clean builds, Java trumps Kotlin.
- Larger runtime for simple projects: Even when you are building a simple project with Kotlin, the runtime requirements make it complicated. Even a lightweight app becomes a little heavy after compilation due to extra runtime dependencies.
1.18 Dart

Dart is a class-based, high-level, object-oriented programming language used for building web, desktop, mobile, and server applications. Initially, Google built this language for client-side development, but Dart eventually expanded into a full-stack language. Many developers and companies utilize this language as an alternative to JavaScript.
Although the first version of Dart was released in 2011, it garnered real popularity in 2017 when Google introduced Flutter beta for cross-platform mobile application development.
Features of Dart
- Asynchronous programming: With this feature, your program can operate without getting blocked. Dart is a single-threaded language. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that developers can perform their tasks without interruption.
- Built-in libraries: By default, Dart provides numerous packages and libraries full of ready-made functionalities for common web development tasks. This helps reduce manual effort and speed up the development process.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) and Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation: By supporting a JIT compiler, Dart allows hot reloading and faster iterations. And with AOT compilation, it generates optimized standalone executables.
Pros of Dart
- Beginner-friendly: Dart is relatively easy to learn. Once you are familiar with the basic principles of the language, you can start coding right away. Detailed documentation is available for all the features of Dart to guide you through web development.
- High speed: Dart offers high performance as its programs run faster in comparison to JS-based programs.
- Production-grade app development: Dart is considered a stable programming language that developers can leverage to create production-quality real-time apps. It also supports optional typing, interface inheritance, and other features. Dart uses JIT and AOT compilation.
Cons of Dart
- Limited resources: Dart lacks the support of a large and cohesive community of developers. Therefore, it doesn’t have a rich ecosystem of tools, libraries, and plugins.
- New language: Dart is still new for developers, so it is rarely used in the market, and there is rarely any demand for a Dart programmer.
- High development costs: Since the language is still growing, you have to use multiple third-party plugins to create a functional app or provide native support, which can be very costly and overwhelming.
1.19 NoSQL

A non-schema alternative to the RDBMS and SQLs, NoSQL is designed for storing, processing, and analyzing large sets of unstructured data. They provide flexible schema structures that help create sophisticated applications.
NoSQL databases are popular for their scalability, functionality, and ease of use. NoSQL uses JSON documents instead of rows and columns, as is the case with traditional relational databases.
In Database design, NoSQL is an approach providing a mechanism to store and retrieve data, modeled differently from tabular relations used in relational databases. However, a common misconception about NoSQL is that it isn’t used for Structured data. The reality is that NoSQL databases are suitable for structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. They also support multiple data types like documents, graphs, key-value pairs, and hierarchical data.
Features of NoSQL
- Peer-to-Peer architecture: This database has a masterless, peer-to-peer architecture where all nodes are the same. This allows easy scaling to adapt to increasing data volume and app complexity, leading to high read/write speed and continuous availability.
- Global data distribution: Having multiple data centers and cloud regions for read-write operations across different locations enables the NoSQL database to distribute copies of data across the globe.
- Multiple data model compatibility: Being compatible with multiple data forms provides flexibility and easy data management, ensuring that ingested data is well-structured.
Pros of NoSQL
- Low data maintenance: NoSQL replicates information across nodes and can automatically partition, resulting in reduced database administration. This also helps bring down the costs.
- Flexible Schema: NoSQL doesn’t have to define the schema to store and manage dynamic, unstructured, or semi-structured data. This helps you avoid schema migration overhead and quickly adapt to changing data requirements.
- Horizontal scalability: NoSQL’s capability to scale horizontally saves money that goes into expensive hardware. It allows you to scale easily using sharding and replication techniques.
Cons of NoSQL
- Limited ACID Support: ACID compliance is a necessity in many projects, and not every NoSQL database offers it. Its support is specific to use cases. So, developers have to analyze the trade-off before getting started with NoSQL.
- Tooling and Ecosystem Maturity: NoSQL databases are less mature than SQL databases in terms of community resources, third-party integrations, and libraries. As a result, developers may face challenges regarding monitoring, maintaining, and debugging their apps.
- Learning Curve: It is difficult to learn NoSQL databases, especially if you regularly work with relational database paradigms. The concepts, query languages, and data models here are new and take some time to adapt and master.
1.20 R

R is a free software environment. This programming language is designed specifically for graphics and statistical computing. Developers predominantly use this language for visualization, statistical modeling, and data analysis.
Features of R
- Graphics: R comes with comprehensive capabilities for graphical data visualization. In addition to the base graphics, R also offers packages for advanced plotting abilities.
- Data management tools and packages: The R programming language is rich in terms of user-contributed packages, which help extend its capabilities. The Comprehensive R Archive Network repository has thousands of packages. R offers a wide range of tools for data analysis and management operations, including wrangling, cleaning, and importing data.
- Statistical analysis: R is a tool designed for statistical analyses like hypothesis testing, time series analysis, linear and non-linear modeling, etc, using ready-made functions from its libraries. They also help perform complex statistical tasks demanding different levels of expertise.
Pros of R
- Extensive Package Ecosystem: With the support of a massive active community, R now boasts over 18000 packages on CRAN covering a diverse range of fields from finance to ecology to fulfill their data analysis requirements.
- Data visualization: Visualization libraries like ggplot2 provide a versatile approach for generating different kinds of data visualizations, like graphs, plots, and charts, to represent insights derived from the data effectively and elegantly.
- Community support: In addition to building tools and libraries, the community also offers extensive documentation, tutorials, and expert guidance through online forums to help learn or overcome issues.
Cons of R
- Steep learning curve: R feels unintuitive, especially to users who are new to programming. The syntax is different, so it takes time to get used to concepts in R like data frames and vectorization.
- Performance limitations: When using R for complex calculations or managing large volumes of data, web developers may face performance issues because of its interpreted nature. So, you can’t use the language for high-performance computations.
- Inefficient memory management: On top of performance issues, when dealing with large datasets in R, you may also experience issues with memory allocation.
2. Conclusion
In a nutshell, we can say there are many front-end and back-end developments, and choosing the best web development languages is not an easy task. There are front-end languages, full-stack development languages, server-side scripting languages, object-oriented languages and many other general-purpose languages too. These languages are flexible with desktop, web, and mobile apps. Companies hire a well-educated and skilled workforce who have an understanding of popular web development languages. These are ways to create faster, more efficient, and high-performing web applications.





Comments
Leave a message...