
Delivering reliable, high-quality software is not easy. Development teams must follow a specific set of steps across the different stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). Among those phases, performance testing is important for assessing the quality and performance of the product within a dedicated performance testing environment.
In this phase, the software undergoes various types of testing, checking it against certain parameters or test cases. One basic requirement for testing is a test environment. The test environment comes in different shapes and sizes and can be found in almost every stage of the SDLC, but it is largely used in the testing phase.
As a reputed software testing company, we understand the importance of a test environment. Therefore, we present this article to share valuable insights on setting up and managing a test environment in software testing.
1. What is a Test Environment?
A test environment is a setup that mimics the conditions of the actual device or browser, where software will run. It is used to detect defects, code errors, and vulnerabilities through manual or automated testing.
A testing environment is created to verify whether the developed software product meets the user requirements. If it does not, the environment helps identify the gap between the actual results and the expected outcomes. A stable and controlled environment is required for efficient testing. Prepared test cases cannot produce accurate results if the test environment is affected by unexpected or external variables.
A test environment consists of a combination of servers, hardware, software, and network configurations used to run the testing software. These configurations are set up according to prepared test cases to test the software across different devices, browsers, operating systems, and various real-life scenarios.
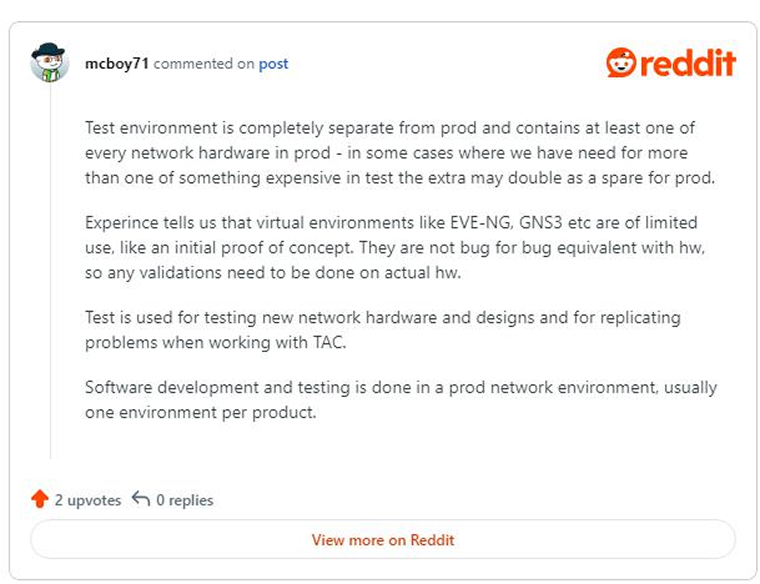
A Reddit user thread about the Test Environment.
1.1 Importance of Test Environment
You can’t release untested software to the public. Even a beta version must be thoroughly tested before being deployed in a production environment for beta testing. A comprehensive software testing requires a carefully prepared test environment.
The test environment is a dedicated space for testers to isolate and examine the code. Even when new or modified code is tested on the same server where the existing code runs, the test environment ensures that the testing doesn’t affect the application output.
A test environment in software testing is important for the following reasons:
- Risk Mitigation: By mirroring the production environment, a test environment reduces the risks of releasing faulty software by detecting issues and errors that may occur in various instances.
- Streamlining Testing Activities: A test environment allows the test cycles to run smoothly. Testers and QA experts can easily coordinate schedules and use shared test assets within the same test environment, which helps streamline testing activities. This improves testing efficiency and helps prevent delays in the software launch.
- Bug Identification: The primary purpose of managing test environments is to provide the necessary setups for running different tests. A faulty environment can prevent the detection of errors in the code. Accurate bug identification is possible, thanks to the effective test environment.
- Increased Automations: Using a test environment reduces the burden on testers. Because the test environment automates most of the activities, including running test cases. Reducing manual testing also decreases errors and costs. Moreover, increased automation in testing activities helps ensure greater data compliance.
- Training & Demonstration: Testing environment provides a parallel interface that allows users to train or familiarize themselves with new software features in a beta version without affecting the existing application operations. A test environment also acts as a stage for testers to demonstrate the new capabilities of the software to stakeholders.
- Test New Features: Testing new features is the primary purpose of a test bed. Testers can assess the performance of these features under real-life scenarios using a test environment.
1.2 Types of Test Environment
In a software development life cycle, testers must create different test environments to meet specific testing needs. This section provides a brief discussion on each type of software testing environment and its purpose.
1. Security Testing Environment
This test environment analyzes software for security gaps, flaws, and vulnerabilities, focusing especially on data confidentiality, compliance, user authentication, and authorization. A security testing environment helps both internal and external cybersecurity experts identify which parts of the software are most likely to be targeted and determine how malicious code can infiltrate the system.
2. Integration Testing Environment
It is to test if various modules can easily integrate to form a fully-functional software because often these modules consist of source codes, third-party applications, clients, app servers, and shared databases. Testers use this environment to simulate the production environment to check the integration functionalities of the software.
3. Chaos Testing Environment
Sometimes, software in production environments suddenly faces an extreme surge in traffic, putting significant stress on the network and the application servers. Chaos testing allows you to check how your software would perform under extreme circumstances or when exposed to sudden stress or pressure. Different sets of conditions are set up to imitate real-life stressful situations in this software testing environment.
4. Staging Environment
It’s an environment where you create an instance of the app to demonstrate it to stakeholders and not end users. This environment accurately simulates the production environment but is restricted to selected people. Only the developer team, whitelisted IP addresses, and approved email addresses can access and use the application in the staging environment.
5. Production Environment
It’s the environment where the application runs on the production server and is accessible to real users. However, before making it officially live for all the users, the software is given to selected groups of people for beta testing in a dedicated beta testing environment. Here, the users would test the software to identify any issues, especially those related to performance. If any defects or bugs are found, they are immediately fixed before deploying it to everyone.
So, if the software application is in the production environment, then it doesn’t mean all the tests are completed. The product can still undergo beta testing in the production environment, which provides a more accurate understanding of the app’s performance and helps validate its functionalities.
1.3 Key Elements For Setting Up a Test Environment
You need various elements to set up a stable test environment that supports efficient and consistent testing of software applications. Here’s what you need:
- Test Data: Testers and QA experts need consistent, accurate, and complete test data to create effective test cases. This data is often sourced or gathered from relevant databases and servers.
- Network Protocols: Network configurations are essential for testing software applications under various conditions. These protocols allow you to set configurations according to your testing needs, like testing the app on wireless networks, local area networks, or private networks.
- Hardware and Operating System: Check if the targeted devices and platforms can support your software applications. Use hardware, like mobile phones and desktops, along with platforms like iOS and Windows, to test your app’s code execution.
- Automation Testers: Automated testing tools increased the speed and efficiency of testing processes. They help automate the creation of test scripts and execution of test cases, among other activities.
- Manual Testers: The testers and QA experts perform tests manually without using automated scripts or tools.
- Documentation: For proper testing, testers need documentation, installation guides, configuration guides, and user manuals to understand the system. This information helps them design appropriate test cases.
2. Process of Test Environment Setup
Follow a step-by-step process explained below to set up your software testing environment:
Step 1: Know What You’re Testing
The first step in setting up a testing environment is to understand what you will be testing. Necessarily, you must have clarity on testing requirements and objectives. Gather the details about the scenarios to configure every aspect of the software product under testing. If necessary, review the installation guides, user manuals, and documentation to gain a thorough understanding of the product you will be testing.
Step 2: Install Required Software
After determining what you need to test, it’s time to decide on the software and hardware required for testing. For example, you may need a different operating system, middleware, application server, or other components to run tests on your software.
Ensure to involve only those things that would help simulate the production environment, making your tests more accurate. Many software applications may require additional configuration to meet the identified testing requirements.
Step 3: Set Up the Network
After installing the necessary software, you need to set up an appropriate network for the testing environment. Some software runs on a local area network, whereas others run on a private or wireless network. So, you need to set up a suitable network with the necessary configurations to mimic real-life scenarios like a sudden spike in web traffic. Connect the network with devices on which you are running the tests.
Step 4: Prepare Test Data
Create data that reflects the real-world scenarios to test the software. Ensure the data covers all test cases and edge conditions relevant to the application. The next step is to load all the test data into the testing environment.
Step 5: Execute and Quick Check the Result
Once you have a stable test environment with reliable data, it is time to execute the predefined test cases. If you use automated tools, the tests can be performed simultaneously. Meanwhile, manual testing tends to be more time-consuming.
If all the intended tests are performed without any issues, it means your test environment works as intended. If you face any issues during execution, then assess it to identify the problem. Meanwhile, these tests will help uncover faults in the software.
Step 6: Maintain the Environment
After successfully running the tests once, your environment requires regular maintenance and updates to remain stable and useful for other test runs. If any issues are detected, then ensure that they are addressed immediately.
For that, you must monitor the health of the test environment and implement necessary updates to its hardware and software. Regular monitoring also helps identify potential issues that may cause problems in the future. It’s best to proactively address them to maintain the integrity and performance of the testing environment.
3. Examples of Test Environment
Let’s say you are testing the Hospitality Management service website. You’d need:
- Operating System (OS): Windows 10, macOS Ventura.
- Browser: Chrome (latest version), Edge, Firefox, Safari.
- Database: MongoDB.
- Test Automation Tool: Playwright.
- API testing tool: Postman.
- Security Tools: OWASP ZAP (security vulnerability scanning).
If you also want to test on mobiles, consider mobile environments:
Mobile Devices:
iPhone 15 Pro (iOS 18)
Samsung Galaxy S24 (Android 14)
Google Pixel 7 (Android 13)
Mobile Browsers:
Safari (iOS)
Chrome Mobile (Android/iOS)
4. Challenges in Test Environment
We discussed the six-step process to set up the environment, but it’s easier said than done. Testers and organizations often face many difficulties in setting up a stable and reliable testing environment.
4.1 Automating the Tests
Automation enhances the speed and efficiency of testing activities. Therefore, quality analysts often prioritize automated testing instead of manual testing. However, test automation involves technology-intensive activities, such as writing test scripts and managing automation frameworks.
So, the process demands the supervision of an expert with strong technical knowledge and experience in test automation. Tools like Testgrid allow you to run scriptless tests, but even those tests require minimal coding knowledge. In short, it’s highly challenging for non-tech professionals to set up or run automated tests in a test environment.
4.2 Planning Resource Utilization
Improper resource allocation and utilization can lead to unfinished tasks, conflicts between teams, poor outcomes, and other issues. The entire testing process can get derailed from its objective if the resources of the test environment are not managed efficiently.
4.3 Acquiring the Necessary Browsers and Devices
Testers often use emulators and simulators to replicate real-life conditions on actual devices and platforms. But they aren’t accurate enough. Instead, using the actual devices and browsers would certainly help mimic the test scenarios and obtain more accurate results.
But the difficulty here lies in purchasing and configuring the devices or operating systems. The process will be complex, time-consuming, and very expensive. Additionally, you must acquire and maintain new or updated devices upon their release in your test environment.
Now, if you are targeting multiple devices and platforms, then maintaining them all in your test environment can be both expensive and overwhelming.
4.4 Timely Feedback & Communication
Testers have the opportunity to provide updates on the progress of their testing and QA processes, like developers do for development processes. Providing regular updates can help testing teams receive valuable feedback on how to move forward with the software testing and align testing objectives with overall project goals.
Moreover, poor coordination or communication between the product manager and the testers or quality experts can create serious gaps in the testing process, leading to ineffective tests. As a result, you may end up launching faulty software with high business risks.
4.5 Setting Up Complex Tests
Some test cases require extensive configuration of the test environment. Performing such complex tests demands that testing teams consider all necessary resources, including time, software, and devices. Doing everything manually in a complex test can lead to errors and poor results. So, handling complex tests manually is challenging for testing teams.
5. Best Practices For Test Environment Setup
Without an efficient and stable test environment, the testing process cannot deliver effective results. Therefore, it is necessary to implement best practices to ensure a reliable test environment setup.
5.1 Maintaining Environmental Consistency
Configuration drift occurs in a testing environment due to manual changes and inconsistent updates applied over time. As a result, unexpected issues begin to appear in the test environment, making troubleshooting more difficult.
With the help of tools like CloudFormation or Terraform, you can adopt Infrastructure as Code (IaC) practices to prevent this issue. Taking this approach allows you to maintain the consistency of the test environments. And it becomes easier to replace or scale it as per requirements.
5.2 Separate Testing Environments
Keep test, staging, and development environments separate. Moreover, if possible, use different testing environments for different types of tests. This helps prevent mixing or confusion between various test results.
5.3 Use Realistic Data but Keep It Secure
To obtain accurate results, it is essential to use realistic test data. Only then can a test environment closely replicate the production environment and real-world conditions. However, sometimes to get better results, organizations make the mistake of using real data that exposes sensitive business or user information, which can lead to security and privacy risks.
So, make sure to use realistic data, but not the one that carries security risks with it. If you need to use sensitive data for testing, then limit access to the test environment and its data.
5.4 Implement Automation and CI/CD Pipelines
Use tools like CircleCI and Jenkins to automate the testing processes, such as setting up the test environment, preparing test scripts, running test cases, and generating comprehensive reports. Automation reduces human error, and implementing CI/CD pipelines enables faster iterations and more reliable releases.
5.5 Regularly Monitor and Analyze Your Testing Environments
Continuous monitoring and assessment of the test environment helps identify errors and optimize it accordingly. Tracking key metrics, such as resource utilization, test execution time, and failure rates, provides valuable data necessary for developing and implementing effective testing strategies. It also enables informed decision-making, allowing you to take proactive measures and create backup plans in case of failures or unexpected events.
5.6 Mock Outside Services
Reliance on external services during testing can be risky. Because if those services go down, the testing process would be halted indefinitely. It’s better to use tools that can simulate these external services. This will act as an accurate representation of the production environment where the app communicates with the external services.
5.7 Document Everything
Testers and QA experts should always document the entire testing process, including testing objectives and test environment setup of various test cases and test outcomes with detailed analysis. This will allow you to understand the testing process, keep a record of applied changes, and help quickly fix the issues.
6. Conclusion
The test environment plays a crucial role in building software applications. It ensures quality assurance by enabling the quick delivery of reliable and bug-free solutions. The testing environment reduces the risk of production failures by providing a safe and controlled space for testers and QA experts to test their software against various scenarios.
However, to set up an effective test environment, follow a step-by-step procedure while adhering to best practices. This task can be challenging, but we have already briefed you on the potential issues and ways to resolve them. If you have any more queries, feel free to contact our experts.
FAQs
What is the Test Environment for UAT?
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is the final phase of software testing with a dedicated setting specific to the end users. To run this test, a testing environment mimics real-world scenarios to check if the software meets the user requirements and whether it performs up to user expectations.
How Many Testing Environments Are There?
Different types of testing environments, such as development, staging, and production. Each environment has distinct settings that support specific types of testing. Therefore, you must use them separately. Otherwise, the results will get all mixed up, and you may end up with faulty software or a delayed product launch.





Comments
Leave a message...