
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software has transformed the functioning of modern industries. Besides large organizations, it is increasingly being adopted by small and medium-sized industries. ERP integrates core business functions and presents consolidated data, simplifying business operations. The finance module in the ERP system is a foundation pillar containing various components related to accounting, reporting, and finance.
In this blog, we will explore the ERP Finance module, focusing on its key features and benefits. The real-life examples of widely adopted ERP Finance modules developed by finance software development companies will further enhance your understanding. You will also learn about the scenarios in which selecting the most suitable Finance module is essential.
1. What is an ERP Finance Module?
The finance module, also known as ERP core finance, is one of the key components of an organization’s ERP software. It manages the organization’s accounting and financial operations and functions as the central nervous system of the ERP. Accounting software primarily manages the financial activities of an organization, whereas the ERP Finance module has a broad scope. It integrates financial data with various business processes to provide centralized management of financial flows.
1.1 ERP Finance Module Features
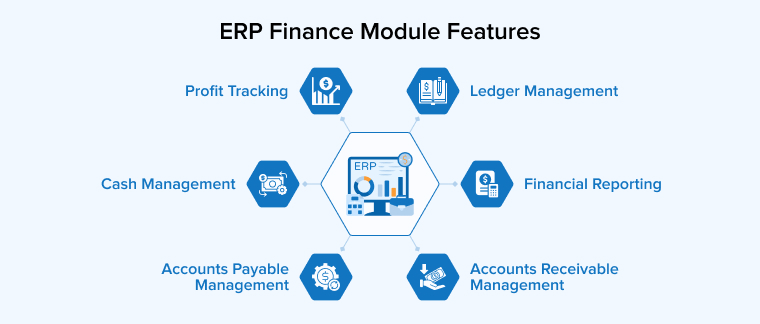
The properties of ERP core finance may vary across ERP systems used by organizations, depending on their scale.
1. Accounts Payable Management
The Accounts Payable component manages payments a company must make to external parties, such as banks, investors, vendors, clients, or customers for goods and services purchased. The component processes large invoices, shares them with the relevant parties, schedules and tracks payments, and manages vendor accounts. It helps companies gain a comprehensive view of their financial status by indicating current liabilities on the balance sheet, thereby improving relationships with suppliers and customers.
2. Accounts Receivable Management
Accounts receivable, or AR, functions as the opposite of accounts payable. A company must maintain a proper record of how much external parties owe to the business, in addition to how much the company owes. The AR component generates invoices, receives orders, sends reminders about unpaid invoices, collects due amounts, etc. All these details are recorded in an AR subledger or invoice register.
3. Ledger Management
A general ledger (GL) is the central component of the ERP finance module that provides an overall view of a company’s financial health. It is a comprehensive record of a company’s financial transactions for the current financial year. The GL covers purchases, income, expenses, capital accounts, cash flow, sales, fixed assets, liabilities, and inventory transactions. It imports and organizes data from all sources by classifying them into accounts such as payables, receivables, cash, and inventory, and thereby preparing accurate reports and statements.
4. Cash Management
Businesses need to keep track of liquidity inflow and outflow for effective cash management. The cash management component, also referred to as treasury management, processes and analyzes all cash flow transactions, including bank activities, invoices, payments, and receipts. It involves setting up bank accounts and tax accounts according to regulatory standards, as well as performing bank reconciliations to ensure that records align with bank statements. In addition to managing domestic transactions, it also oversees foreign accounts for transactions in international currencies across global financial institutions.
5. Profit Tracking
The profit tracking feature of the finance module provides an overview of the profit margin in the company’s financial transactions. It helps identify which products and services sales contribute to profit and which are underperforming. The analysis not only determines current profitability but also predicts future trends.
6. Financial Reporting
Generally, ERP finance modules have built-in reporting and analytics features that generate various types of reports in different formats to provide helpful insights.
1.2 Benefits of ERP Financial Modules
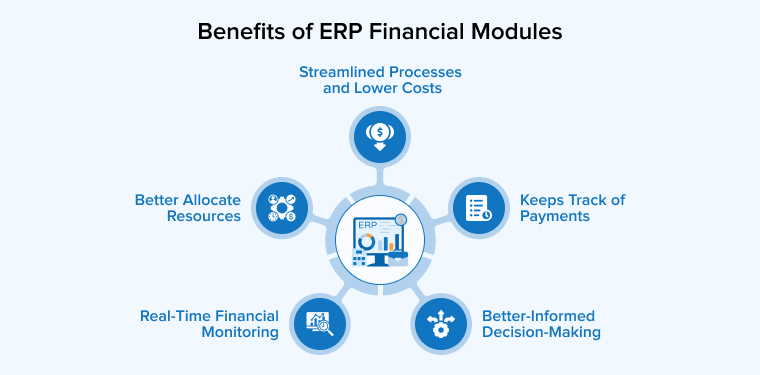
The automation of financial processes plays a major role in the overall functioning of ERP software, as money is the focal point of business operations. Here are the top five advantages an organization gains from using the ERP finance module:
1. Better-Informed Decision-Making
The finance module provides accurate real-time reports, scorecards, and dashboards that present data in a clear and understandable format. It is crucial for the company, as well as for banks, tax regulatory agencies, and stakeholders. The business analysts can determine and analyze trends across key financial performance metrics. It will help higher management adjust and develop strategies needed to align expected results with business objectives. They can better understand the outcome of their decisions and prepare accurate budgets and plans, supporting effective strategic planning.
2. Keeps Track of Payments
It maintains a record of customer payments, tracks revenue, and manages credit. The finance module monitors invoices in real-time and sends automated alerts and notifications to remind users about upcoming payments. Companies can set automatic payment deductions on specific dates to avoid delayed or missed payments.
3. Streamlined Processes and Lower Costs
With the use of the finance module, the burden of repetitive manual work and administrative overhead has been reduced for employees and staff. Manual entries are time-consuming and prone to errors, which can lead to accounting issues. The ERP core finance module eliminates this possibility to a large extent through built-in controls.
Now, companies are no longer required to subscribe to multiple platforms for different tasks, which benefits them not only in cost management but also by reducing task duplication and manual data entry. This allows businesses to focus their time and resources on core activities, increasing productivity and profitability.
4. Real-Time Financial Monitoring
A company must maintain strict control over its financial operations. ERP finance provides detailed, real-time oversight of all transactions and their financial implications, enabling timely and accurate decision-making. Relevant personnel can detect any unusual financial activity, supporting effective risk management to mitigate future risks.
5. Better Allocate Resources
The automation of manual processes and real-time visibility of financial operations helps in preparing optimized budgets, thereby improving resource allocation. Financial transparency guides investment resources in the right direction and manner.
2. Examples of the Finance Module in ERP
Let’s discuss some of the most widely used ERP finance modules and understand the factors behind their high popularity:
2.1 QuickBooks Online
QuickBooks Online by Intuit Inc. is a cloud-based finance module within an ERP system, best suited for small and medium-sized businesses. It is used across various industries, including retail, construction, healthcare, manufacturing, and wholesale.
Features
- Inventory Management: It provides end-to-end inventory management by monitoring stock levels, sending reminders for stockouts, tracking sales and purchases, creating purchase orders, and managing vendor tasks.
- Invoicing: QuickBooks eliminates manual invoicing by allowing companies to send customized invoices to clients. It tracks unpaid invoices, sends payment due notifications, matches payments, and improves cash flow management.
- Multi-user Access: QuickBooks allows multiple users to log in simultaneously, enabling Finance team members from different teams to collaborate and coordinate on the same task with varying permissions and access levels.
Advantages
- Smooth Integration: Businesses require multiple tools to manage different aspects. QuickBooks easily integrates with financial tools like PayPal, Expensify, and Gusto, and syncs all the data seamlessly.
- Easy to Use: QuickBooks offers a great user experience, allowing even those with limited experience to perform basic accounting tasks. Video tutorials and online lessons help guide users in using the platform.
- Cost-efficient: QuickBooks is one of the most affordable accounting software programs, making it helpful for startups and businesses in their initial years of operation.
2.2 Zoho Books
Zoho Books, a part of the Zoho product suite, is a cloud-based ERP solution designed for small and medium-sized businesses. It includes all the necessary tools and functionalities that small business owners or freelancers would need to manage their finances efficiently.
Features
- Simple Setup: It’s easy to get started with the Zoho accounting software by simply connecting your bank accounts. The user interface is designed for easy navigation and efficient execution of complex processes.
- Multi-currency Support: If a company deals with clients abroad, Zoho Bookkeeping supports transactions in foreign currencies to ensure smooth international operations. It automates the tracking and conversion processes.
- Data Security: Industry-standard protocols such as two-factor authentication, SSL, and IP restrictions protect sensitive financial information from unauthorized access and ensure its confidentiality.
Advantages
- Tax Compliance: Zoho Books supports local tax compliance through its web-based accounting program. Account professionals can generate tax summary reports to accurately calculate and understand taxes.
- Cloud-based Convenience: As Zoho is a cloud-based software, authorities can access financial details from any location at any time. Cloud data storage also facilitates backup and restore to reduce data loss.
- Scalable: Zoho adapts to growing business requirements. The software plans can be upgraded, and integration with payroll and other DCRM tools is possible, allowing businesses the flexibility to expand.
2.3 Acumatica
Acumatica is an integrated, cloud native ERP platform. Its finance module is a comprehensive suite of tools designed to manage financial operations ranging from simple to complex.
Features
- Deferred Revenue Accounting: Acumatica calculates deferred revenue based on established schedules and posts it automatically. It ensures that financial statements include all deferred revenues.
- Cash Management: The accounting software manages day-to-day transactions, forecasts cash flows, handles fund transfers, performs bank account reconciliation, maintains audit trails, etc.
- Currency Management: The software tracks currency losses and gains, revalues General Ledger accounts, and complies with FASB-52 standards.
Advantages
- Customizability: Companies can customize the workflows of different modules in Automatica according to their work requirements.
- Boosts Efficiency: Employees’ productivity and work output increase with automated tax filing reports, gain and loss calculations, and tax codings.
- Scalable: Accumatica is designed to be extensible to accommodate growing business needs. Users can add modules and features to support new business operations without affecting the existing ones.
3. Factors to Consider When Choosing an ERP Finance Module
With the rising demand for ERP solutions, users often find it overwhelming to select the appropriate software for their financial operations. There are multiple factors to evaluate beyond just the pricing structure. So, are you in need of a robust ERP Finance module but new to this domain? Are you struggling to find the best solution?
Read the following parameters and develop your vision of choosing the right software.
3.1 Assess Your Business Requirements
Analyze the need for a finance module. This is the first and foremost step. Conduct an audit of the business processes, consult with all the stakeholders, and get their opinions. Afterwards, based on their feedback, create a list of requirements that justify the need for ERP software.
3.2 Integration Capabilities
Your organization may be using different software applications such as CRM, supply chain management, and other third-party tools. It is important that the ERP system you develop or purchase can integrate with these existing systems to ensure smooth operations. Evaluate whether integration with the ERP will require vendor support or if it can be done automatically.
3.3 Vendor Credibility
Today, the software industry has made significant progress in developing enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. The market is filled with ERP vendors claiming to offer custom ERP solutions. Therefore, before selecting a vendor, it is important to conduct thorough research into their past projects, on-site support, market reputation, customer reviews, training resources, targeted industries, and more. This approach will not only be cost-efficient now but also help avoid future expenses.
You can consider partnering with reputable finance software development companies like TatvaSoft to get the best custom ERP finance module.
3.4 Scalability and Customization
The business requirements evolve with technological advancements and user needs, leading to the processing of a large volume of transactions. Therefore, ERP implementation must be carried out with future expansion and growth in mind. The solution must be flexible enough to allow customization of modules based on industry needs.
3.5 User-Friendliness
If the module has an intuitive and easy-to-understand user interface, the organization’s training cost may be reduced. Hence, assess the technical capabilities and understanding of the employees who will use the system, in addition to evaluating the user-friendliness of the ERP’s UI.
3.6 Regulatory Compliance
The Finance module must adhere to the industry regulations and standard accounting workflows. Since tax laws vary by location, manually ensuring compliance becomes cumbersome. Therefore, the ERP must ensure automatic compliance with the standard tax laws of the country.
4. Final Thoughts
ERP Finance modules offer long-term advantages and are becoming essential in today’s business environment. Their agility and scalability are key drivers of success. However, their development is highly challenging and complex. With the advent of AI, this complexity graph is increasing further. Therefore, a deep technical understanding of the required development technologies and market trends is necessary to create a relevant and cost-effective ERP Finance module.
FAQs
What is the use of ERP in finance?
ERP systems can manage an organization’s financial operations by automating many fundamental processes and providing a comprehensive picture of the organization’s financial condition.
What are the 5 components of ERP?
Below are the five main components of ERP software:
- Human Resources
- Supply Chain Management
- Accounting and Financial Management
- Logistics and Manufacturing
- Customer Relationship Management






Comments
Leave a message...