
Continuous testing in DevOps ensures that software is tested automatically at every stage of the software development lifecycle. This approach makes testing an ongoing activity rather than a final step, providing rapid feedback and detecting issues before they grow into costly problems.
For businesses facing high competition, continuous testing ensures agility, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Partnering with a skilled software testing company can help organizations design robust test frameworks and implement continuous testing strategies effectively. In this blog, we will explore continuous testing, its role in DevOps, the implementation process, its benefits, challenges in implementation, and best practices for adoption.
1. What is Continuous Testing in DevOps?
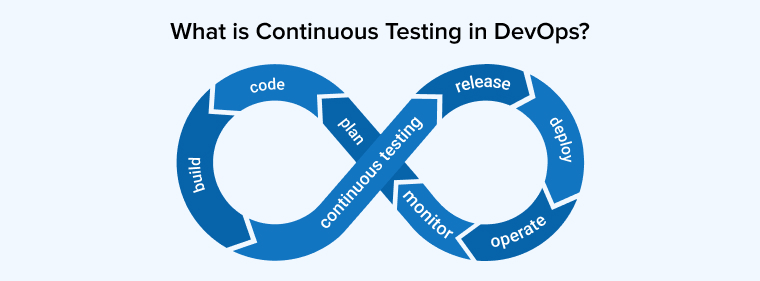
Continuous testing in DevOps is the practice of running automated tests throughout the software development process to ensure that code changes are reliable, functional, and release-ready at any time. Unlike traditional testing, which is often left until the final stages, continuous testing integrates quality checks directly into the CI/CD pipeline. This means tests are automatically triggered with every code commit, build, or deployment, providing immediate feedback to developers and testers. By validating everything from small user stories to complete system requirements, this approach ensures that software remains stable as new features and updates are introduced.
Here is what an X user says about continuous testing in DevOps.
Continuous Testing in #DevOps is less about testing constantly and more about testing in continuity of events (code check-in, dependency update, infrastructure change, …)
— 🌤️livier Jacques (@ojacques2) January 13, 2021
1.1 How Does Continuous Testing Play a Vital Role in DevOps?
Let’s discuss how continuous testing plays a key role in DevOps:
1. Integrating Testing
In a continuous integration (CI) setup, automated tests run whenever new code is merged into the shared repository. These tests confirm that modules and components interact properly, ensuring smooth collaboration among developers’ contributions. Continuous integration testing prevents functional regressions, safeguards software stability, and maintains overall code integrity as the application grows and evolves.
Here’s what a Quora user shared about integrating testing.
2. Deployment Readiness
Testing at regular intervals helps teams assess whether the product is ready for deployment. Software that comes out of the delivery pipeline should be production-ready. The goal is to keep a software version ready for production at any point in the pipeline, ensuring smooth deployments
3. Feedback Loop
A continuous feedback loop gives developers instant insights from automated tests, allowing them to identify and fix issues early. This reduces costly late-stage errors, supports faster iterations, and encourages continuous improvement. By promoting timely decision-making and collaboration it strengthens overall software quality and development efficiency.
4. Risk Mitigation and Efficiency
Continuous testing effectively detects critical bugs early in the process, mitigating the risk of costly fixes later and optimizing time and resource allocation. This proactive approach allows teams to address issues as they arise, preventing them from escalating and affecting subsequent stages, ultimately producing higher-quality software and faster delivery.
1.2 Benefits of Continuous Testing in DevOps
Continuous testing offers multiple advantages in the development of modern applications following modern architectures such as microservices, serverless, or event-driven patterns to meet evolving demands. Below are the common benefits of continuous testing in DevOps:
1. Early Detection of Bugs
Continuous testing begins at the development stage with unit tests written by developers. This early focus ensures defects are detected and fixed at their source, preventing them from growing into larger issues. By addressing problems quickly, teams save time, reduce costs, and improve overall code quality. Early defect detection ultimately produces a stronger, more stable, and more reliable application that supports smoother delivery and better user experiences.
2. Team Integration
In traditional software development, teams often operate in isolation, which leads to communication breakdowns, slower release cycles, and more errors. In DevOps, continuous testing bridges the gap between development, quality assurance, and operations, making testing a shared responsibility.
3. Improved Software Quality
Running tests at regular intervals reduces errors and helps deliver a cleaner product. Validating quality standards at every stage minimizes issues, ensures features work as expected, and gives users a smoother, more reliable experience.
4. Reduce Testing Efforts
Continuous testing reduces testing effort by introducing automation and moving tests earlier in the development cycle. This proactive approach identifies issues sooner, streamlines processes, and enables faster, more efficient delivery of high-quality software.
5. Better Test Coverage
Performing automated tests from the early stages of the software development lifecycle, when risks are lower, is a proactive and comprehensive testing approach. Developers and testers then have sufficient time to perform various tests, such as integration and end-to-end testing, to evaluate the application from multiple perspectives.
Here’s what a Reddit user had to say about improving test coverage:
Comment
byu/bigboybamo from discussion
incsharp
6. Faster Releases
Continuous testing of both new and existing code prevents launches from being delayed due to unfinished pre-release tests. It gives developers quick feedback so they can make necessary changes and keep the code release-ready. Continuous testing also enables companies to deliver features and updates faster, ensuring a steady flow of high-quality software that helps maintain a competitive advantage.
2. How to Implement Continuous Testing in DevOps?
Let us now discover a well-planned strategy with clear aims, suitable tools, and continuous collaboration and improvement to implement continuous testing in the DevOps pipeline:
2.1 Define Clear Testing Objectives
Defining clear testing objectives at every stage of development is crucial for achieving reliable outcomes. By setting specific goals, such as identifying bugs early, verifying functionality, ensuring performance, or meeting security standards, teams can align testing activities with project requirements.
Establishing measurable targets like 80% code coverage provides a clear benchmark for progress. Continuous feedback from test results enables developers to take corrective action promptly. With well-defined objectives, testing becomes more focused, structured, and effective, ensuring both quality assurance and alignment with overall project goals throughout the software lifecycle.
2.2 Select the Right Testing Tools
Now that you’re clear on the testing goals and the tests you will perform, it’s time to select the tools. The tools must not only align with your project requirements but also support multiple testing types, the language used for test cases, organizational goals, and the project team’s skill sets, as well as integration with the DevOps pipeline and scalability for future growth.
Certain aspects, such as robust technical support, code reusability, and comprehensive reporting, must also be considered when evaluating continuous testing tools. It isn’t easy to find the right tool; you may need to use a trial-and-error approach to identify the most appropriate one.
To help you out, here’s a consolidated list of automation testing tools you can consider for different stages of the testing process:
| Type of Tool | Name of the Tool | Tool Description |
|---|---|---|
| Build Tools | Maven | Automates the building of mainly Java projects |
| Gradle | Popular Android development open-source build automation tool | |
| Version Control Systems (VCS) | Git | An open-source distributed version control system to manage source code |
| Subversion (SVN) | An open-source centralized version control system used to manage source code | |
| Test Management Tools | TestRail | Web-based multipurpose test case management tool |
| Continuous Integration (CI) Tools | Jenkins | Open source Java-based continuous integration (CI) server to automate building, testing, and deploying code |
| Travis CI | Cloud-based CI/CD service to build and test projects hosted on GitHub, BitBucket, etc. | |
| Functional Testing | Selenium | Open-source web browser automation tool |
| Ranorex | GUI test automation framework for desktop, web, and mobile applications | |
| Cypress | JavaScript-based front-end web application testing framework | |
| Security Testing | OWASP ZAP | Open-source web application security scanner |
| Burp Suite | Penetration testing software package for web applications | |
| Monitoring and Logging | New Relic | Real-time cloud-based performance monitoring and management tool |
| Datadog | SaaS based monitoring and analytics platform | |
| Test Environments | Docker | An open-source containerization platform to pack an application and its Dependencies |
| AWS (Amazon Web Services) | Cloud infrastructure for scalable test environments | |
| Deployment Tools | Jenkins | Automates application deployment into different environments |
| Ansible | Automation tool used for infrastructure as code | |
| Kubernetes | A container orchestration platform to deploy, scale, and manage containerized applications |
2.3 Integrate Test Automation into CI/CD Pipelines
Automated test suites should be embedded in the CI/CD pipeline so tests run automatically when code is committed, merged, or deployed. This ensures consistent test execution and a steady stream of test results throughout development. The test setup must produce accurate reports, identify defects and issues introduced by new code, and, when appropriate, suggest last-minute changes to developers.
2.4 Monitor and Analyze Test Results
Configuring automated test execution does not mark the end of implementing continuous testing. You must regularly monitor and analyze test results to verify whether the chosen testing strategy is producing the expected outcomes according to predefined performance metrics and meeting project goals. Identify trends and root causes of failures, assess whether adjustments are possible, highlight areas requiring special attention, and detect bottlenecks. Also, track defect rate and other key indicators using the test outcomes.
The data-driven decisions provide a solid foundation for continuously improving testing strategies and practices. Optimize automation frameworks and test cases based on industry trends, real-world insights, and historical test data.
2.5 Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
We know that continuous testing (CI) is an ongoing process; therefore, development, operations, and testing teams must coordinate to increase efficiency. Quality must be a shared responsibility, so evaluation and refinement of the testing strategy should be continuous. Collaboration fosters a culture of continuous learning and improvement, creates an effective feedback loop, reinforces a DevOps mindset, aligns teams with business objectives, promotes shared responsibility, and more.
3. Challenges in Implementing Continuous Testing
There are multiple sets of challenges you’ll come across while implementing continuous testing in the DevOps pipeline:
3.1 Integration with DevOps
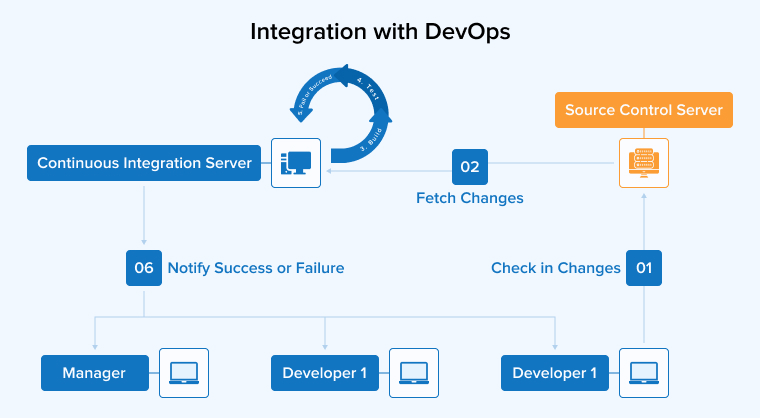
Achieving true continuous testing relies heavily on extensive test automation. CI uses a diverse set of tools for version control, CI/CD, testing, monitoring, and more. Different teams adopt different tools and configurations, which can cause toolchain incompatibilities and make integration difficult. Often, standard tools aren’t available, so teams rely on in-house test automation that lacks proper documentation and maintenance. This further complicates integration.
As a variety of automation tools is available, selecting the right ones can be overwhelming. Using these tools requires proper training, which is often lacking because of resource constraints or other reasons.
Here’s what a Quora user says about integration with DevOps.
3.2 Regular Code Integration
When multiple developers’ code changes aren’t merged regularly, problems can arise — for example, merge conflicts from duplicate or incompatible code. It can also be difficult to keep the test environment aligned with the latest integrated code. Any discrepancy will affect the accuracy of the test results.
3.3 Updating Testing Strategies
The traditional testing strategy involves testing only after development is complete, so bugs are detected late, and fixing them can be expensive and time-consuming. This contrasts with the continuous testing approach, a shift-left practice. Conventional testing may fail to uncover all vulnerabilities in modern applications. Using outdated or poorly managed test data can misrepresent real-world scenarios, producing inconsistent and error-prone results.
3.4 Performance Bottlenecks
Performance testing and functional testing require substantial infrastructure and resources, resulting in an entire system slowdown if not managed properly. Test execution is time-consuming and therefore requires careful planning for integration into the CI/CD pipeline. Generating realistic test data is complex and can affect performance results, making it harder to identify the real performance bottlenecks.
3.5 Maintenance
Automated test scripts must be synchronized with every change, whether from new features, changes in UI design, updates, etc. Test results are sensitive to small application changes, so test scripts should be revised regularly to maintain complete test coverage.
Major difficulties arise with the scaling of systems as test scripts become complex and hence difficult to maintain. If the development and testing team do not work in coordination, or if automation skills are not up to the mark, the project may face multiple challenges.
4. Best Practices for Continuous Testing in DevOps
Let’s understand the top five best practices that you must implement while integrating continuous testing in the DevOps pipeline:
4.1 Integrate with CI/CD
Integrate automated tests into the CI/CD pipeline to get immediate feedback on every code change and ensure timely validation. To do this, configure the chosen CI/CD tool, for example, Jenkins, to execute the relevant test suites automatically on every commit. Define pipeline stages corresponding to the types of tests you want to run, and implement a mechanism that immediately notifies the team if any test fails.
4.2 Developing or Adopting a Test Framework
A robust test framework is essential for continuous testing in DevOps because it standardizes testing processes and ensures consistency across teams. Developing or adopting a reliable framework enables automated test execution, faster feedback, and easier maintenance. It also supports scalability by allowing new tests to be added seamlessly as applications evolve.
4.3 Utilize the Right Tracking Metrics
Tracking both failed and successful tests is important for measuring test success and failure rates. Select performance metrics according to your testing goals. Examples include test execution time, pass/fail rates, defect density, and test coverage. These metrics provide actionable insights into the testing process and software quality.
Tracking these metrics gives you an accurate picture of the application’s performance at a particular stage of development. As a result, you can design a more robust and effective testing strategy that will improve the application’s long-term functionality.
4.4 Adopt Automation Wherever Possible
Manual testing is time-consuming and labor-intensive, and does not guarantee accurate results because human error rates can be high. Therefore, adopt extensive automation to replace manual tasks and reduce the possibility of mistakes at every stage of development. This will increase the speed of delivering thoroughly tested releases. Automation lets the team concentrate on more complex work and eliminates repetitive, routine tasks.
4.5 Test at Every Stage of the Development Cycle
In DevOps, continuous testing emphasizes verifying software quality at every stage of the development cycle. By integrating tests early and running them consistently, teams can detect defects before they escalate, reducing overall costs and risk. Applying continuous testing methodologies ensures that code remains stable and functional as new features and updates are introduced. Embedding testing as a core practice builds confidence in deployments, accelerates delivery, and supports the creation of reliable, high-performing applications that meet user expectations.
5. Final Thoughts
Continuous testing in DevOps is more than just automating tests; it is about embedding quality into every stage of the software delivery pipeline. By integrating testing within CI/CD, teams gain immediate feedback, reduce risks, and ensure that applications remain stable as they evolve. An effective continuous testing strategy relies on selecting the right tools, frameworks, and environments that align with organizational needs, while supporting flexibility and scalability. In today’s competitive market, adopting continuous testing is not optional but necessary for enterprises that want to deliver reliable, high-performing software quickly. By embracing this approach, organizations can stay ahead, meet user expectations consistently, and maintain an edge in the ever-changing digital landscape.
FAQs
What are the different types of testing in DevOps?
DevOps includes different types of testing, such as unit testing, integration testing, functional testing, end-to-end testing, and API testing.
Which of the following is a continuous testing tool used in DevOps?
Tools such as Selenium, Jenkins, Git, and Maven are commonly used in continuous testing within DevOps.




Comments
Leave a message...